Challenges and Efficient Operation Mechanism of Shale Oil Exploration and Development in China
-
摘要:
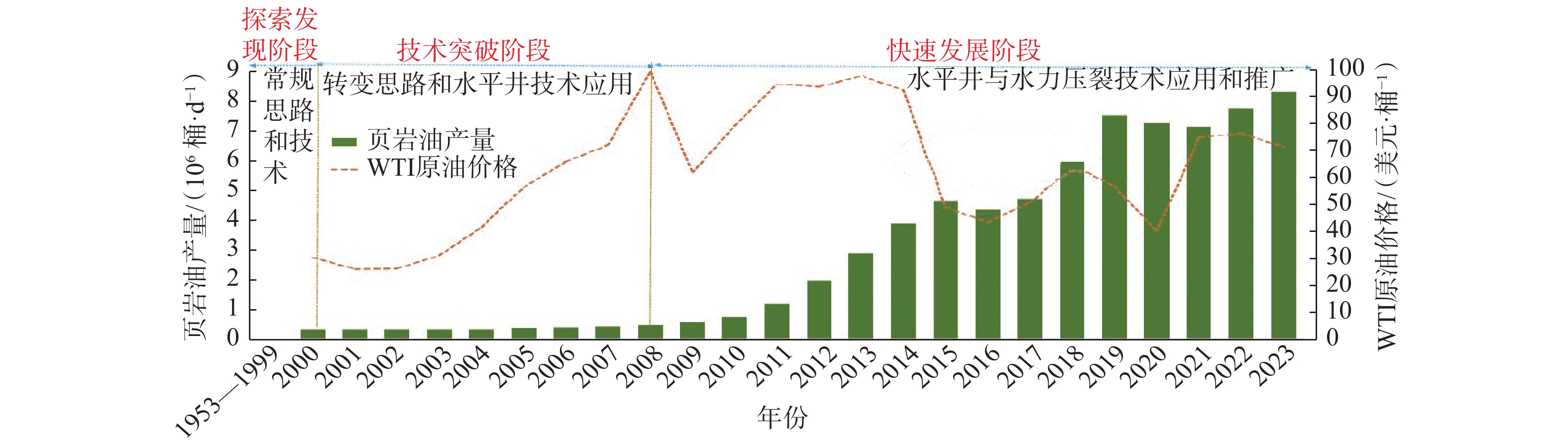
中国页岩油资源丰富,并在多个盆地取得重大勘探开发突破,已成为石油战略接替新领域,但页岩油勘探开发时间相对较短,顶层的战略规划与政策导向尚未明确,存在勘探突破难、开发成本高和组织运营不畅等问题。为此,调研剖析了中美页岩油经营理念、宏观环境、资源配置、生产运行、科技水平和信息化程度等现状,深入思考中国页岩油勘探开发的痛点、难点和阻点,认为当前中国页岩油勘探开发主要面临理念思路、技术能力、运营管理和绿色发展等4大挑战。围绕中国能源战略,提出了实现中国页岩油高效运营的对策建议:谋划稳中求进的页岩油发展战略,构建市场机制下多主体融合的战略合作共同体,打造多兵种协作的生产运行新模式,建立迭代式创新的科技发展新机制,建立数智化赋能的信息支撑新范式,开创绿色低碳化的产业发展新格局,营造高契合友好的外部运营新环境。
Abstract:China has abundant shale oil resources and has made significant exploration and development breakthroughs in multiple basins, which unveils a new field for implementing China’s petroleum strategy. However, the exploration and development of shale oil in China has a relatively short history, and the top-level strategic planning and policy guidance are not yet clear. There are a series of issues to be solved such as difficulties in exploration breakthroughs, high development costs, and inefficient organizational operation, etc. To this end, a comprehensive literature review was conducted to explore the current status of shale oil management concept, macro environment, resource allocation, production and operation, science and technology level, and informatization state in China and the U.S, and in-depth considerations were performed to fully understand the pain points, difficulties, and obstacles of shale oil exploration and development in China. It is believed that currently there are four major challenges in shale oil exploration and development in China, including conceptual thinking, technical capabilities, operation management, and green developmentl etc. Based on the national energy strategy, countermeasures and suggestions were proposed to achieve efficient operation of shale oil in China, including implementing shale oil development strategy in a steady manner, building a strategic cooperative community with multi-subject integration under the market mechanism, creating a new mode of production and operation with multi-force collaboration, establishing a new mechanism of iterative technological development and innovation, developing a new information support paradigm empowered by digital intelligence, opening a new landscape of green and low-carbon industrial development, and fostering a new highly compatible and friendly external operation environment.
-
渤海P油田位于渤海中南部海域,由多个断块组合而成,在纵横向上具有多套油水系统,属于典型的疏松砂岩稠油油藏,以陆相河流相、三角洲相沉积为主,平面及纵向非均质性强。该油田采用大段防砂、强注强采的开发模式,水驱开发效率低,目前油田综合含水率已达83.1%,但采出程度仅15.1%;另外,由于注入水水质差、注水强度高,致使注水井无机堵塞严重,注水压力长期居高不下,难以满足配注要求[1]。
为解决该问题,经广泛调研发现,层内生成CO2调驱技术无需天然气源、注入工艺简单,能够很好地克服常规CO2驱的局限性,得到国内外学者的广泛关注,并开展了相关研究和矿场试验[2-6]。1999年,Kh. Kh. Gumersky等人[7]最先发现碳酸(氢)盐在地层条件下能够与酸发生反应生成大量的CO2,并于2000–2004年在Novo-Pokursky油田开展了矿场驱油试验,3个月累计增油量超过2 700 t;2010年,B. J. B. Shiau等人[8]系统研究了可在储层自发生成CO2的氨基甲酸铵和氨基甲酸甲酯等化学药剂及其调驱机理。国内也相继开展了层内生成CO2调驱技术研究和先导性试验,邓建华等人[9]依据层内生成CO2的机理研制了KD-79单液生CO2体系和KD-79双液生CO2体系,驱替试验表明,这2种体系都可以起到调剖、驱油的作用;赵仁保等人[10]利用填砂管进行了层内自生CO2的试验研究,结果表明向生CO2体系中添加起泡剂可有效控制CO2气体在高渗管中的窜流;2008年3月开始,河南油田魏岗和江河井区的9口井实施了层内生CO2深部解堵增注措施,措施后平均注入压力为3.64 MPa,累计增注量61 179 m3,有效期长达322 d[11];2016年,李文轩等人[12]通过室内试验筛选出以盐酸和小苏打为主剂的层内自生CO2解堵体系,矿场试验表明,该体系具有优良的的暂堵分流能力和增油效果。
笔者针对渤海P油田的储层特征及开发特点,提出采用集调剖、驱油、增注于一体的层内生成CO2调驱技术,然后通过室内试验优选了适用于渤海P油田的生CO2体系及配套的泡沫体系,并将其规模化应用于现场,取得了良好的调整注水井吸水剖面、降压增注和稳油控水效果,为渤海P油田的高效开发提供了技术手段。
1. 层内生成CO2调驱基本原理
层内生成CO2调驱技术通过向目的层分段塞交替注入生气剂和释气剂,2种药剂在油层内发生化学反应放热并释放出CO2气体,与注入的发泡体系共同作用于油层。该技术在保留常规CO2驱优点的同时克服了其缺点,能够同时实现近井调剖、解堵和远井驱油的功能,其具体作用原理如下:
1)解堵作用。生气剂和释气剂反应放热可解除有机堵塞,起降压增注作用。
2)调剖作用。生成的CO2与发泡体系作用形成CO2泡沫,并与添加的稳定剂配合,可以封堵高渗层,改善水驱效果。
3)驱油作用。CO2溶于原油,使原油体积膨胀,原油黏度和油水界面张力降低。
4)降黏作用。生气剂与释气剂发生化学反应放出的热量可以降低原油的黏度。
2. 层内生成CO2调驱关键技术
针对渤海P油田储层非均质性严重和近井地带污染等问题,根据调剖、解堵和驱油一体化的思路,进行层内生气调剖关键技术研究,主要进行了生气体系优选、泡沫体系筛选和稳定剂优选。
2.1 生气体系优选
利用化学反应釜考察了生气剂和释气剂对生气量和生气速率的影响,以获得最优生气体系。层内生气试验装置如图1所示。
分别选用相同浓度的生气剂A,B和C与释气剂D,E和F,预先将生气剂A,B和C溶液置于图1中的广口烧瓶中,然后用酸式滴定管加入相同浓度的释气剂D,E和F,考察其生气量和生气效率,60 ℃下的生气效果见表1。
表 1 不同生气体系的生气效果(60 ℃)Table 1. Statistics of system components and gas generation effects (60℃)生气体系 生气量/mL 理论生气量/mL 生气效率,% 生气剂A+释气剂D 279 290 96.2 生气剂B+释气剂D 280 290 96.6 生气剂C+释气剂D 279 290 96.2 生气剂A+释气剂E 242 290 83.4 生气剂B+释气剂E 249 290 85.9 生气剂C+释气剂E 267 290 92.1 生气剂A+释气剂F 66 290 22.8 生气剂B+释气剂F 78 290 26.9 生气剂C+释气剂F 123 290 42.4 从表1可以看出,生气剂A,B和C与释气剂D反应的生气量最大,生气效率最高,生气量在280 mL左右,生气效率均达到96.0%以上。考虑经济性和稳定性,选择生气剂A+释气剂D的生气体系。
2.2 泡沫体系筛选
2.2.1 发泡剂筛选
在100 mL模拟地层水中分别加入不同量的发泡剂,配制成发泡剂溶液,采用Waring Blender法考察其发泡体积和析液半衰期,结果如图2、图3所示。
从图2和图3可以看出,发泡剂加量较小时,不同发泡剂的发泡体积和析液半衰期均随着加量增加而增加;但发泡剂加量过大时,其发泡体积和析液半衰期反而略有下降。这是因为发泡剂加量增加到一定程度时,其分子在气液表面排列的无序度增加,致密度降低,造成泡沫液膜强度减弱,稳定性随之降低。从图2和图3还可以看出:发泡剂2~5不仅发泡体积大,且泡沫的稳定性好,因此选取发泡剂2~5进行复配,进行下一步筛选。
2.2.2 发泡剂复配筛选
发泡剂加量控制在0.3%,将发泡剂2~5分别以2∶1和1∶2的比例进行复配,考察复配后的发泡性能,结果如图4所示(图4中,发泡体系1为发泡剂2和发泡剂3按2∶1复配;发泡体系2为发泡剂2和发泡剂3按1∶2复配;发泡体系3为发泡剂2和起泡剂4按2∶1复配;发泡体系4为发泡剂2和发泡剂4按1∶2复配;发泡体系5为发泡剂2和发泡剂5按2∶1复配;发泡体系6为发泡剂2和发泡剂5按1∶2复配;发泡体系7为发泡剂3和发泡剂4按2∶1复配;发泡体系8为发泡剂3和发泡剂4按1∶2复配;发泡体系9为发泡剂3和发泡剂5按2∶1复配;发泡体系10为发泡剂3和发泡剂5按1∶2复配;发泡体系11为发泡剂4和发泡剂5按2∶1复配;发泡体系12为发泡剂4和发泡剂5按1∶2复配)。从图4可以看出,发泡体系5(发泡剂2和发泡剂5以2∶1的比例复配)的发泡体积为740 mL,析液半衰期达219 s,表现出优良的协同效应。因此,选0.2%发泡剂2+0.1%发泡剂5作为发泡体系。
2.3 稳定剂的筛选
为保证泡沫在渗流过程中能封堵优势渗流通道,需要加入稳定剂。利用渗透率2 000~10 000 mD的填砂模型进行流动试验,考察泡沫加入不同稳定剂后对不同渗透率渗流通道的封堵能力,结果如图5所示。从图5可以看出,泡沫加入稳定剂1对高渗渗流通道的封堵率基本保持在90%左右,封堵性能最好;泡沫加入稳定剂2对低渗渗流通道的封堵性较好,但由于其溶解性好,易被冲刷,封堵率随渗透率升高下降很快,稳定性较差;泡沫加入稳定剂3和稳定剂4的封堵性能比加入稳定剂1差,但比加入稳定剂2强。综上所述,选用稳定剂1。
3. 现场应用
渤海P油田先后进行了5批次15井组的层内生成CO2调驱作业,累计注入调剖剂15 423 m3,措施后累计增注量69 986 m3,累计增油量达33 413 m3,措施成功率100%,取得了显著的调剖、降压增注和稳油控水效果。下面以渤海P油田B1注采井组为例介绍该技术的具体应用情况。
根据渤海P油田B1注采井组的地质油藏特征,利用室内优选的生气体系和发泡体系,进行层内生成CO2方案设计,以降低该井组注水井的注入压力,增加注水量的同时提高驱油效率,提高油井产油量。具体步骤为:
1)根据注水井和生产井的井距、注水层有效厚度、油层孔隙度等油藏资料,利用层内生成CO2数学模型,计算出措施井注入药剂的量。
2)根据井组的具体情况确定药剂的段塞组合,以确保药剂在地层中能充分混合反应。B1注采井组注水井B1井的注入段塞组合如表2所示。
表 2 B1井层内生成CO2注入段塞组合Table 2. Slug formation form in-situ CO2 generation in Well B1注入顺序 生气剂体积/m3 隔离水体积/m3 释气剂体积/m3 段塞1 60 3 60 段塞2 60 3 60 段塞3 60 3 60 段塞4 30 3 30 段塞5 30 3 30 段塞6 30 3 30 段塞7 30 3 30 3)按照设计在钻井液池中配制药剂溶液,分别使用钻井泵和酸化泵以油管正注的方式将生气剂、释气剂和稳定剂笼统注入目的层位,作业方式为不动管柱作业,施工周期短,作业成本低。
4)注入过程中根据现场地层吸水测试结果不断优化药剂注入排量。前期控制注入速度,使药剂优先进入高渗层进行封堵;后期适当提高注入速度,启动低渗层。
表3为B1注采井组注水井B1井应用层内生成CO2调驱技术前后吸水剖面测试结果。由表3可知,应用层内生成CO2调驱技术后,强吸水层的吸水能力降低,弱吸水层的吸水能力增强,如吸水能力较弱的第4小层的吸水量占比大幅提高(从5%增至73%),而主力吸水层第3小层的吸水量占比显著减小(从69%降至13%),表明层内生成CO2调驱技术取得了良好的调剖效果。
表 3 层内生成CO2调驱技术应用前后注水井B1井吸水剖面测试结果Table 3. Comparison of water absorption profile in Well B1 before and after measurement of in-situ CO2 generation小层号 吸水量占比,% 应用前 应用后 1 25 5 2 1 9 3 69 13 4 5 73 应用层内生成CO2调驱技术后,注水井B1井的视吸水指数提高了24.6%,累计增注量达20 721 m3。与注水井B1井对应的8口受效生产井累计净增油量2 430 m3,考虑递减后的增油量4 724 m3,平均有效期长达5个月。
4. 结 论
1)针对渤海P油田注水开发存在的问题,采用了集调剖、驱油和增注于一体的层内生成CO2调驱技术,通过室内试验优选出了层内生成CO2体系配方:生气剂A+释气剂D构成生气体系,0.2%起泡剂2+0.1%发泡剂5+稳定剂1构成发泡体系。
2)现场应用表明,层内生成CO2调驱技术可以解决渤海P油田注水开发存在的问题,建议在该油田推广应用。
-
表 1 美国水力压裂工艺迭代升级情况
Table 1 Iterative upgrading of fracturing technology in the U.S.
时间 井间距/m 水平段长度/m 段间距/m 簇间距/m 加砂强度/(t·m−1) 2008—2014 400 1500 100~150 15~25 1.5 2015—2017 200 1500~3000 50~80 9~15 4.5 2018 100~150 1500~3000 <30 6~15 >7.5 2019至今 50~100 1500~3000 30~50 6~10 4.5~6.0 -
[1] 王敏生,光新军,耿黎东. 页岩油高效开发钻井完井关键技术及发展方向[J]. 石油钻探技术,2019,47(5):1–10. WANG Minsheng, GUANG Xinjun, GENG Lidong. Key drilling/completion technologies and development trends in the efficient development of shale oil[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2019, 47(5): 1–10.
[2] 闫林,陈福利,王志平,等. 我国页岩油有效开发面临的挑战及关键技术研究[J]. 石油钻探技术,2020,48(3):63–69. YAN Lin, CHEN Fuli, WANG Zhiping, et al. Challenges and technical countermeasures for effective development of shale oil in China[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2020, 48(3): 63–69.
[3] U. S. Energy Information Administration. U. S. crude oil and natural gas proved reserves, year-end 2017[R]. Washington, D. C. : U. S. Department of Energy, 2018.
[4] U. S. Energy Information Administration. Annual energy outlook 2022[R]. Washington, D. C. : U. S. Department of Energy, 2022: 13-25.
[5] 唐玮,梁坤,冯金德,等. 低油价下美国页岩油困境对我国油田勘探开发的启示[J]. 石油科技论坛,2020,39(4):26–30. TANG Wei, LIANG Kun, FENG Jinde, et al. Enlightenment from dilemma of us shale oil development under low oil prices[J]. Petroleum Science and Technology Forum, 2020, 39(4): 26–30.
[6] 吕建中,刘嘉,张焕芝,等. 技术组合是油气上游增产降本提效的关键:美国页岩油气开发的成功实践与启示[J]. 国际石油经济,2019,27(7):34–38. LYU Jianzhong, LIU Jia, ZHANG Huanzhi, et al. Technology combination: the key to achieve “increase production, decrease cost and improve efficiency” in upstream:successful practice and enlightenments of the US shale oil and gas development[J]. International Petroleum Economics, 2019, 27(7): 34–38.
[7] 张焕芝,杨金华,张嘉铭,等. 北美页岩油气生产经验对中国页岩油气降低桶油成本的启示[N]. 石油商报,2018-03-07(08). ZHANG Huanzhi, YANG Jinhua, ZHANG Jiaming, et al. Inspiration of North American shale oil and gas production experience on reducing barrel oil costs for shale oil and gas in China[N]. petroleum Business News, 2018-03-07(08).
[8] 杨金华,张焕芝,刘知鑫. 美国二叠盆地页岩油气开发10大举措[J]. 世界石油工业,2022,29(4):80–81. YANG Jinhua, ZHANG Huanzhi, LIU Zhixin. Top 10 measures for shale oil and gas development in the Permian Basin of the United States[J]. World Petroleum Industry, 2022, 29(4): 80–81.
[9] 齐黎明,荆克尧,田雨露,等. 美国页岩油气公司应对油价暴跌经营策略[J]. 国际石油经济,2021,29(7):92–99. QI Liming, JING Keyao, TIAN Yulu, et al. Analysis on operation strategies of U. S. shale oil & gas companies under oil prices plunging[J]. International Petroleum Economics, 2021, 29(7): 92–99.
[10] 周庆凡,杨国丰. 美国页岩油气勘探开发现状与发展前景[J]. 国际石油经济,2018,26(9):39–46. ZHOU Qingfan, YANG Guofeng. Status and prospects of shale oil & gas exploration in the United States[J]. International Petroleum Economics, 2018, 26(9): 39–46.
[11] XIONG Hongjie. The effective cluster spacing plays the vital role in unconventional reservoir development: Permian Basin case studies[R]. SPE 199721, 2020.
[12] 郭旭升,黎茂稳,赵梦云. 页岩油开发利用及在能源中的作用[J]. 中国科学院院刊,2023,38(1):38–47. GUO Xusheng, LI Maowen, ZHAO Mengyun. Shale oil development and utilization and its role in energy industry[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2023, 38(1): 38–47.
[13] 汪天凯,何文渊,袁余洋,等. 美国页岩油低油价下效益开发新进展及启示[J]. 石油科技论坛,2017,36(2):60–68. WANG Tiankai, HE Wenyuan, YUAN Yuyang, et al. Latest development in US cost-effective development of shale oil under background of low oil prices[J]. Petroleum Science and Technology Forum, 2017, 36(2): 60–68.
[14] 李亚茜,姜杉钰,牛琮凯. 从国内外经验谈重庆页岩油气产业集聚发展[J]. 世界石油工业,2023,30(5):19–25. LI Yaxi, JIANG Shanyu, NIU Congkai. Thought on the development of Chongqing shale oil and gas industry agglomeration[J]. World Petroleum Industry, 2023, 30(5): 19–25.
[15] XU Tao, ZHENG Wei, BAIHLY J, et al. Permian Basin production performance comparison over time and the parent-child well study[R]. SPE 194310, 2019.
[16] BARBA R, VILLARREAL M. The economics of refracturing in the Haynesville[R]. SPE 212371, 2023.
[17] JARIPATKE O A, BARMAN I, NDUNGU J G, et al. Review of Permian completion designs and results[R]. SPE 191560, 2018.
[18] TABATABAIE S H, BURROUGH T, CADENA C R. A machine learning approach to benchmarking operators performance: a new perspective utilizing factor contribution analysis[R]. SPE Journal, 2022, 27(6): 3314-3327.
[19] Rystad Energy. US shale oil producers generated the highest FCF in industry history[EB/OL]. (2020-11-19) [2024-01-20].https://www.rystadenergy.com/clients/articles/shalewell/2020/shale-financial-update/.
[20] 金之钧,白振瑞,高波,等. 中国迎来页岩油气革命了吗?[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2019,40(3):451–458. JIN Zhijun, BAI Zhenrui, GAO Bo, et al. Has China ushered in the shale oil and gas revolution?[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2019, 40(3): 451–458.
[21] 赵群,赵萌,赵素平,等. 美国页岩油气发展现状、成本效益危机及解决方案[J]. 非常规油气,2023,10(5):1–7. ZHAO Qun, ZHAO Meng, ZHAO Suping, et al. The development status, cost-effectiveness crisis and solution of shale oil and gas in the United States[J]. Unconventional Oil & Gas, 2023, 10(5): 1–7.
[22] 周庆凡,金之钧,杨国丰,等. 美国页岩油勘探开发现状与前景展望[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2019,40(3):469–477. ZHOU Qingfan, JIN Zhijun, YANG Guofeng, et al. Shale oil exploration and production in the U. S. : status and outlook[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2019, 40(3): 469–477.
[23] 邓正红. 页岩战略:美联储在行动[M]. 北京:石油工业出版社,2017. DENG Zhenghong. Shale strategy: the federal reserve in action[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2017.
[24] 周雪. 美国页岩油勘探开发现状及其对中国的启示[J]. 现代化工,2022,42(7):5-9. ZHOU Xue. Current situation of U. S. A. shale oil exploration and development, and enlightenment to China[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2023, 42(7): 5-9.
[25] 国家能源局. 2023年全国油气勘探开发十大标志性成果[EB/OL]. (2024-01-09)[2024-01-20].https://www.nea.gov.cn/2024-01/09/c_1310759352.htm. National Energy Administration. Ten landmark achievements in national oil and gas exploration and development in 2023[EB/OL]. (2024-01-09) [2024-01-20].https://www.nea.gov.cn/2024-01/09/c_1310759352.htm.
[26] 袁建强. 济阳坳陷页岩油多层立体开发关键工程技术[J]. 石油钻探技术,2023,51(1):1–8. YUAN Jianqiang. Key engineering technologies for three-dimensional development of multiple formations of shale oil in Jiyang Depression[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2023, 51(1): 1–8.
[27] 李民峰,刘楠. 独家| 10问10答!权威详解大庆油田古龙页岩油[EB/OL]. 黑龙江日报,2021-08-25 [ 2024-01-20].https://new.qq.com/rain/a/20210825A04DFJ00. LI Minfeng, LIU Nan. Exclusive | 10 questions and answers! Authoritative detailed explanation of Gulong shale oil in Daqing Oilfield[EB/OL]. Heilongjiang Daily, 2021-08-25 [2024-01-20].https://new.qq.com/rain/a/20210825A04DFJ00.
[28] 吴钧,于晓红,王权,等.松辽盆地古龙页岩油勘探开发全息智能生态系统设计与开发[J].大庆石油地质与开发,2021,40(5):181-190. WU Jun,YU Xiaohong,WANG Quan,et al. Design and development of holographic intelligent ecosystem for exploration and development of Gulong shale oil in Songliao Basin[J].Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing,2021,40(5):181-190.
[29] 克拉玛依融媒. 吉木萨尔:石头缝里 “榨” 油[EB/OL]. (2023-08-30)[2024-01-20].https://roll.sohu.com/a/716280276_121119059. Karamay Financing Media. Jimsar: Squeezing oil from a crack in the stone[EB/OL]. (2023-08-30)[2024-01-20].https://roll.sohu.com/a/716280276_121119059.
[30] 余果林,肖丹. 又见春风过陇塬:长庆陇东页岩油规模效益开发纪略[N]. 中国石油报,2023-06-27(01). YU Guolin, XIAO Dan. Spring breeze over Longyuan again: a brief account of the scale benefit development of Longdong shale oil in Changqing[N]. China Petroleum Daily, 2023-06-27(01).
[31] 徐佳,高鹏. “改” 出新活力 “革” 出新路径:长庆油田创新生产组织模式助推高质量发展纪实[N]. 中国石油报,2022-12-13(04). XU Jia, GAO Peng. “Transforming” into new vitality and “innovating” into new paths: Changqing Oilfield innovative production organization model to promote high-quality development documentary[N]. China Petroleum Daily, 2022-12-13(04).
[32] 张东清,万云强,张文平,等. 涪陵页岩气田立体开发优快钻井技术[J]. 石油钻探技术,2023,51(2):16–21. ZHANG Dongqing, WAN Yunqiang, ZHANG Wenping, et al. Optimal and fast drilling technologies for stereoscopic development of the Fuling Shale Gas Field[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2023, 51(2): 16–21.
[33] 孙焕泉. 济阳坳陷页岩油勘探实践与认识[J]. 中国石油勘探,2017,22(4):1–14. SUN Huanquan. Exploration practice and cognitions of shale oil in Jiyang Depression[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2017, 22(4): 1–14.
[34] 赵福豪,黄维安,雍锐,等. 地质工程一体化研究与应用现状[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2021,43(2):131–138. ZHAO Fuhao, HUANG Weian, YONG Rui, et al. Research and application status of geology-engineering integration[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2021, 43(2): 131–138.
[35] 何骁,周鹏,杨洪志,等. 页岩气地质工程一体化管理实践与展望[J]. 天然气工业,2022,42(2):1–10. HE Xiao, ZHOU Peng, YANG Hongzhi, et al. Management practice and prospect of shale gas geology-engineering integration[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(2): 1–10.
[36] 林腊梅,程付启,刘骏锐,等. 济阳坳陷渤南洼陷沙一段页岩油资源潜力评价[J]. 中国海上油气,2022,34(4):85–96. LIN Lamei, CHENG Fuqi, LIU Junrui, et al. Evaluation of shale oil resource potential in the Es1 Member in Bonan Sag, Jiyang Depression[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2022, 34(4): 85–96.
[37] 舒逸,郑有恒,包汉勇,等. 四川盆地复兴地区下侏罗统页岩油气富集高产主控因素[J]. 世界石油工业,2023,30(5):26–38. SHU Yi, ZHENG Youheng, BAO Hanyong, et al. Main controlling factors for high yield and enrichment of shale oil and gas in the Lower Jurassic in the Fuxing area of Sichuan Basin[J]. World Petroleum Industry, 2023, 30(5): 26–38.
[38] 康玉柱. 中国非常规油气勘探重大进展和资源潜力[J]. 石油科技论坛,2018,37(4):1–7. KANG Yuzhu. Significant exploration progress and resource potential of unconventional oil and gas in China[J]. Petroleum Science and Technology Forum, 2018, 37(4): 1–7.
[39] 敬民. 如何赢得页岩油革命[J]. 中国石油石化,2023(24):34–37. JING Min. How to win the shale oil revolution[J]. China Petrochem, 2023(24): 34–37.
[40] 邹才能,潘松圻,荆振华,等. 页岩油气革命及影响[J]. 石油学报,2020,41(1):1–12. doi: 10.1038/s41401-019-0299-4 ZOU Caineng, PAN Songqi, JING Zhenhua, et al. Shale oil and gas revolution and its impact[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2020, 41(1): 1–12. doi: 10.1038/s41401-019-0299-4
[41] 邹才能,马锋,潘松圻,等. 全球页岩油形成分布潜力及中国陆相页岩油理论技术进展[J]. 地学前缘,2023,30(1):128-142. ZOU Caineng, MA Feng, PAN Songqi. Formation and distribution potential of global shale oil and the developments of continental shale oil theory and technology in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 30(1): 128-142.
[42] 赵文智,胡素云,侯连华,等. 中国陆相页岩油类型、资源潜力及与致密油的边界[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2020,47(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(20)60001-5 ZHAO Wenzhi, HU Suyun, HOU Lianhua, et al. Types and resource potential of continental shale oil in China and its boundary with tight oil[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(1): 1–10. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(20)60001-5
[43] 马永生,蔡勋育,赵培荣,等. 中国陆相页岩油地质特征与勘探实践[J]. 地质学报,2022,96(1):155–171. MA Yongsheng, CAI Xunyu, ZHAO Peirong, et al. Geological characteristics and exploration practices of continental shale oil in China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2022, 96(1): 155–171.
[44] 马永生,蔡勋育,赵培荣. 中国页岩气勘探开发理论认识与实践[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2018,45(4):561–574. MA Yongsheng, CAI Xunyu, ZHAO Peirong. China’s shale gas exploration and development: Understanding and practice[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(4): 561–574.
[45] 付茜,刘启东,刘世丽,等. 中国 “夹层型” 页岩油勘探开发现状及前景[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2019,41(1):63–70. FU Qian, LIU Qidong, LIU Shili, et al. Exploration & development status and prospect of sandwich-type shale oil reservoirs in China[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2019, 41(1): 63–70.
[46] 慕立俊,拜杰,齐银,等. 庆城夹层型页岩油地质工程一体化压裂技术[J]. 石油钻探技术,2023,51(5):33–41. MU Lijun, BAI Jie, QI Yin, et al. Geological engineering integrated fracturing technology for Qingcheng interlayer shale oil[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2023, 51(5): 33–41.
[47] 田启忠,戴荣东,王继强,等. 胜利油田页岩油丛式井提速提效钻井技术[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2023,45(4):404–409. TIAN Qizhong, DAI Rongdong, WANG Jiqiang, et al. An efficient and fast shale oil cluster well drilling technology for Shengli Oilfield[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2023, 45(4): 404–409.
[48] 朱海燕,焦子曦,刘惠民,等. 济阳坳陷陆相页岩油气藏组合缝网高导流压裂关键技术[J]. 天然气工业,2023,43(11):120–130. ZHU Haiyan, JIAO Zixi, LIU Huimin, et al. A new high-conductivity combined network fracturing technology for continental shale oil and gas reservoirs in the Jiyang Depression[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2023, 43(11): 120–130.
[49] 杨国丰,周庆凡,卢雪梅. 页岩油勘探开发成本研究[J]. 中国石油勘探,2019,24(5):576–588. YANG Guofeng, ZHOU Qingfan, LU Xuemei. Study on the cost of shale oil exploration and development[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2019, 24(5): 576–588.
[50] U. S. Energy Information Administration. Trends in U. S. oil and natural gas upstream costs[R]. Washington, D. C. : U. S. Department of Energy, 2016.
[51] 袁士义,雷征东,李军诗,等. 陆相页岩油开发技术进展及规模效益开发对策思考[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版),2023,47(5):13–24. YUAN Shiyi, LEI Zhengdong, LI Junshi, et al. Progress in technology for the development of continental shale oil and thoughts on the development of scale benefits and strategies[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum(Edition of Natural Science), 2023, 47(5): 13–24.
[52] 郭焦锋,王婕,孟凡达. 对标国际一流,切实推进中国页岩油上游产业高质量发展[J]. 中国石油勘探,2019,24(5):547–552. GUO Jiaofeng, WANG Jie, MENG Fanda. Promoting the high-quality development of China’s shale oil upstream industry by following international first-class standard[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2019, 24(5): 547–552.
[53] 王敏生,闫娜,光新军. 国际油田服务公司低碳发展策略与启示[J]. 油气与新能源,2023,35(2):13–20. WANG Minsheng, YAN Na, GUANG Xinjun. Strategy and revelation on low carbon development in international oilfield service companies[J]. Petroleum and New Energy, 2023, 35(2): 13–20.
[54] 孙德强,许金华,潘教峰,等. 基于智库研究双螺旋法的中国页岩油科技创新治理体系构建[J]. 智库理论与实践,2022,7(5):29-35. SUN Deqiang, XU Jinhua, PAN Jiaofeng, et al. Construction of Chinese shale oil technology innovation governance system based on the double helix structure of think tank research[J]. Think Tank: Theory & Practice, 2022, 7(5): 29-35.
[55] 王敏生. 油气井钻完井作业碳减排发展方向与建议[J]. 石油钻探技术,2022,50(6):1–6. WANG Minsheng. Development direction and suggestions for carbon emission reduction during drilling and completion[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2022, 50(6): 1–6.
[56] 李阳,王敏生,薛兆杰,等. 绿色低碳油气开发工程技术的发展思考[J]. 石油钻探技术,2023,51(4):11–19. LI Yang, WANG Minsheng, XUE Zhaojie, et al. Thoughts on green and low-carbon oil and gas development engineering technologies [J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2023, 51(4): 11–19.
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 李舒展,杨进,朱国倞,黄熠,张珣,万宏宇. 水下井口吸力桩极限贯入深度研究. 中国海上油气. 2024(02): 185-194 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 傅超,杨进,刘华清,殷启帅,王磊,胡志强. 多维度深水浅层建井方式优选方法研究. 石油钻探技术. 2024(03): 40-46 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 李舒展,杨进,朱国倞,黄熠,王宁,万宏宇,马会珍. 深水钻井井口吸力桩稳定性计算和校核方法. 石油钻采工艺. 2024(01): 13-24 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 刘书杰,李文拓,徐一龙,刘正,李清平,李君,曾春珉. 海洋水下钻井井口疲劳损伤性能设计方法. 石化技术. 2024(09): 114-116 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李文拓,刘书杰,徐一龙,于晓东,李清平,徐楷,曾春珉. 海洋井口吸力桩的下入安装施工流程研究. 石化技术. 2024(10): 101-103 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 罗鸣,刘书杰,李文拓,李清平,周思琦,曾春珉. 海洋双井口吸力桩井口间距设计方法. 石化技术. 2024(11): 127-129 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: