Development and Field Test of Probe-Type Intelligent Bit Parameter Measurement Device
-
摘要:
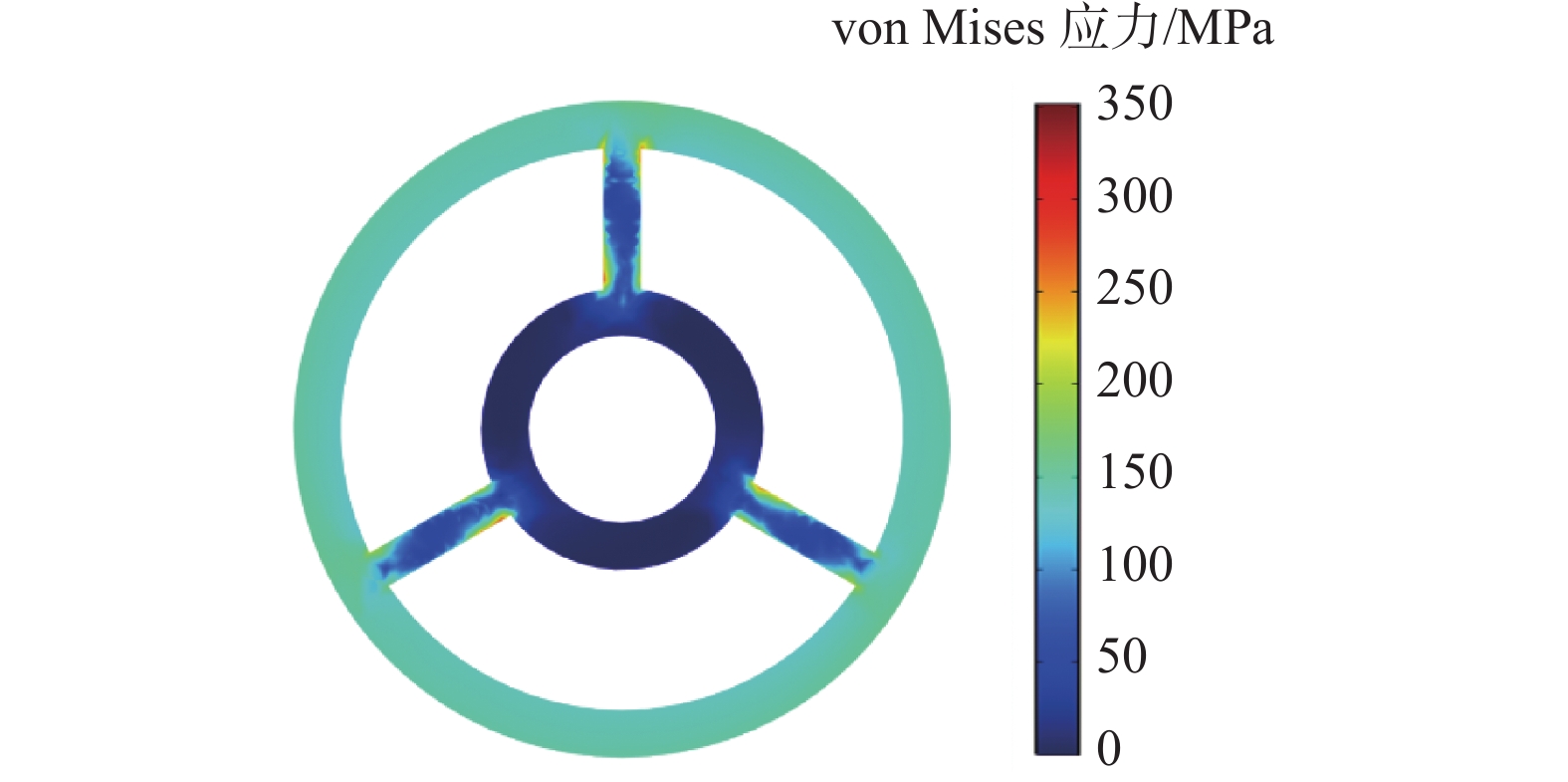
现有螺杆上游的测量装置无法获得钻头位置处的真实数据,智能钻井在决策控制层面存在严重的数据偏见与不可预测的实施风险。为此,研制了一种探管式智能钻头参数测量装置,可以安装在钻头内部,在不改变现有钻具组合与施工工艺的前提下直接采集钻头处的真实数据;硬件结构仿真优化结果表明,30 L/s排量与80 MPa环空压力下,理论水力压耗小于0.1 MPa、安全系数为3.06。同时,基于六面法与ARMA+移动Kalman滤波,实现了该装置的误差标定与降噪。该装置在胜利工区现场试验9井次,配套井下工程参数测量短节进行了装置功能验证与井下数据对比,融合综合录井数据进行了试验井提速分析与参数优化决策。试验结果表明,探管式智能钻头参数测量装置能够获取钻头位置处的真实数据,能够为针对性提速提效分析与钻井参数优化提供可靠依据。
Abstract:The existing measuring device installed on the upside of current PDM motor fails to get the real data at the bit position, and the intelligent drilling suffers from serious data biases and unpredictable implementation risks at decision-making and control level. Therefore, a probe-type intelligent bit parameter measurement device was developed, which could be installed inside the bit and collect the real data of the bit without any change on the existing bottom hole assembly (BHA) and operating process. The hardware structure simulation optimization of the device was performed, and the theoretical hydraulic pressure loss was less than 0.1 MPa with a safety factor of 3.06 under the displacement of 30 L/s and annular pressure of 80 MPa. The error calibration and noise reduction of this device were achieved by six-sided method measurement together with auto regressive moving average (ARMA) model and moving Kalman filter. Field trials of the device have been conducted in 9 wells in Shengli Oilfield. The function of the device was verified, and the downhole data was compared based on the downhole engineering parameter measurement sub. The speed-up analysis and parameter optimization of the pilot wells were carried out through integrating the comprehensive logging data. The test results show that the probe-type intelligent bit parameter measurement device can collect the real data of the bit position, which can provide a reliable basis for the speed-up and efficiency improvement analysis and drilling parameter optimization.
-
-
表 1 不同端部结构探管式装置的循环压耗
Table 1 Circulating pressure loss of probe tube devices with different end structures
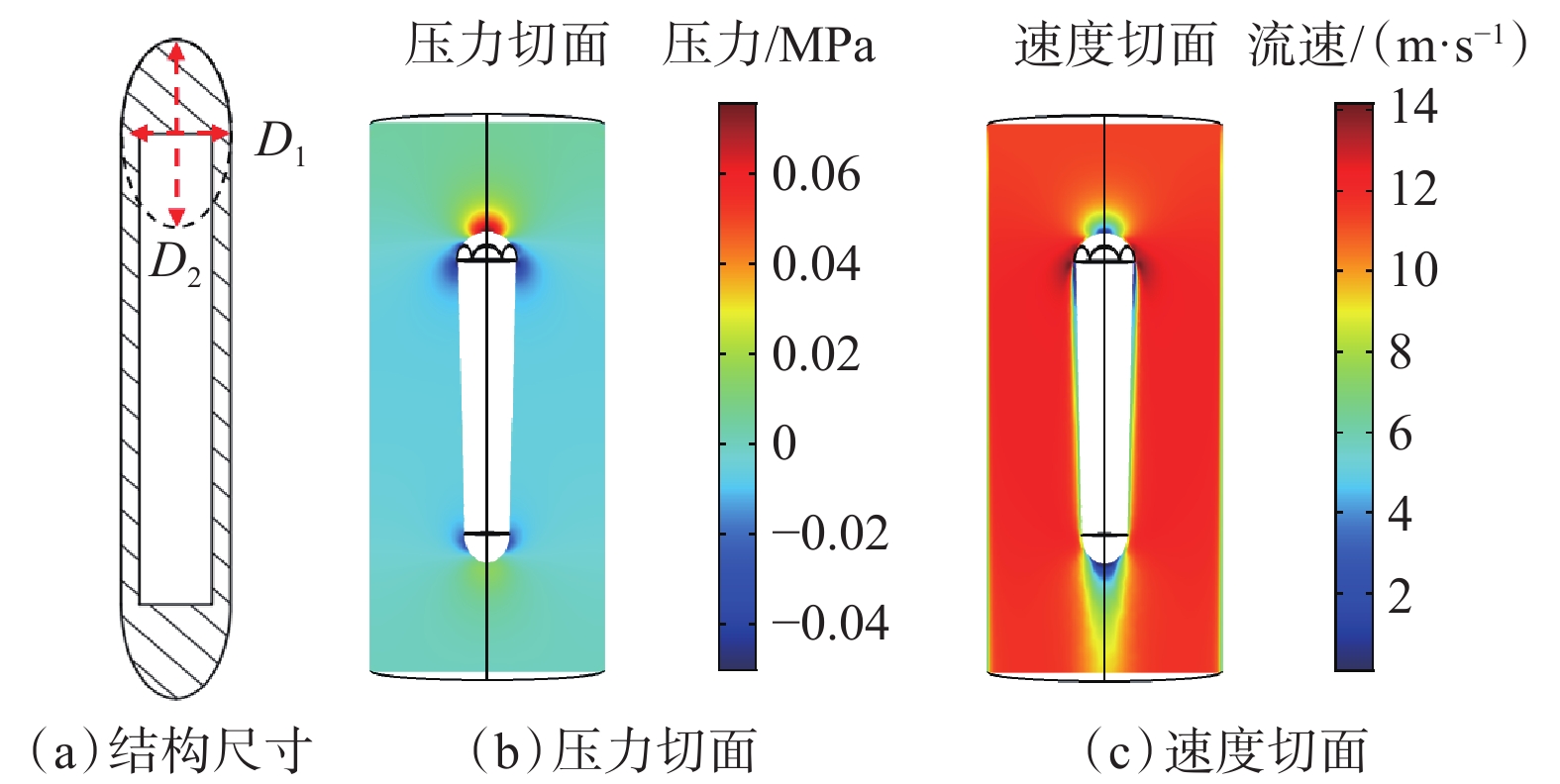
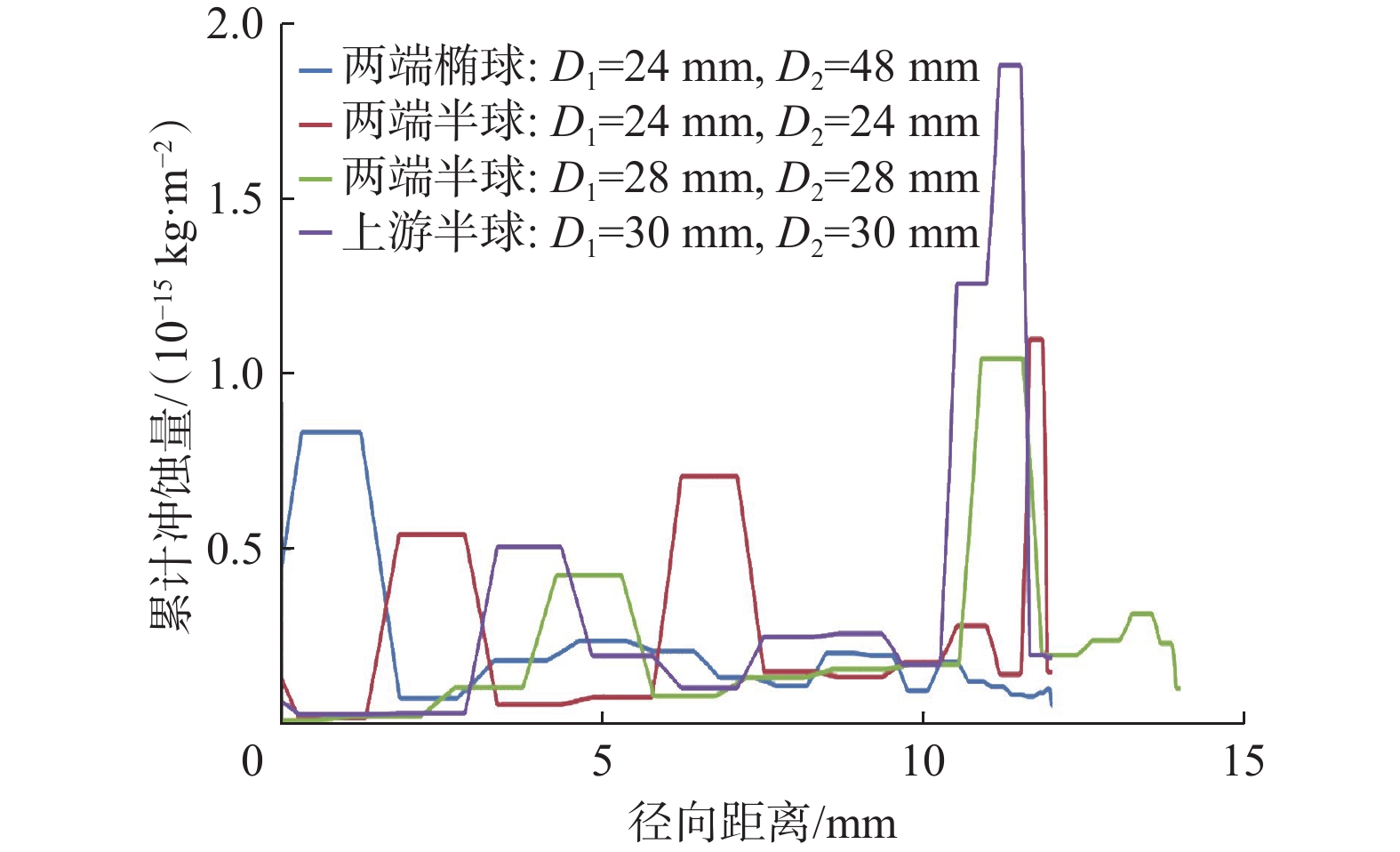
端部结构尺寸 循环压耗/ MPa 外形 外径/ mm 两端结构优化后 上游结构优化后 半球形 D1= D2=24 0.0410 0.1020 半球形 D1= D2=26 0.0540 0.1270 半球形 D1= D2=28 0.0740 0.1560 半球形 D1= D2=30 0.0970 0.1910 椭球形 D1=24,D2=36 0.0350 0.0901 椭球形 D1=24,D2=48 0.0310 0.0904 注:D1为椭球小径或半球直径(与探管直径相等),mm;D2为椭球大径或半球直径,mm。 表 2 探管式智能钻头参数测量装置循环压耗对照(30 L/s)
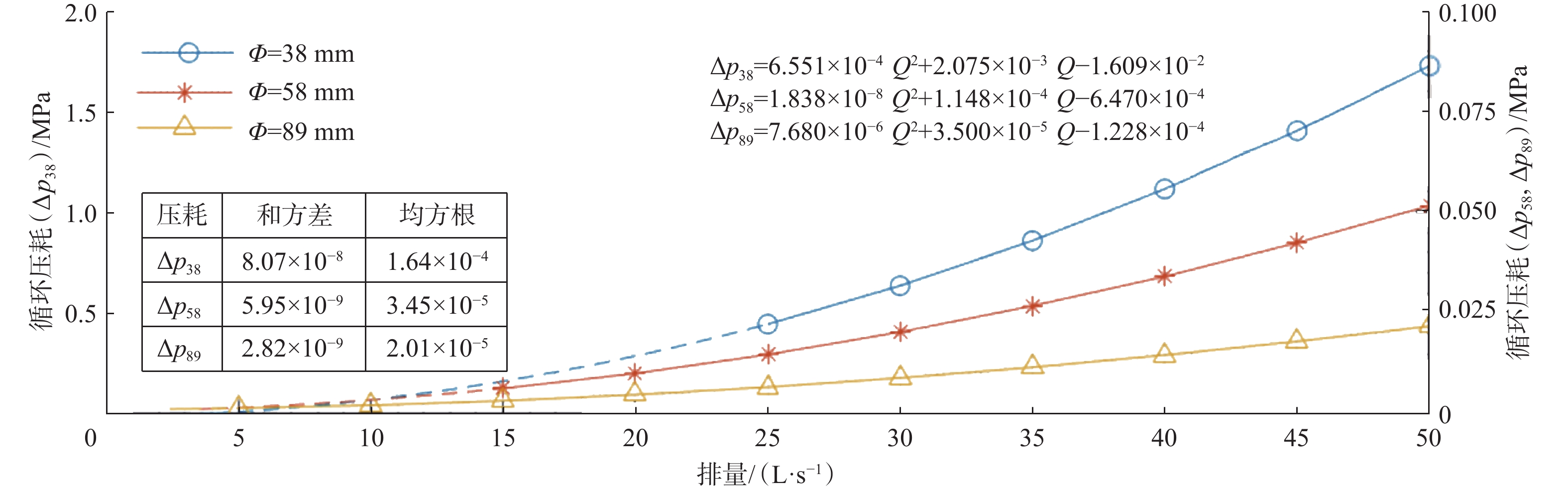
Table 2 Circulating pressure loss of probe-type intelligent bit parameter measurement device (30 L/s)
钻头直径/mm 连接螺纹 内径/mm 循环压耗/MPa 142.9~171.5 3½" REG 38 0.635 550 190.5~212.7 4½" REG 58 0.019 350 241.3~342.9 6⅝" REG 89 0.007 848 表 3 取心钻进段振动特征与作业参数的关系
Table 3 Relationship between vibration characteristics of core drilling section and operation parameters
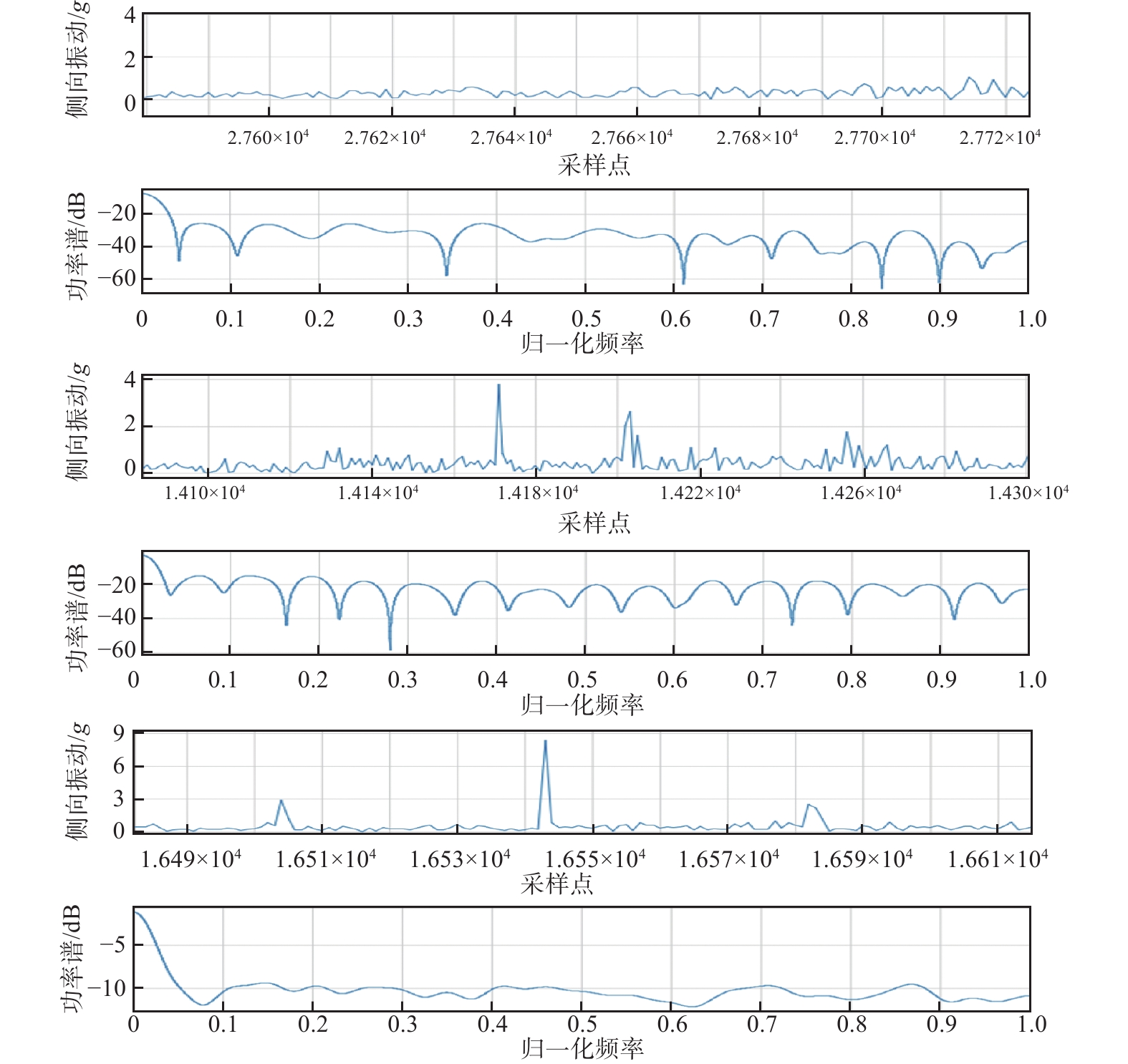
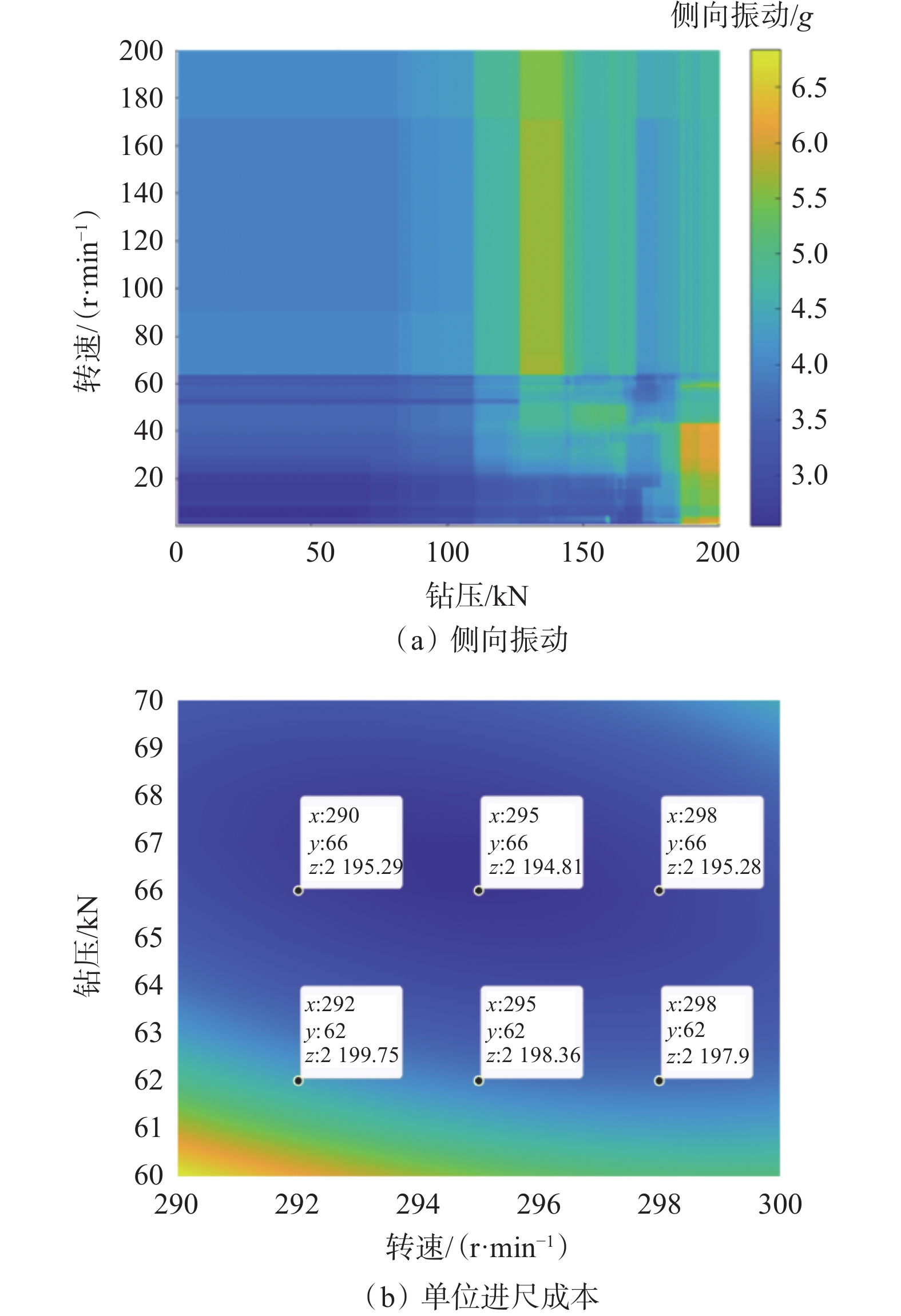
岩心长度/m 钻压/kN 轴向振动加速度/g 侧向振动加速度/g 0~6.0 60~70 0.7 (低) 9.0 (严重) 6.0~10.0 55~60 1.2 (中) 4.5 (高) 10.0~13.0 40~45 1.2 (中) 5.0 (高) 13.0~13.7 55 0.9 (低) 9.0 (严重) 14.3~15.3 35~95 0.7(低) 8.5(严重) 15.3~16.0 85~95 0.6 (低) 7.0 (严重) -
[1] Baker Hughes. MultiSense dynamics mapping system[EB/OL]. [2023-01-20].https://www.bakerhughes.com/drilling/drilling-optimization-services/multisense-dynamics-mapping-system.
[2] Halliburton. Cerebro® in-bit sensing[EB/OL]. [2023-01-20].https://www.halliburton.com/en/products/cerebro-bit-sensor-package.
[3] NOV. BlackBox eclipse II tool[EB/OL]. [2023-01-20].https://www.nov.com/products/blackbox-eclipse-ii-tool.
[4] LEDGERWOOD III L W, JAIN J R, HOFFMANN O J, et al. Downhole measurement and monitoring lead to an enhanced understanding of drilling vibrations and polycrystalline diamond compact bit damage[J]. SPE Drilling & Completion, 2013, 28(3): 254–262.
[5] CORNEL S, VAZQUEZ G. Use of big data and machine learning to optimise operational performance and drill bit design[R]. SPE 202243, 2020.
[6] PELFRENE G, CUILIER B, EZZEDDINE D, et al. Setting a new standard: PDC bits equipped with compact vibration recorders monitor entire run and reveal stick-slip mitigation system dysfunction and downhole motor under performance[R]. SPE 204112, 2021.
[7] TOWNSEND T, MOSS W, HEINISCH D, et al. Advanced high frequency in-bit vibration measurement including independent, spatially separated sensors for proper resolution of vibration components including lateral, radial, and tangential acceleration[R]. SPE 208110, 2021.
[8] XIAO Y, QIU H, BUTT S D. Measurement and analysis of drill-bit motions: a case study for passive-vibration assisted rotary drilling (pVARD) tool[R]. ARMA-2020-2036, 2020.
[9] SUGIURA J, JONES S. A drill bit and a drilling motor with embedded high-frequency (1600 Hz) drilling dynamics sensors provide new insights into challenging downhole drilling conditions[J]. SPE Drilling & Completion, 2019, 34(3): 223–247.
[10] CHEN Shilin, WISINGER J, DUNBAR B, et al. Identification and mitigation of friction- and cutting-action-induced stick/slip vibrations with PDC bits[J]. SPE Drilling & Completion, 2020, 35(4): 576–587.
[11] 李根生, 宋先知, 田守嶒. 智能钻井技术研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 石油钻探技术,2020,48(1):1–8. LI Gensheng, SONG Xianzhi, TIAN Shouceng. Intelligent drilling technology research status and development trends[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2020, 48(1): 1–8.
[12] 黄哲. 面向油气钻井振动测量的空间三轴加速度传感器阵列研究[J]. 电子测量技术,2021,44(8):155–160. HUANG Zhe. Method of drilling vibration measurement based on spatial array of accelerometers[J]. Electronic Measurement Technology, 2021, 44(8): 155–160.
[13] HUANG Zhe, YAN Xiuliang, DAI Yanan. Vibration control in optimized drilling and key issues to be applied in new clean geo-energy exploitation[C]//Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Green Energy, Environment and Sustainable Development (GEESD2022). Amsterdam: IOS Press, 2022: 38-48.
[14] CHEN Xiwu, HUANG Zhe. Novel tool of in-bit measurement for new clean geo-energy exploitation[C]//Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Green Energy, Environment and Sustainable Development (GEESD2022). Amsterdam: IOS Press, 2022: 1223-1232.
[15] 黄哲,吴仲华,李成,等. 智能钻头技术研究与应用探索[J]. 石油机械,2023,51(10):67–76. HUANG Zhe, WU Zhonghua, LI Cheng, et al. Research and application of intelligent bit technology[J]. China Petroleum Machinery, 2023, 51(10): 67–76.
-
期刊类型引用(23)
1. 车继勇,丁鹏,王红月,马永刚. 组合钻具定向钻井造斜及提速技术方法. 设备管理与维修. 2024(08): 98-100 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 熊浪豪,巢世伟,柏尚宇,陈君,范乘浪,崔建峰. E Zhanbyrshy-3井钻井实践及技术难点分析. 内蒙古石油化工. 2023(05): 63-66+120 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 汪伟,柳贡慧,李军,查春青,连威,夏铭莉. 脉动式扭转冲击钻井工具工作特性分析与测试. 石油钻探技术. 2022(05): 63-69 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 宋周成,翟文宝,邓昌松,徐杨,徐席明,汪鑫,文涛. 富满油田超深井井身结构优化技术与应用. 钻采工艺. 2022(06): 36-41 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王涛,刘锋报,罗威,晏智航,陆海瑛,郭斌. 塔里木油田防漏堵漏技术进展与发展建议. 石油钻探技术. 2021(01): 28-33 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 崔月明,史海民,张清. 吉林油田致密油水平井优快钻井完井技术. 石油钻探技术. 2021(02): 9-13 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 苏崭,王博,盖京明,李玮,赵欢,陈冰邓. 复合式扭力冲击器在坚硬地层中的应用. 中国煤炭地质. 2021(05): 47-50+57 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 张强,饶志华,秦世利,金勇. 南海东部深层古近系高效开发技术探索与实践. 石油化工应用. 2021(06): 34-38 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 李银婷,董小虎. 顺北油田钻井参数强化的提速效果评价. 钻探工程. 2021(07): 72-78 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 陈冬毅,徐鲲,张作伟,吕广,张鑫,郭小明. 恒压恒扭工具在渤海油田中的应用. 科学技术创新. 2021(22): 153-154 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 严德,张玉山,宋玲安,陈彬,李彬,刘保波. 深水高温高压井钻井技术探索与实践. 中国石油和化工标准与质量. 2021(13): 193-194 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 张喆,闫楚旋,冯震,脱直霖,石朝龙. 塔里木油田HLHT区块优快钻井技术研究. 云南化工. 2021(10): 127-129 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 李双贵,于洋,樊艳芳,曾德智. 顺北油气田超深井井身结构优化设计. 石油钻探技术. 2020(02): 6-11 .  本站查看
本站查看
14. 袁国栋,王鸿远,陈宗琦,母亚军,席宝滨. 塔里木盆地满深1井超深井钻井关键技术. 石油钻探技术. 2020(04): 21-27 .  本站查看
本站查看
15. 张智亮,王威,伊明,刘强. 井下安全监控系统设计与实现. 石油钻探技术. 2020(06): 65-70 .  本站查看
本站查看
16. 周波,汪海阁,张富成,纪国栋,韩泽龙,武强. 温度压力对岩石可钻性和破岩效率影响实验. 石油钻采工艺. 2020(05): 547-552 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 李林涛,万小勇,黄传艳,潘丽娟,郭知龙,曹宗波,张伟博. 双向卡瓦可回收高温高压封隔器的研制与应用. 石油机械. 2019(03): 81-86 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 路宗羽,赵飞,雷鸣,邹灵战,石建刚,卓鲁斌. 新疆玛湖油田砂砾岩致密油水平井钻井关键技术. 石油钻探技术. 2019(02): 9-14 .  本站查看
本站查看
19. 江波,任茂,王希勇. 彭州气田PZ115井钻井提速配套技术. 探矿工程(岩土钻掘工程). 2019(08): 73-78 .  百度学术
百度学术
20. 郑振国,黎红胜,赵海艳,温慧芸,孙东方. 哥伦比亚Matambo区块深井钻井关键技术. 石油钻探技术. 2018(02): 30-37 .  本站查看
本站查看
21. 丁红,宋朝晖,袁鑫伟,邢战,张宏阜,张仪. 哈拉哈塘超深定向井钻井技术. 石油钻探技术. 2018(04): 30-35 .  本站查看
本站查看
22. 李世昌,闫立鹏,李建冰,白文路,杨秀丽,闫天宇. 自循环粒子射流钻井提速工具机理研究. 中国锰业. 2018(03): 98-102 .  百度学术
百度学术
23. 陈养龙,席宝滨,晁文学,朱伟厚. 顺北区块Ⅰ号断裂带钻井分层提速技术. 断块油气田. 2018(05): 649-652 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)




 下载:
下载: