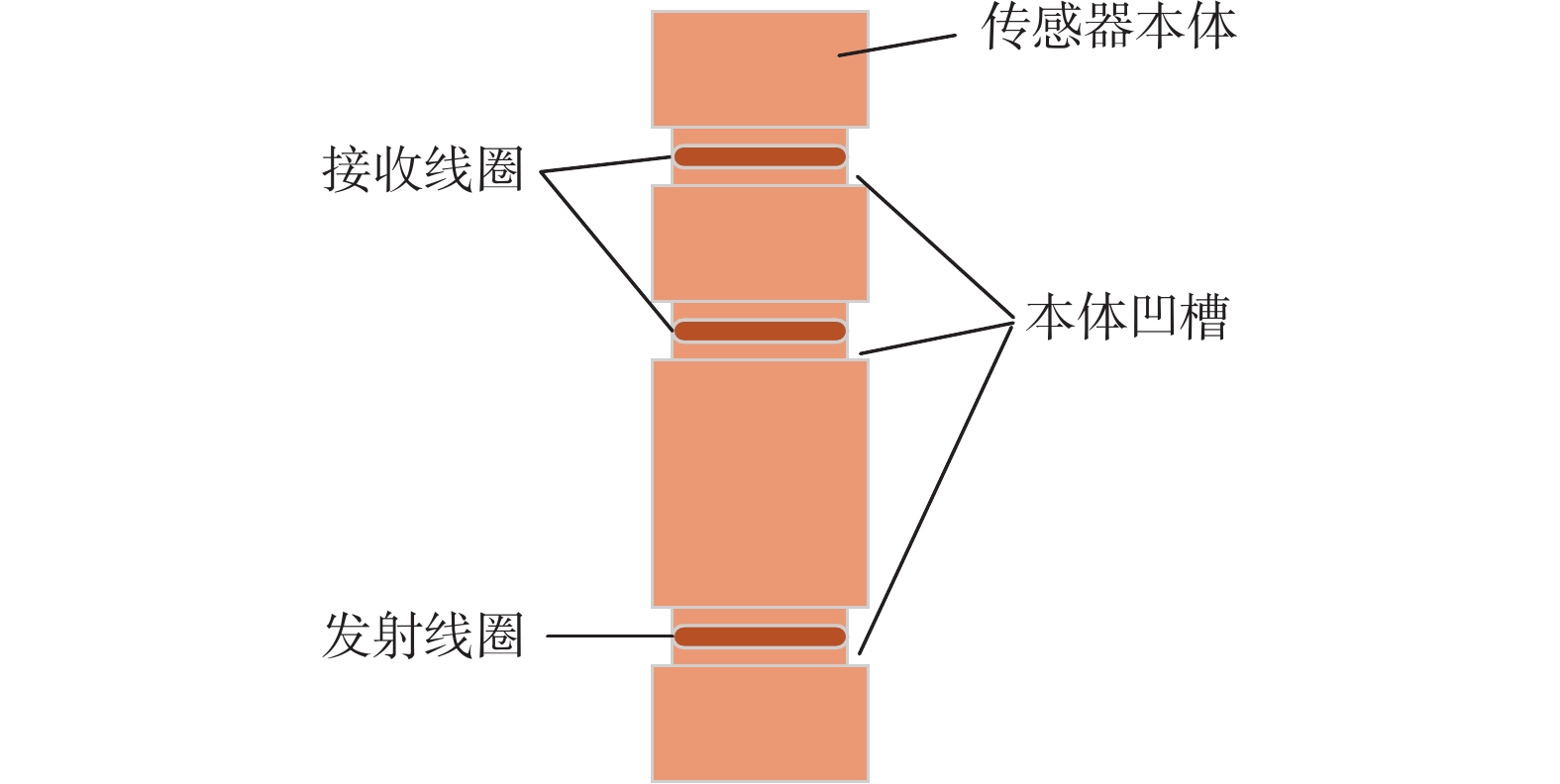
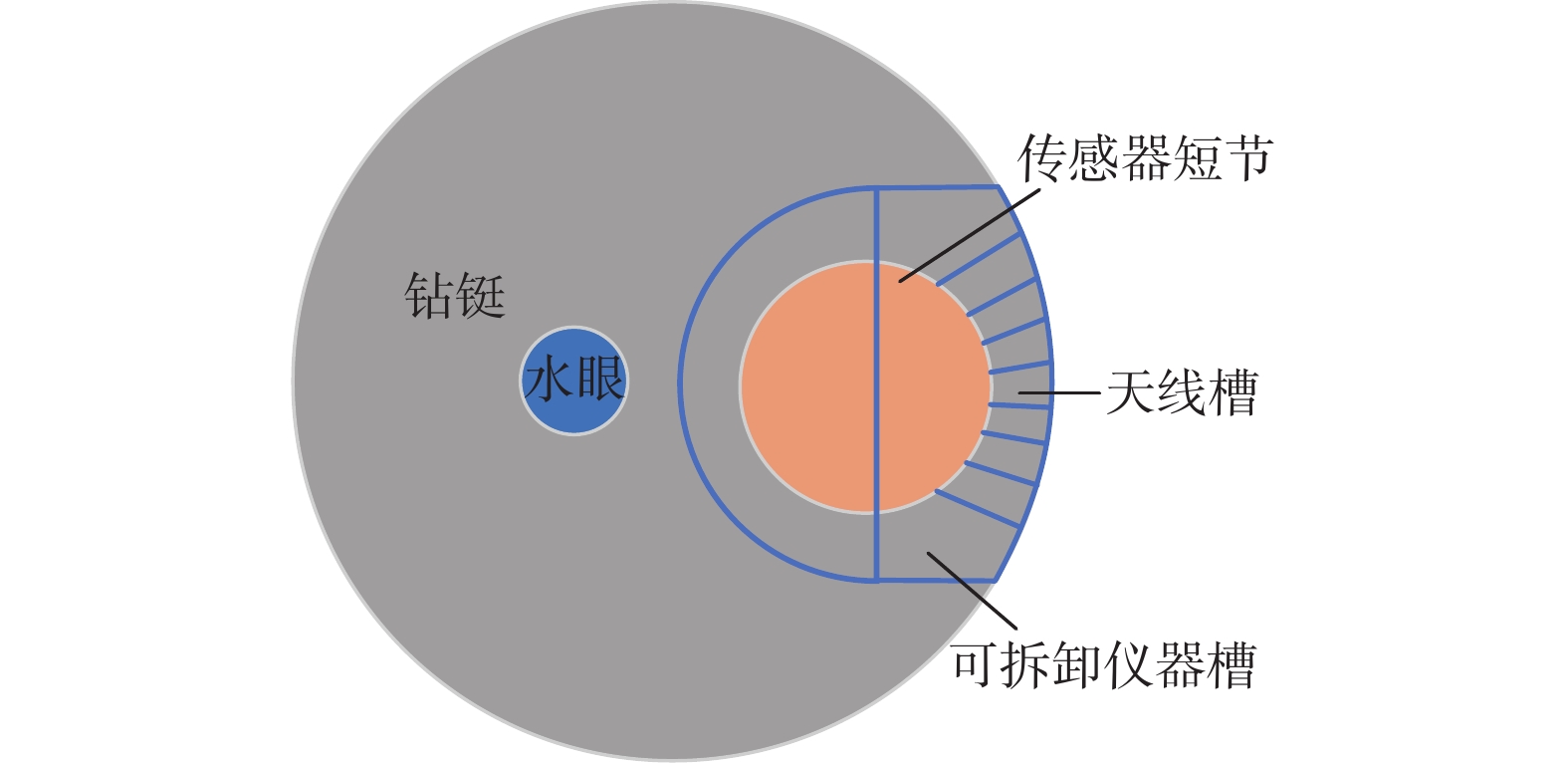
Influence of Structure of Modular Electromagnetic Logging While Drilling Instrument on Measurement Signals
-
摘要:
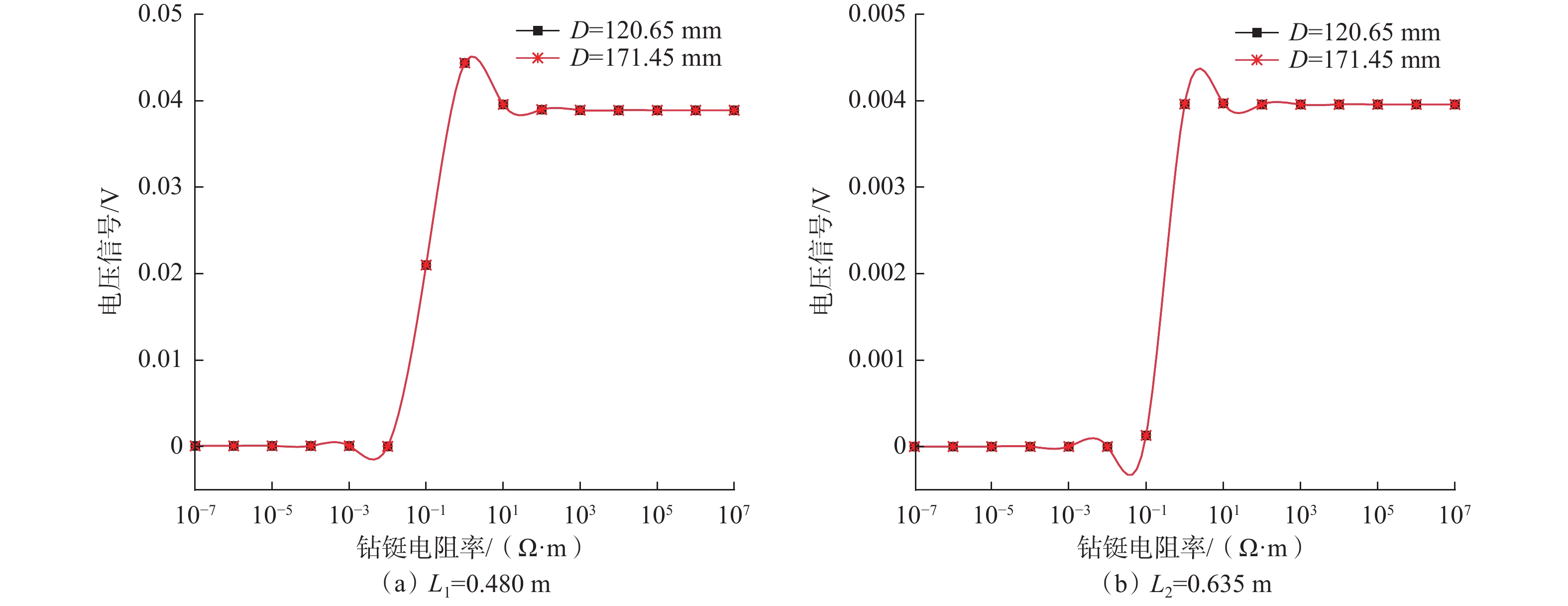
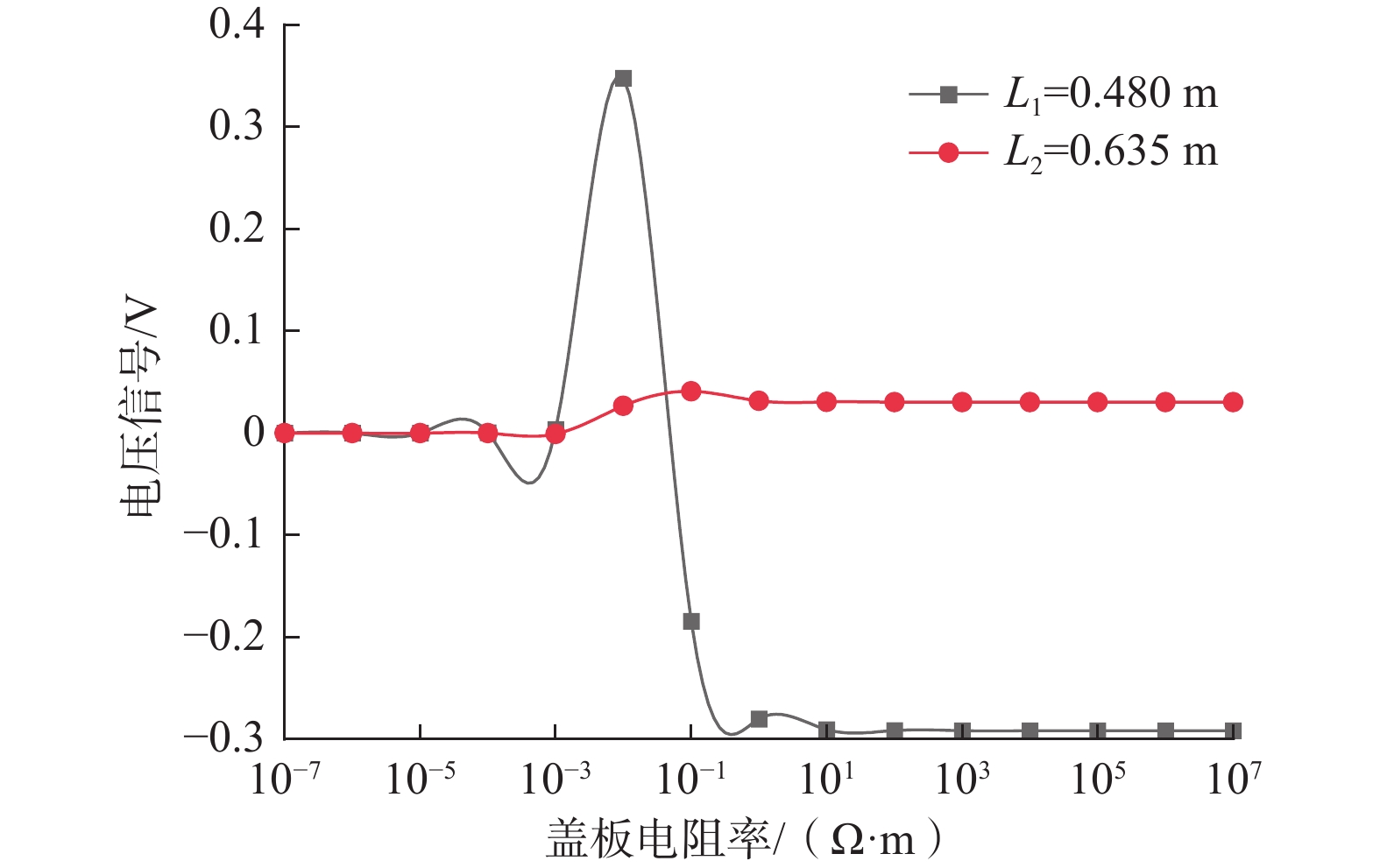
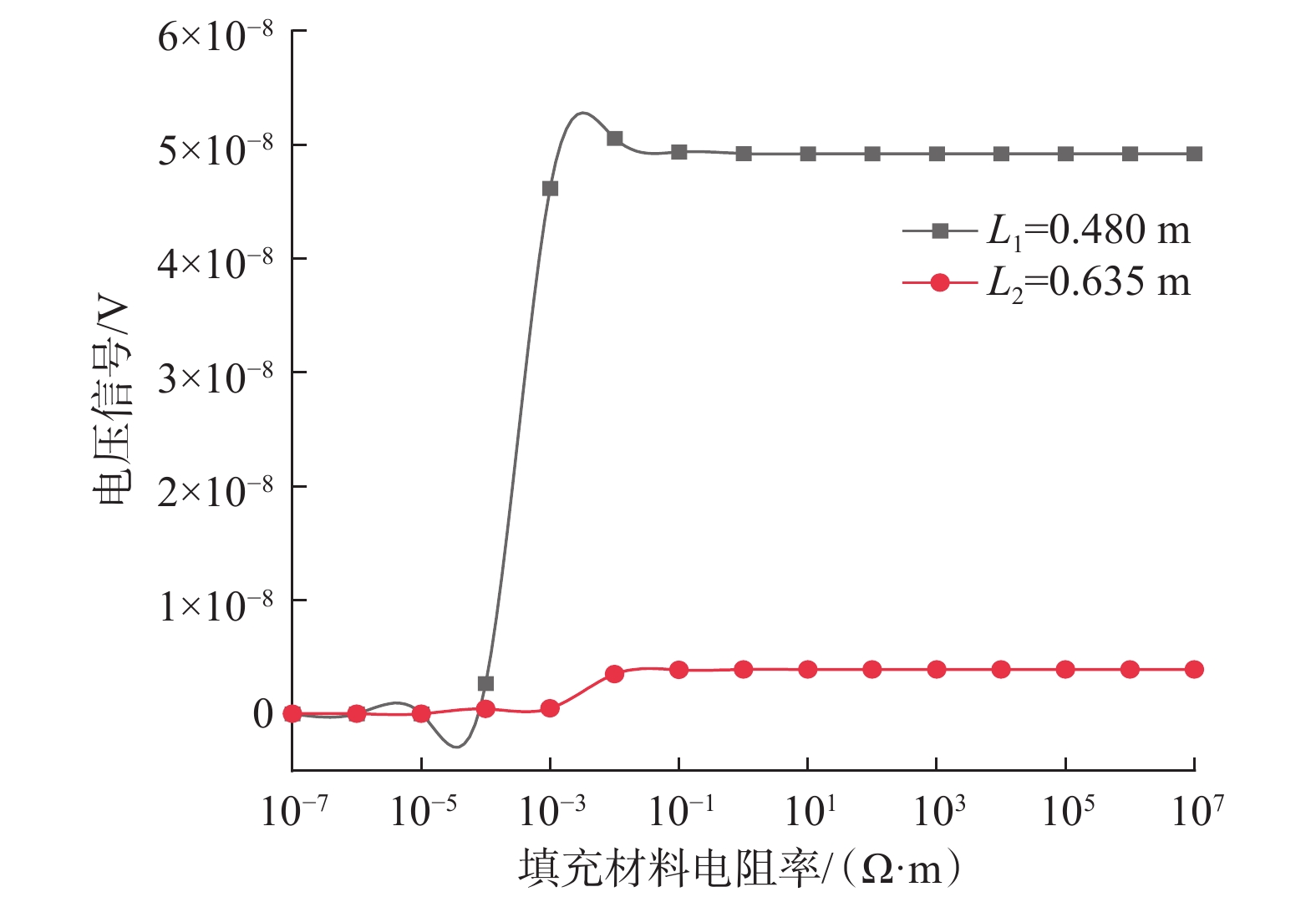
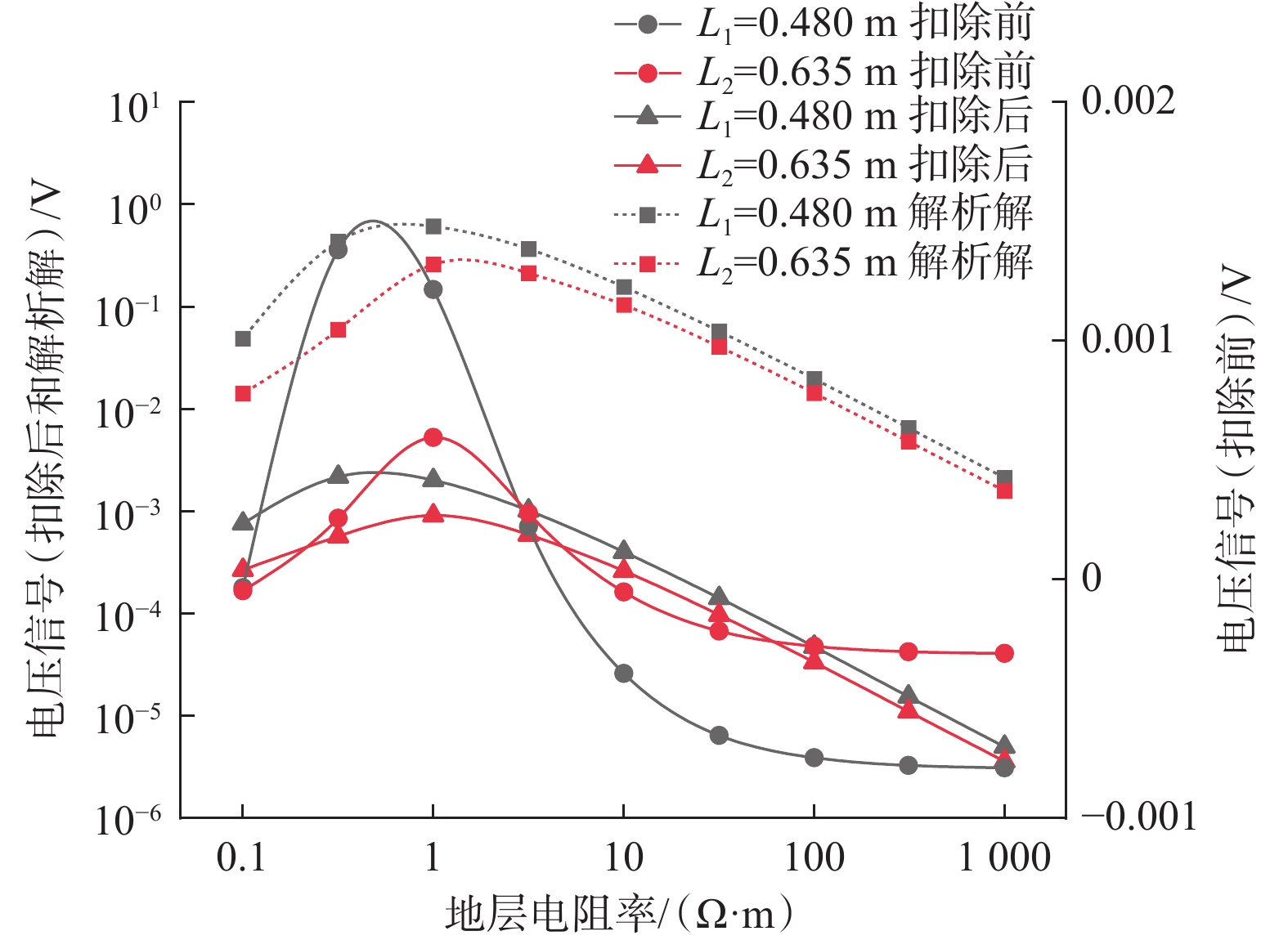
常规的随钻电磁波测井是一种重要的地层流体评价方法,但其不具有方位特性。为此,提出了一种具有较好方位探测特性的新型模块化随钻电磁波测井仪器结构。为准确了解模块化随钻电磁波测井仪器结构对测量电压信号的影响情况,采用有限元法建立了三维模型,探究了仪器各部分的影响规律。研究得出:随着钻铤和天线槽填充物电阻率增大,接收电压信号出现了突变区间且与仪器的频率和几何尺寸密切相关;盖板材料的电阻率对接收信号强度的影响较大,盖板应选择电阻率比金属稍低的材料,而测量信号随传感器本体电阻率增大而增大,因此传感器本体应选择非金属材料;钻铤和填充物的电阻率较小时,接收电压信号有明显的衰减,填充物电阻率较大时其影响可以忽略;通过扣除空气介质中的仪器响应,可以较好地消除仪器结构的影响,扣除仪器结构影响后线圈中磁通量减小,导致仪器信号低于扣除前。该研究结果可为实际测井仪器的设计制造提供理论依据。
Abstract:Conventional electromagnetic logging while drilling is an important method for evaluating stratigraphic fluids, but it does not have azimuth property. In this paper, a new modular electromagnetic logging while drilling instrument was proposed with good azimuth detection property. In order to accurately understand the influence of modular electromagnetic logging while drilling instrument on the measured voltage signal, a 3D model was established using the finite element method, and the influence laws of various instrument parts were explored. The results show that with the increased resistivity of the drill collar and antenna slot filling material, the received voltage signal has a sudden change, which is closely related to the frequency and geometric size of the instrument. The resistivity of the cover plate material has a great influence on the intensity of the received signal, and the cover plate should be selected with a little lower resistivity than metal. The measurement signal increases with the increasing resistivity of the sensor body, so the non-metallic material should be selected as the sensor body. When the resistivity of the instrument structure such as drill collar and filling material is low, the received voltage signal has obvious attenuation, and its influence can be ignored when the resistivity of the filling material is high. By deducting the instrument response in the air medium, the influence of the instrument structure can be well eliminated. After deducting the influence of the instrument structure, the magnetic flux in the coil decreases, resulting in a smaller instrument signal than before. The research results can provide a theoretical basis for the design and manufacture of actual logging instruments.
-
-
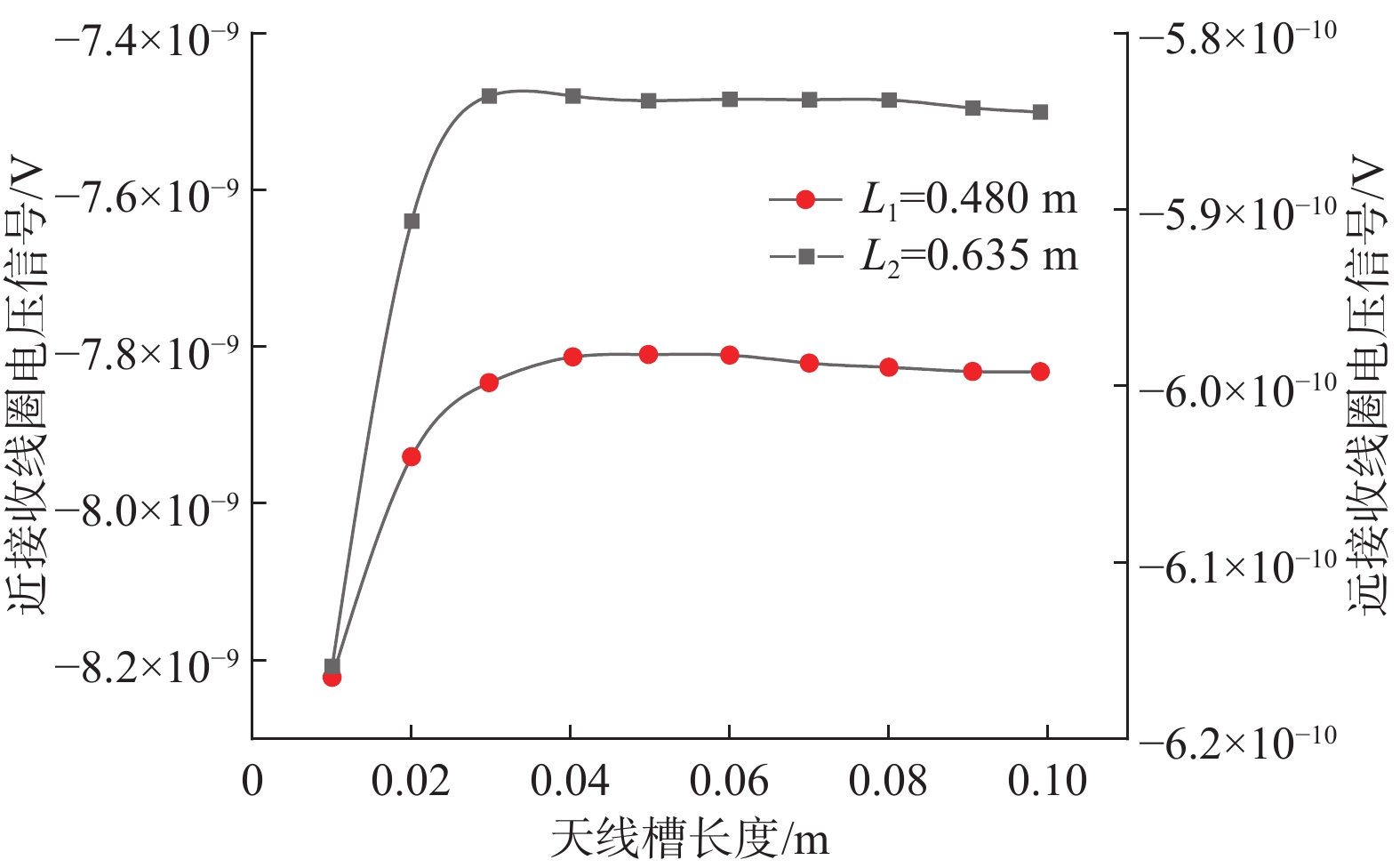
表 1 天线槽占空比对接收电压的影响
Table 1 Influence of antenna slot duty cycle on received voltage
天线槽数/个 长度/m L1=0.480 m L2=0.635 m 电压实部/V 电压虚部/V 电压实部/V 电压虚部/V 4 0.02 −1.11×10−8 4.43×10−9 −8.12×10−10 −1.32×10−9 0.04 −3.80×10−8 1.53×10−8 −2.85×10−9 −4.43×10−9 0.06 −5.12×10−8 2.12×10−8 −3.93×10−9 −5.98×10−9 0.08 −5.67×10−8 2.39×10−8 −4.33×10−9 −6.53×10−9 0.10 −5.89×10−8 2.52×10−8 −4.61×10−9 −6.81×10−9 0.12 −6.01×10−8 2.59×10−8 −4.72×10−9 −6.91×10−9 0.14 −6.04×10−8 2.61×10−8 −4.71×10−9 −6.92×10−9 0.16 −6.06×10−8 2.62×10−8 −4.79×10−9 −6.95×10−9 2 0.02 −3.05×10−9 1.38×10−9 −2.31×10−10 −3.55×10−10 0.04 −1.06×10−8 4.52×10−9 −1.82×10−10 −1.24×10−9 0.06 −1.45×10−8 6.33×10−9 −1.14×10−9 −1.73×10−9 0.08 −1.60×10−8 7.12×10−9 −1.32×10−9 −1.85×10−9 0.10 −1.67×10−8 7.39×10−9 −1.33×10−9 −1.92×10−9 0.12 −1.70×10−8 7.62×10−9 −1.35×10−9 −1.94×10−9 0.14 −1.70×10−8 7.68×10−9 −1.36×10−9 −1.95×10−9 0.16 −1.71×10−8 7.69×10−9 −1.41×10−9 −1.97×10−9 -
[1] 刘亚伟. 随钻电磁波电阻率测井仪结构设计与性能分析[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2017. LIU Yawei. Structure design and performance analysis of electromagnetic wave resistivity logging tool while drilling[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum(East China), 2017.
[2] 汪昊, 高杰, 陈航. 各向异性地层随钻电磁波电阻率测井信号处理方法研究[C]//2019年中国地球科学联合学术年会论文集(二十九)——专题77: 井孔地球物理学及深部钻测; 专题78: 地球化学进展; 专题79: 地球深部碳循环; 专题80: 航空地球物理勘查技术与应用. 北京: 中国和平音像电子出版社, 2019: 58−61. WANG Hao, GAO Jie, CHEN Hang. Study on signal processing method of electromagnetic wave resistivity logging while drilling in anisotropic formation[C]//Proceedings of the 2019 China Earth Science Joint Academic Annual Conference (29)—Special Topic 77: Well geophysics and deep drilling; Special Topic 78: Progress in geochemistry; Special Topic 79: Deep earth carbon cycle; Special Topic 80: Aerial geophysical exploration technology and applications. Beijing: China Heping Audio Video Electronic Publishing House, 2019: 58−61.
[3] 唐海全,肖红兵,李翠,等. 基于随钻测井的地层界面识别方法[J]. 天然气勘探与开发,2016,39(4):8–12. TANG Haiquan, XIAO Hongbing, LI Cui, et al. Methods to identify formation boundary based on logging-while-drilling[J]. Natural Gas Exploration and Development, 2016, 39(4): 8–12.
[4] 林发武,田超国,耿学杰,等. 随钻电磁波测井响应函数理论及探测特性[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版),2021,45(1):60–68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2021.01.007 LIN Fawu, TIAN Chaoguo, GENG Xuejie, et al. Theory of response function and analysis of detecting characteristic of electromagnetic logging while drilling[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum(Edition of Natural Science), 2021, 45(1): 60–68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2021.01.007
[5] 仵杰,任垚煜,贺秋利,等. 电磁远探测仪器参数设计[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版),2021,36(1):105–112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-064X.2021.01.015 WU Jie, REN Yaoyu, HE Qiuli, et al. Parameter design of remote detection tool with electromagnetic method[J]. Journal of Xi’an Shiyou University(Natural Science Edition), 2021, 36(1): 105–112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-064X.2021.01.015
[6] 岳喜洲,刘天淋,李国玉,等. 随钻方位电磁波测井响应快速正演方法与地质导向应用[J]. 地球物理学报,2022,65(5):1909–1920. doi: 10.6038/cjg2022P0233 YUE Xizhou, LIU Tianlin, LI Guoyu, et al. An analytically fast forward method of LWD azimuthal electromagnetic measurement and its geo-steering application[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2022, 65(5): 1909–1920. doi: 10.6038/cjg2022P0233
[7] 张晓彬. 随钻方位电磁波电阻率测井仪线圈系设计方法研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2017. ZHANG Xiaobin. Research on the design of coil system for azimuthal propagation resistivity LWD instrument[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum(East China), 2017.
[8] 仵杰,姬玉,成志刚,等. 泥浆侵入对随钻电磁波电阻率测井响应的影响[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版),2020,35(1):49–54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-064X.2020.01.007 WU Jie, JI Yu, CHENG Zhigang, et al. Influence of mud invasion on response of electromagnetic wave resistivity logging while drilling[J]. Journal of Xi’an Shiyou University(Natural Science Edition), 2020, 35(1): 49–54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-064X.2020.01.007
[9] 仵杰,叶雨,白茹宝,等. 随钻双感应测井仪背景影响研究[J]. 石油管材与仪器,2015,1(3):46–50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9134.2015.03.013 WU Jie, YE Yu, BAI Rubao, et al. The background influence research of LWD dual-induction logging instrument[J]. Petroleum Tubular Goods & Instruments, 2015, 1(3): 46–50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9134.2015.03.013
[10] 杨震,肖红兵,李翠. 随钻方位电磁波仪器测量精度对电阻率及界面预测影响分析[J]. 石油钻探技术,2017,45(4):115–120. YANG Zhen, XIAO Hongbing, LI Cui. Impacts of accuracy of azimuthal electromagnetic logging-while-drilling on resistivity and interface prediction[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2017, 45(4): 115–120.
[11] 吴世伟,刘得军,赵阳,等. 层状介质水力裂缝电磁响应的有限元正演模拟[J]. 石油钻探技术,2022,50(2):132–138. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2022060 WU Shiwei, LIU Dejun, ZHAO Yang, et al. Finite-element forward modeling of electromagnetic response of hydraulic fractures in layered medium[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2022, 50(2): 132–138. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2022060
[12] WANG T, TCHAKAROV B J. Modular resistivity sensor for downhole measurement while drilling: US 9638819 B2[P]. 2017−05−02.
[13] 康正明,秦浩杰,张意,等. 基于LSTM神经网络的随钻方位电磁波测井数据反演[J]. 石油钻探技术,2023,51(2):116–124. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2023047 KANG Zhengming, QIN Haojie, ZHANG Yi, et al. Data inversion of azimuthal electromagnetic wave logging while drilling based on LSTM neural network[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2023, 51(2): 116–124. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2023047
[14] MA Zhonghua, LIU Dejun, LI Hui, et al. Numerical simulation of a multi-frequency resistivity logging-while-drilling tool using a highly accurate and adaptive higher-order finite element method[J]. Advances in Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2012, 4(4): 439–453. doi: 10.4208/aamm.10-m11158
[15] 魏宝君,徐丹,王莎莎. 通讯槽对电磁波传播随钻测量信号的影响[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版),2011,35(1):56–60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2011.01.010 WEI Baojun, XU Dan, WANG Shasha. Influence of communication slots on signal of electromagnetic propagation measurement while drilling[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum(Edition of Natural Science), 2011, 35(1): 56–60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2011.01.010
[16] 刘得军,马中华,苑赫,等. 自适应高阶矢量有限元方法在随钻电阻率测井中的应用[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版),2012,36(4):77–83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2012.04.014 LIU Dejun, MA Zhonghua, YUAN He, et al. Application of adaptive higher-order vector finite element method to simulate resistivity logging-while-drilling tool response[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2012, 36(4): 77–83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2012.04.014
[17] 宋殿光,段宝良,魏宝君,等. 金属钻铤对随钻电磁波电阻率测井仪测量信号的影响[J]. 测井技术,2014,38(2):201–205. SONG Dianguang, DUAN Baoliang, WEI Baojun, et al. The influence of metal mandrel on electromagnetic resistivity logging responses[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2014, 38(2): 201–205.
[18] 许巍,柯式镇,李安宗,等. 随钻电磁波测井仪器结构影响的三维有限元模拟[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版),2016,40(6):50–56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2016.06.006 XU Wei, KE Shizhen, LI Anzong, et al. Structural effects analysis of an electromagnetic wave propagation resistivity LWD tool by 3D finite element method[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2016, 40(6): 50–56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2016.06.006
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 陈德春,张文宣,阳成,常峰,邴绍强,张鹏,王亮亮,马硕. 基于井口流体温度的含水率计算模型. 断块油气田. 2025(03): 514-521 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 魏锋,陈现,王迪,夏瑜. 海上少井条件下含水率计算方法研究及应用. 海洋石油. 2022(04): 63-66 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王谦,谭茂金,石玉江,李高仁,程相志,罗伟平. 径向基函数神经网络法致密砂岩储层相对渗透率预测与含水率计算. 石油地球物理勘探. 2020(04): 864-872+704 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王谦,石玉江,谭茂金,李高仁. 基于孔隙结构分类的致密砂岩含水率计算模型——以鄂尔多斯盆地陇东西部延长组长8_1储层为例. 石油物探. 2019(05): 669-680 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)




 下载:
下载: