Three-Dimensional Simulation of Erosion Life of Metal Mesh Screen Pipe Based on Fluent-DPM Method
-
摘要:
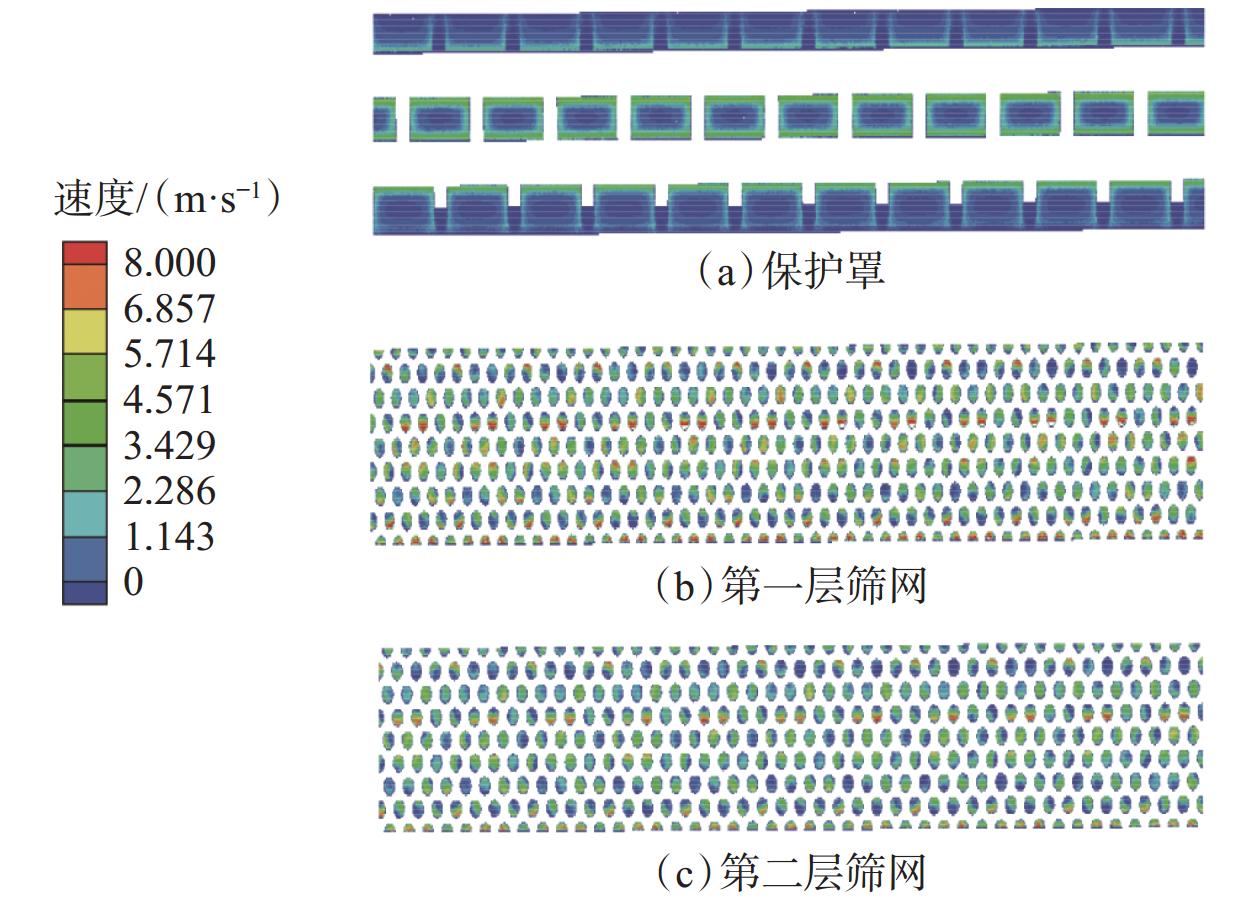
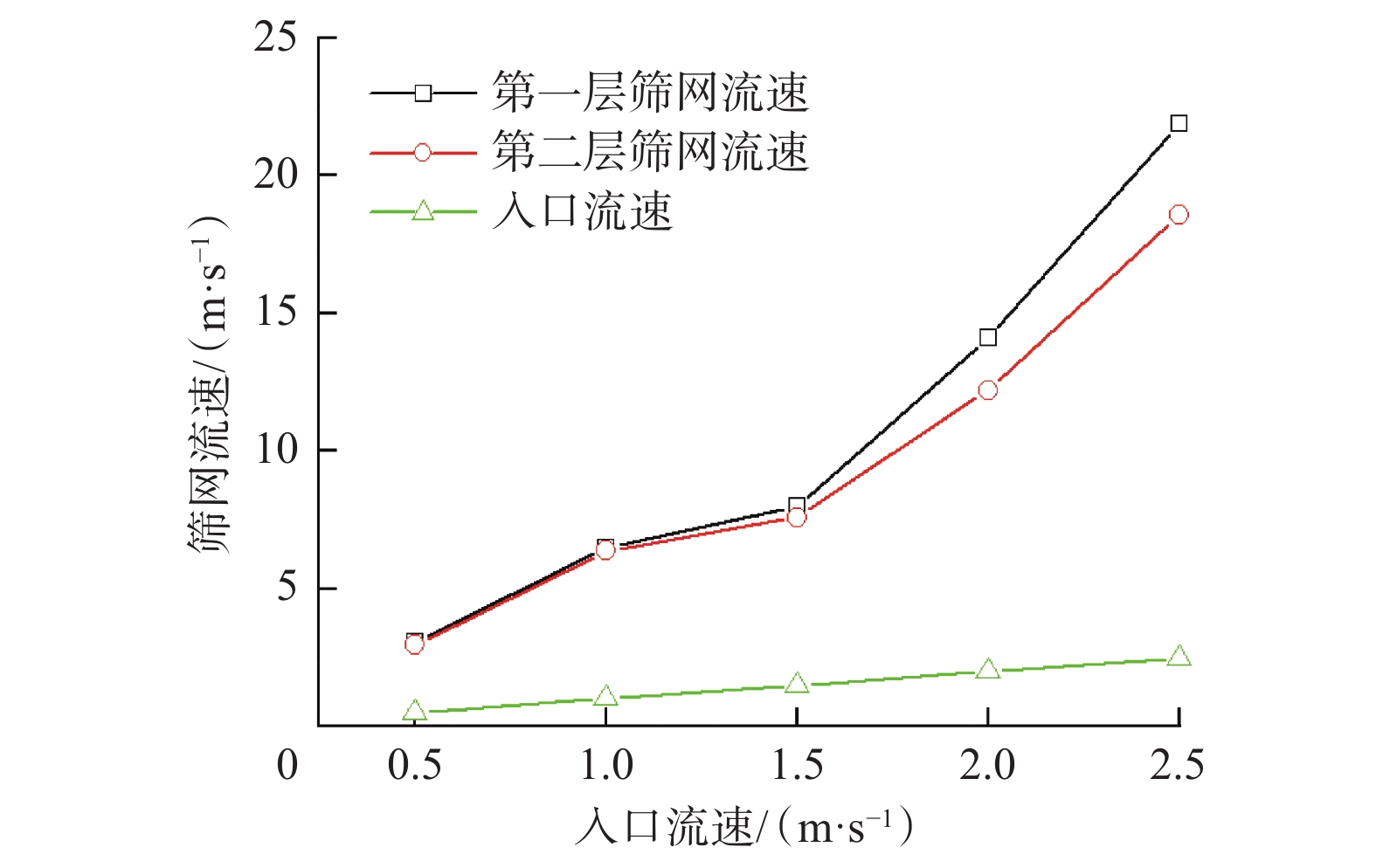
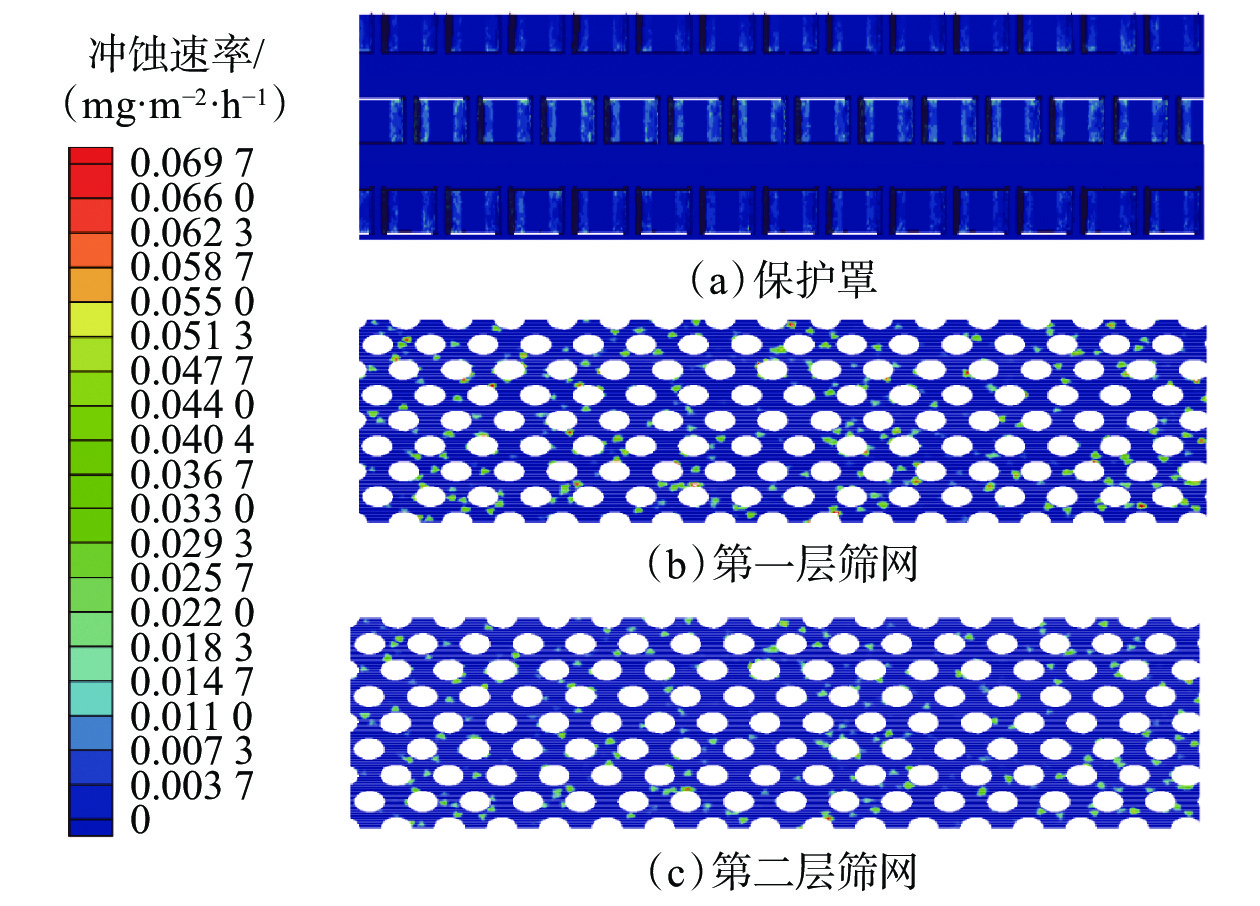
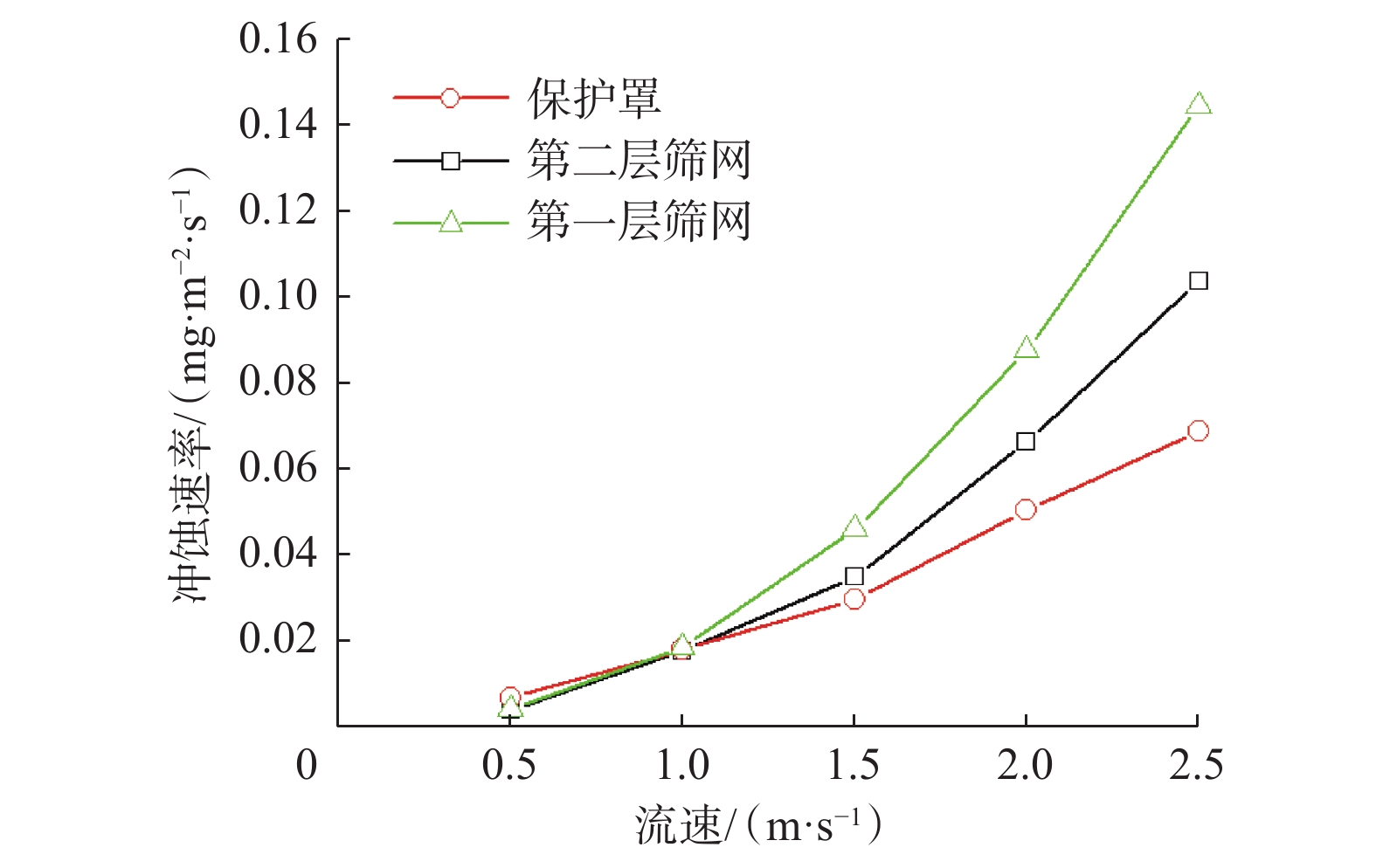
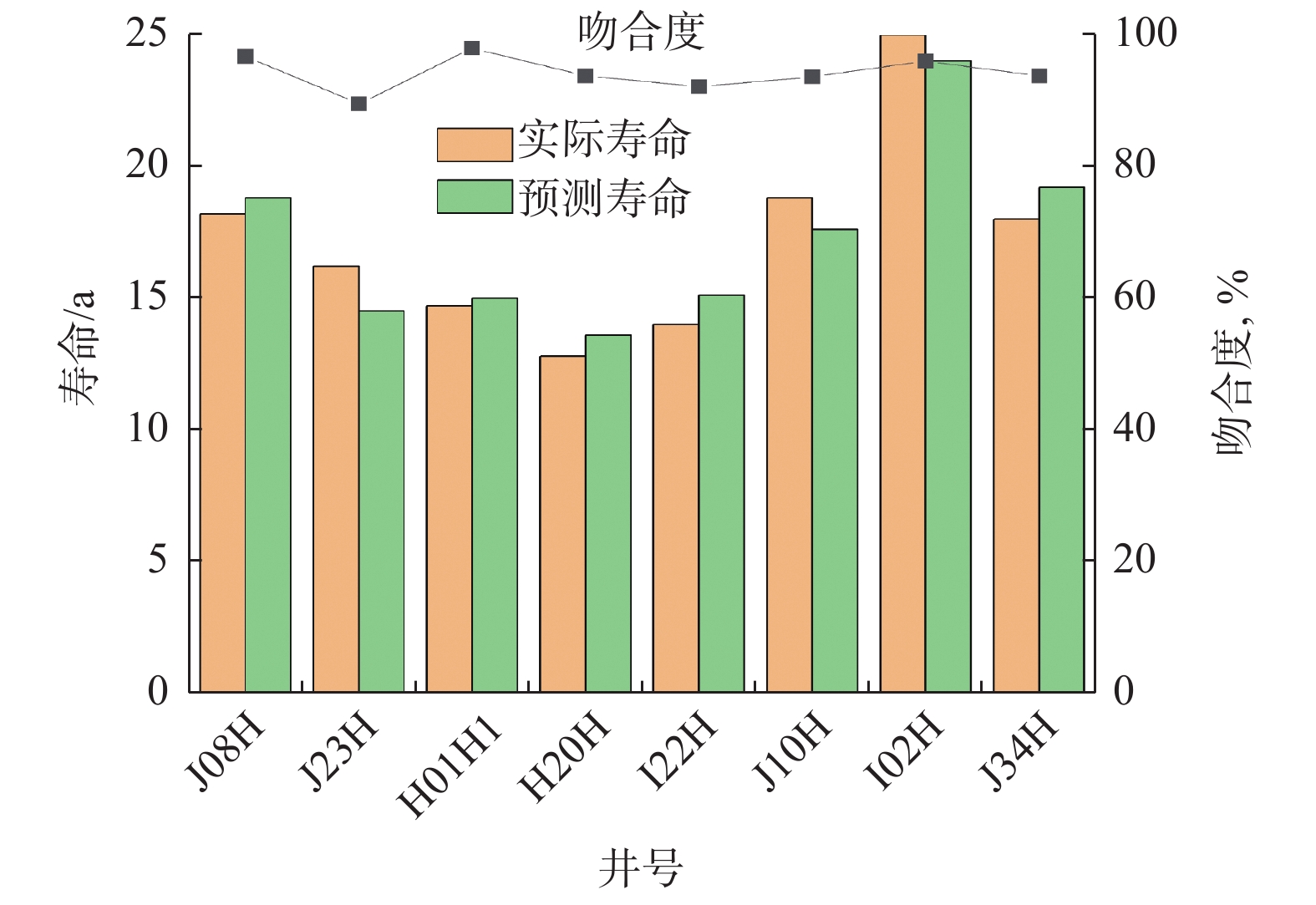
金属网布筛管在砂砾冲蚀作用下破坏严重,筛网冲蚀寿命难以预测。为此,建立了考虑金属网布筛管外层保护罩和内层筛网混合结构的三维仿真数值模拟模型,利用流体动力学离散颗粒流(DPM)方法,模拟了生产过程中砂砾冲蚀金属网布的过程,分析了流速对金属网布筛管冲蚀速率的影响。研究发现,冲蚀破坏的临界流速为1.00 m/s,入口流速小于1.00 m/s时,数值模拟预测的冲蚀速率与试验的冲蚀速率相当;入口流速大于1.00 m/s时,受筛管整体结构的影响,数值模拟预测的冲蚀速率比试验值大2.1倍。金属网布筛管外层保护罩是影响筛网过流流速的主要因素;受保护罩过流面积突然减小的影响,流体经过第一层筛网和第二层筛网的流速远大于外层保护罩入口的流速,导致金属网布产生冲蚀破坏。利用该方法预测了8口生产井筛管的寿命,与实际监测寿命相比,相对误差在10.5%以内,满足实际工程应用要求。研究结果表明,基于三维Fluent-DPM方法预测的金属网布筛管冲蚀寿命与实际情况基本一致,为预测金属网布筛管冲蚀寿命提供了新方法。
Abstract:Metal mesh screen pipe is severely damaged under the erosion of sand and gravel particles, and the erosion life of the screen is difficult to predict. To this end, a three-dimensional numerical simulation model considering the mixed structure of the outer protective cover and the inner screen of the metal mesh screen pipe was established. The hydrodynamic discrete particle flow (DPM) method was used to simulate the process of the erosion of the metal mesh by the sand and gravel particles during production, and the influence of flow velocity on the erosion rate of the metal mesh screen pipe was analyzed. The results show when the critical flow velocity for erosion damage is 1.00 m/s. When the inlet flow velocity is less than 1.00 m/s, the simulated erosion rate is comparable to the test erosion rate. When the inlet flow velocity is greater than 1.00 m/s, the simulated erosion rate is 2.1 times higher than the test one due to the influence of the overall structure of the screen pipe. The structure of the outer protective cover of the metal mesh screen pipe is the main factor affecting the overflow flow velocity through the screen. Affected by the sudden reduction of the overflow area of the protective cover, the flow velocity of the fluid passing through the first and second screen layers is much greater than the inlet velocity of the outer protective cover, resulting in erosion damage of the metal mesh. The method is used to predict the screen pipe life of eight production wells in the field, and relative error is within 10.5% compared with the actual monitoring life, which meets the requirements of practical engineering application. The study shows that the predicted erosion life of metal mesh screen pipe based on the 3D Fluent-DPM method is basically consistent with the actual situation, which provides a new method for predicting the erosion life of metal mesh screen pipe.
-
Keywords:
- sand production /
- erosion /
- screen pipe /
- erosion rate /
- erosion model
-
-
表 1 不同流速下金属网布的冲蚀速率
Table 1 Erosion rate of metal mesh at different flow rates
流速/
(m·s−1)试验冲蚀速率/
(mg·m−2·h−1)数值模拟冲蚀速率/
(mg·m−2·h−1)0.50 0.006 5 0.006 4 1.00 0.018 0 0.018 5 1.50 0.029 6 0.045 9 2.00 0.050 3 0.087 5 表 2 出砂井的生产参数
Table 2 Production parameters of sand-production wells
井号 井眼直径/
mm每米采油量/
(m3·d−1·m−1)平均流速/
(m·s−1)J10H 152.4 2.24 0.71 I02H 152.4 1.10 0.35 J23H 152.4 4.95 1.57 H01H1 152.4 1.89 0.60 H20H 177.8 5.70 1.33 I22H 177.8 2.49 0.58 J34H 177.8 4.12 0.96 J08H 177.8 2.92 0.68 -
[1] 廖华林,董林,牛继磊,等. 砾石充填条件下筛管堵塞与冲蚀特性试验[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版),2019,43(3):90–97. LIAO Hualin, DONG Lin, NIU Jilei, et al. An experimental study on plugging and erosion failures of sand screen in grave-packing conditions[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum(Edition of Natural Science), 2019, 43(3): 90–97.
[2] 董长银,宋洋,周玉刚,等. 天然气水合物储层泥质细粉砂挡砂介质堵塞规律与微观挡砂机制[J]. 石油学报,2020,41(10):1248–1258. DONG Changyin, SONG Yang, ZHOU Yugang, et al. Plugging law and microscopic sand retention mechanism of sand retaining medium of argillaceous fine silt sand in gas hydrate reservoirs[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2020, 41(10): 1248–1258.
[3] 刘新锋,高斐,赵轩康,等. 渤海湾中部疏松砂岩油藏砾石充填适度防砂适应性评价[J]. 科学技术与工程,2019,19(22):129–135. LIU Xinfeng, GAO Fei, ZHAO Xuankang, et al. Moderate sand control adaptability evaluation of gravel packing in loose sandstone reservoirs in central Bohai Bay[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2019, 19(22): 129–135.
[4] 孙岩,楼一珊,曹砚峰,等. 基于冲蚀-动网格耦合的绕丝筛管冲蚀过程数值模拟[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2021,43(2):160–169. SUN Yan, LOU Yishan, CAO Yanfeng, et al. Numerical simulation of the erosion process of wire wrapped screen based on erosion-dynamic grid coupling[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2021, 43(2): 160–169.
[5] 张锐,郝思臻,刘泽华,等. 基于CFD的深水气井防砂筛管冲蚀仿真模拟[J]. 实验室研究与探索,2019,38(11):73–77. ZHANG Rui, HAO Sizhen, LIU Zehua, et al. Simulation experiment of erosion of sand control screen in deep water gas well based on CFD[J]. Research and Exploration in Laboratory, 2019, 38(11): 73–77.
[6] MONDAL S, WU C H, SHARMA M M, et al. Characterizing, designing, and selecting metal mesh screens for standalone-screen applications[J]. SPE Drilling & Completion, 2016, 31(2): 85–94.
[7] GILLESPIE G, JONES C. Sand control screen erosion: when are you at risk?[R]. SPE 122269, 2009.
[8] 刘永红,张建乔,马建民,等. 石油防砂割缝筛管的冲蚀磨损性能研究[J]. 摩擦学学报,2009,29(3):283–287. LIU Yonghong, ZHANG Jianqiao, MA Jianmin, et al. Erosion wear behavior of slotted screen liner for sand control[J]. Tribology, 2009, 29(3): 283–287.
[9] 邱浩,曹砚锋,文敏,等. 基于油井生产动态数据的出砂油井筛管冲蚀模型[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2019,41(6):796–801. QIU Hao, CAO Yanfeng, WEN Min, et al. Screen erosion model for sand-production oil well based on its production performance data[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2019, 41(6): 796–801.
[10] 王志坚,贾彦伯,尚晓峰. 螺旋复合筛管外护管固液两相流冲蚀磨损分析[J]. 石油矿场机械,2016,45(2):6–10. WANG Zhijian, JIA Yanbai, SHANG Xiaofeng. Erosion wear analysis of external protecting pipe with spiral composite screen pipe in solid-liquid two-phase flow[J]. Oil Field Equipment, 2016, 45(2): 6–10.
[11] PARSI M, AGRAWAL M, SRINIVASAN V, et al. CFD simulation of sand particle erosion in gas-dominant multiphase flow[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2015, 27(part 2): 706-718.
[12] 蒋晓斌,高凌霄,曹锴,等. 基于稠密离散相模型的冲缝筛管冲蚀数值模拟研究[J]. 石油工业技术监督,2023,39(4):24–32. JIANG Xiaobin, GAO Lingxiao, CAO Kai, et al. Research on the numerical simulation of calking screen erosion based on dense discrete phase model[J]. Technology Supervision in Petroleum Industry, 2023, 39(4): 24–32.
[13] YAN Wei, LI Fuli, LENG Guangyao, et al. Sand control screen erosion-failure prediction method in weakly consolidated sandstone reservoir[J]. Geoenergy Science and Engineering, 2023, 224: 211616. doi: 10.1016/j.geoen.2023.211616
[14] DENG Fucheng, DENG Ziqiang, HE Liang, et al. Life prediction of slotted screen based on back-propagation neural network[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2021, 119: 104909. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2020.104909
[15] 翟晓鹏,孟文波,孔祥吉,等. 用离散颗粒流数值模拟方法预测气井金属网布筛管冲蚀寿命[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2020,42(5):668–672. ZHAI Xiaopeng, MENG Wenbo, KONG Xiangji, et al. Applying the DPM numerical simulation method to predict the erosion life of metal mesh screen in gas wells[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2020, 42(5): 668–672.
[16] 陈珊珊,时培忠,冯义,等. 不同流速下金属网布筛管冲蚀寿命预测[J]. 石油机械,2021,49(12):77–82. CHEN Shanshan, SHI Peizhong, FENG Yi, et al. Erosion life prediction of wire mesh screen pipe at different flow rates[J]. China Petroleum Machinery, 2021, 49(12): 77–82.
[17] 邱浩,曹砚锋,文敏,等. 海上油气井防砂筛管冲蚀规律和失效预测研究[J]. 中国海上油气,2023,35(2):155–162. QIU Hao, CAO Yanfeng, WEN Min, et al. Erosion law and failure prediction of sand control screen in offshore oil and gas wells[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2023, 35(2): 155–162.
[18] 赵田臣,樊云昌,付华,等. 砂浆冲蚀磨损特性研究[J]. 润滑与密封,2003,28(2):58–59. ZHAO Tianchen, FAN Yunchang, FU Hua, et al. Study of slurry erosive wear[J]. Lubrication Engineering, 2003, 28(2): 58–59.
[19] FINNIE I. Erosion of surfaces by solid particles Oberflächenerosion durch feste teilchen[J]. Wear, 1960, 3(2): 87–103. doi: 10.1016/0043-1648(60)90055-7
[20] 刘宗恩,韩兵奇,张坤. 油气井防砂冲蚀试验装置[J]. 液压气动与密封,2015,35(6):35–37. LIU Zongen, HAN Bingqi, ZHANG Kun. Erosion test device of the sand management for oil and gas well[J]. Hydraulics Pneumatics & Seals, 2015, 35(6): 35–37.
[21] ZHANG Yongli, MCLAURY B S, SHIRAZI S A. Improvements of particle near-wall velocity and erosion predictions using a commercial CFD code[J]. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 2009, 131(3): 031303. doi: 10.1115/1.3077139
[22] YANG Siqi, ZHANG Laibin, FAN Jianchun, et al. Experimental study on erosion behavior of fracturing pipeline involving tensile stress and erosion prediction using random forest regression[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2021, 87: 103760. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2020.103760
[23] 邹林浩,宋杨,苏义脑,等. 水平井分段压裂套管孔眼冲蚀机理研究[J]. 特种油气藏,2024,31(5):127–135. ZOU Linhao, SONG Yang, SU Yinao, et al. Study on the casing erosion mechanism in staged fracturing of horizontal wells[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2024, 31(5): 127–135.
[24] 吕振虎,张羽鹏,石善志,等. 水平井体积压裂高速冲蚀套管内井下行为特征研究[J]. 石油钻探技术,2024,52(6):86–96. LYU Zhenhu, ZHANG Yupeng, SHI Shanzhi, et al. Downhole behavior characteristics of horizontal well volume fracturing in high-speed erosion casing[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2024, 52(6): 86–96.
[25] 艾国生,张波,冯春宇,等. WC-Co硬质合金冲蚀模型研究及应用[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版),2024,46(3):179–188. AI Guosheng, ZHANG Bo, FENG Chunyu, et al. Research and application of WC-Co cemented carbide erosion model[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University(Science & Technology Edition), 2024, 46(3): 179–188.
[26] 卓仁燕,马新仿,李建民,等. 水平井限流压裂对射孔孔眼冲蚀的影响[J]. 钻采工艺,2023,46(2):77–82. ZHUO Renyan, MA Xinfang, LI Jianmin, et al. Effect of limited entry fracturing for horizontal wells on perforation erosion[J]. Drilling & Production Technology, 2023, 46(2): 77–82.
[27] CAMERON J, JONES C. Development, verification and application of a screen erosion model[R]. SPE 107437, 2007.
-
期刊类型引用(23)
1. 车继勇,丁鹏,王红月,马永刚. 组合钻具定向钻井造斜及提速技术方法. 设备管理与维修. 2024(08): 98-100 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 熊浪豪,巢世伟,柏尚宇,陈君,范乘浪,崔建峰. E Zhanbyrshy-3井钻井实践及技术难点分析. 内蒙古石油化工. 2023(05): 63-66+120 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 汪伟,柳贡慧,李军,查春青,连威,夏铭莉. 脉动式扭转冲击钻井工具工作特性分析与测试. 石油钻探技术. 2022(05): 63-69 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 宋周成,翟文宝,邓昌松,徐杨,徐席明,汪鑫,文涛. 富满油田超深井井身结构优化技术与应用. 钻采工艺. 2022(06): 36-41 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王涛,刘锋报,罗威,晏智航,陆海瑛,郭斌. 塔里木油田防漏堵漏技术进展与发展建议. 石油钻探技术. 2021(01): 28-33 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 崔月明,史海民,张清. 吉林油田致密油水平井优快钻井完井技术. 石油钻探技术. 2021(02): 9-13 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 苏崭,王博,盖京明,李玮,赵欢,陈冰邓. 复合式扭力冲击器在坚硬地层中的应用. 中国煤炭地质. 2021(05): 47-50+57 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 张强,饶志华,秦世利,金勇. 南海东部深层古近系高效开发技术探索与实践. 石油化工应用. 2021(06): 34-38 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 李银婷,董小虎. 顺北油田钻井参数强化的提速效果评价. 钻探工程. 2021(07): 72-78 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 陈冬毅,徐鲲,张作伟,吕广,张鑫,郭小明. 恒压恒扭工具在渤海油田中的应用. 科学技术创新. 2021(22): 153-154 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 严德,张玉山,宋玲安,陈彬,李彬,刘保波. 深水高温高压井钻井技术探索与实践. 中国石油和化工标准与质量. 2021(13): 193-194 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 张喆,闫楚旋,冯震,脱直霖,石朝龙. 塔里木油田HLHT区块优快钻井技术研究. 云南化工. 2021(10): 127-129 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 李双贵,于洋,樊艳芳,曾德智. 顺北油气田超深井井身结构优化设计. 石油钻探技术. 2020(02): 6-11 .  本站查看
本站查看
14. 袁国栋,王鸿远,陈宗琦,母亚军,席宝滨. 塔里木盆地满深1井超深井钻井关键技术. 石油钻探技术. 2020(04): 21-27 .  本站查看
本站查看
15. 张智亮,王威,伊明,刘强. 井下安全监控系统设计与实现. 石油钻探技术. 2020(06): 65-70 .  本站查看
本站查看
16. 周波,汪海阁,张富成,纪国栋,韩泽龙,武强. 温度压力对岩石可钻性和破岩效率影响实验. 石油钻采工艺. 2020(05): 547-552 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 李林涛,万小勇,黄传艳,潘丽娟,郭知龙,曹宗波,张伟博. 双向卡瓦可回收高温高压封隔器的研制与应用. 石油机械. 2019(03): 81-86 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 路宗羽,赵飞,雷鸣,邹灵战,石建刚,卓鲁斌. 新疆玛湖油田砂砾岩致密油水平井钻井关键技术. 石油钻探技术. 2019(02): 9-14 .  本站查看
本站查看
19. 江波,任茂,王希勇. 彭州气田PZ115井钻井提速配套技术. 探矿工程(岩土钻掘工程). 2019(08): 73-78 .  百度学术
百度学术
20. 郑振国,黎红胜,赵海艳,温慧芸,孙东方. 哥伦比亚Matambo区块深井钻井关键技术. 石油钻探技术. 2018(02): 30-37 .  本站查看
本站查看
21. 丁红,宋朝晖,袁鑫伟,邢战,张宏阜,张仪. 哈拉哈塘超深定向井钻井技术. 石油钻探技术. 2018(04): 30-35 .  本站查看
本站查看
22. 李世昌,闫立鹏,李建冰,白文路,杨秀丽,闫天宇. 自循环粒子射流钻井提速工具机理研究. 中国锰业. 2018(03): 98-102 .  百度学术
百度学术
23. 陈养龙,席宝滨,晁文学,朱伟厚. 顺北区块Ⅰ号断裂带钻井分层提速技术. 断块油气田. 2018(05): 649-652 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)



 下载:
下载: