Lamination Type Recognition with Artificial Intelligence Based on Optical Thin Section
-
摘要:
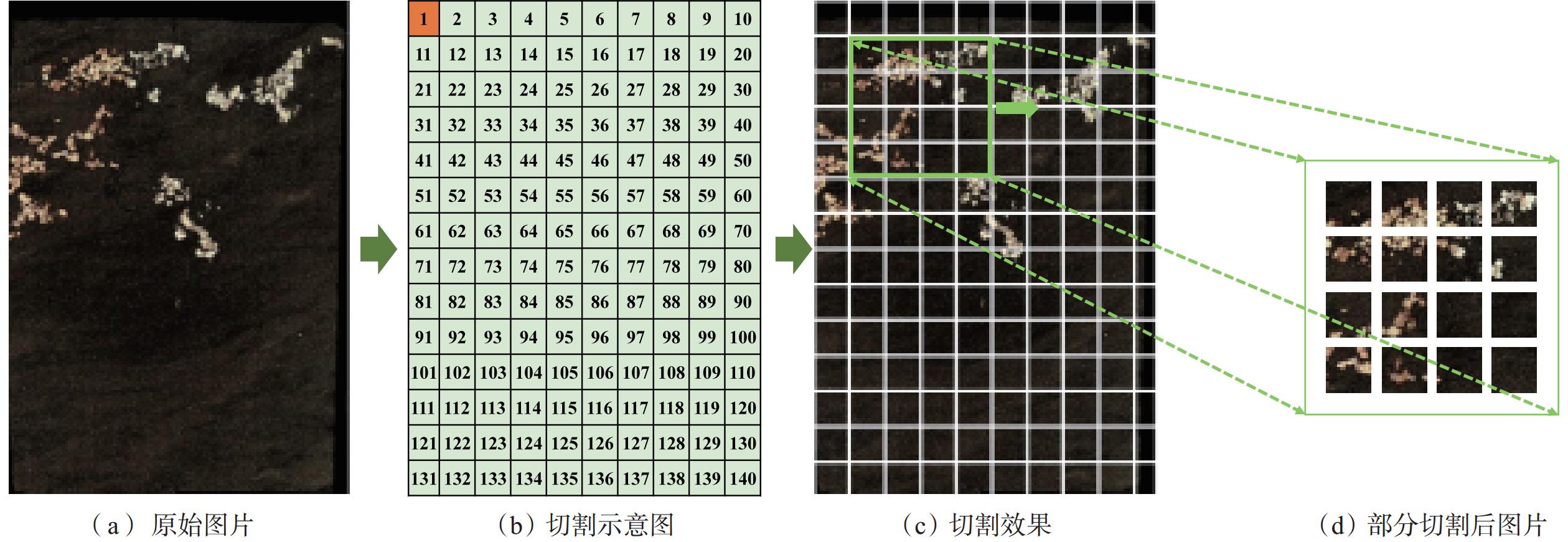
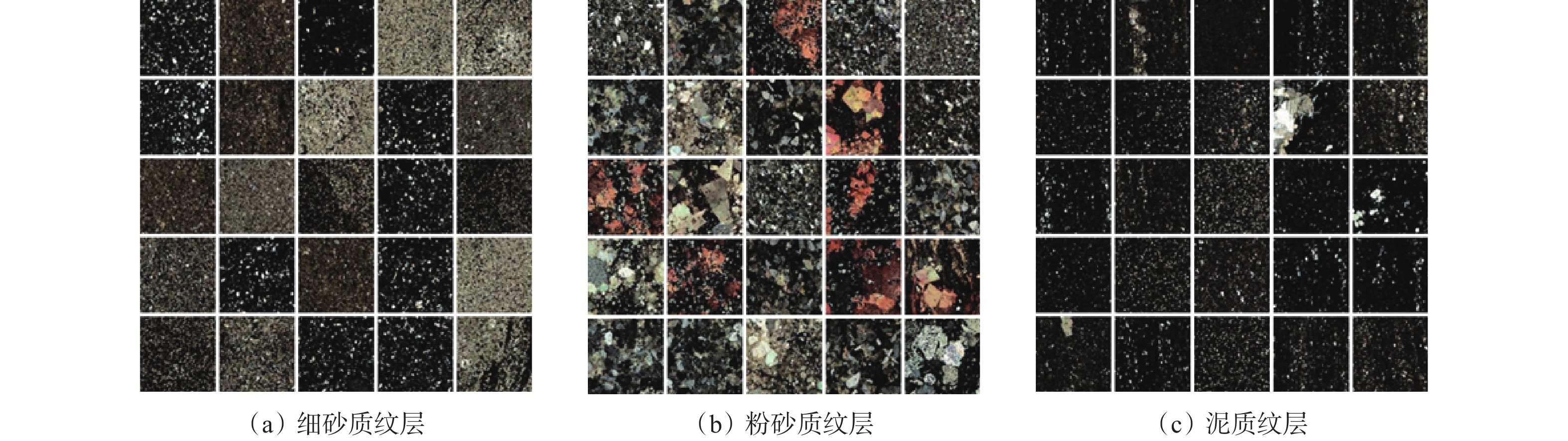
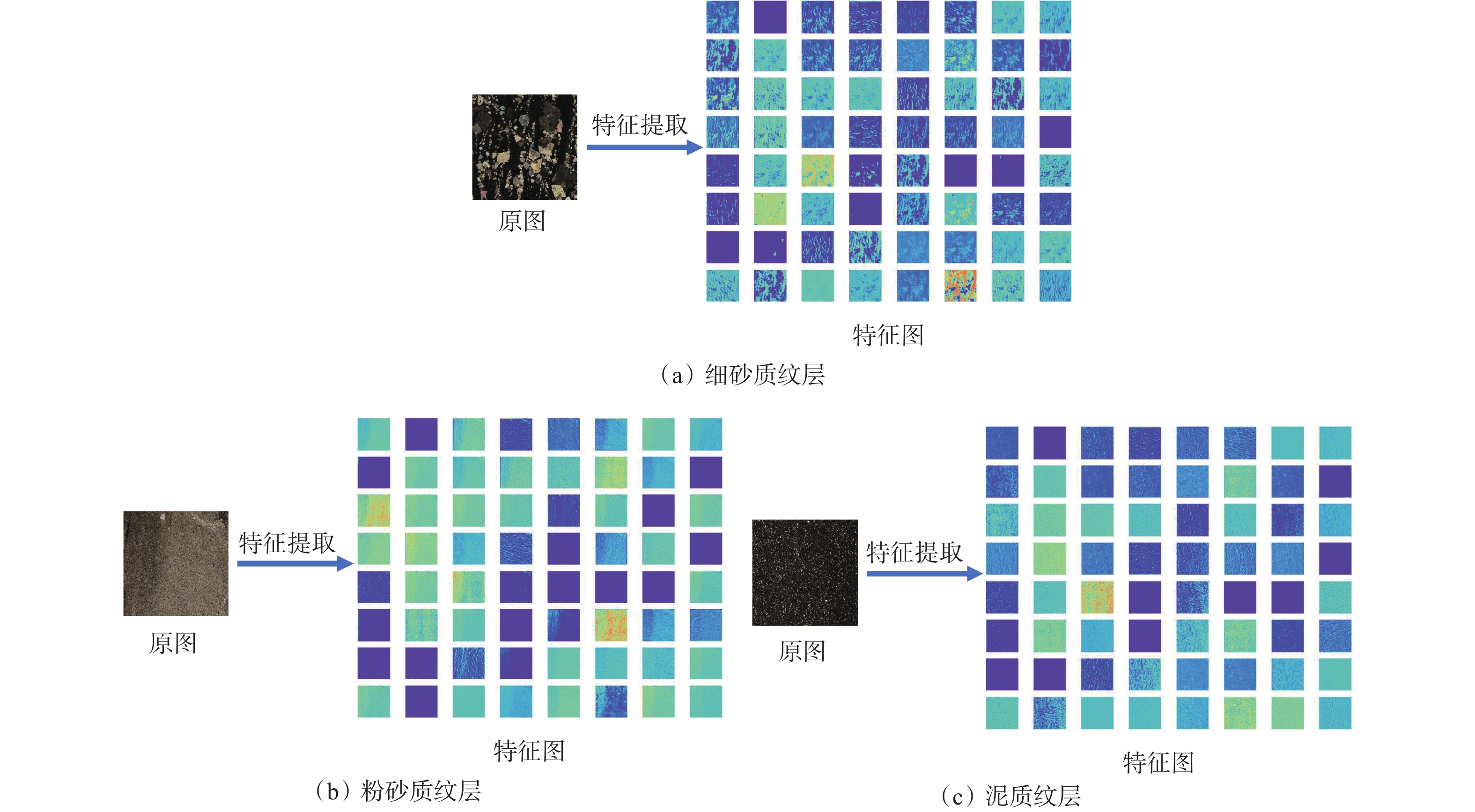
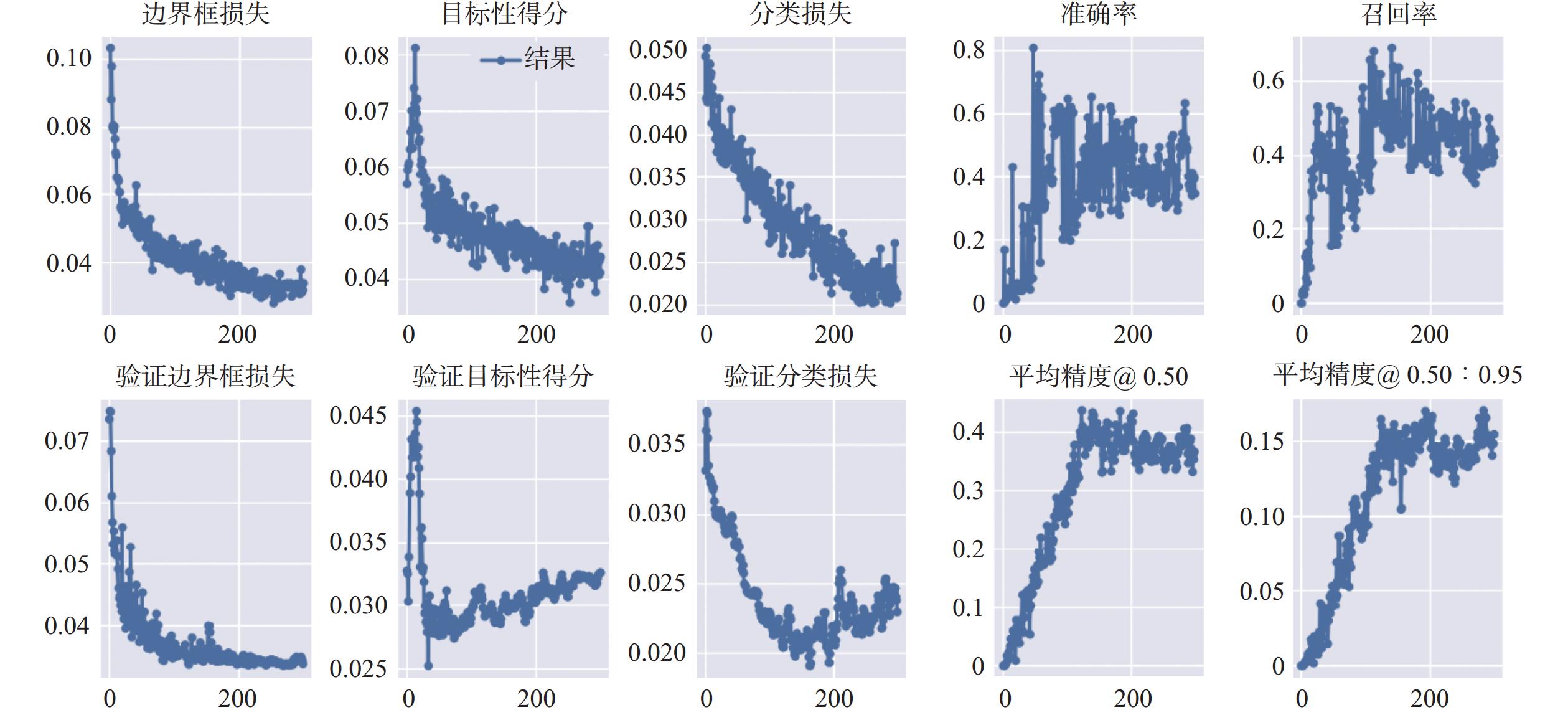
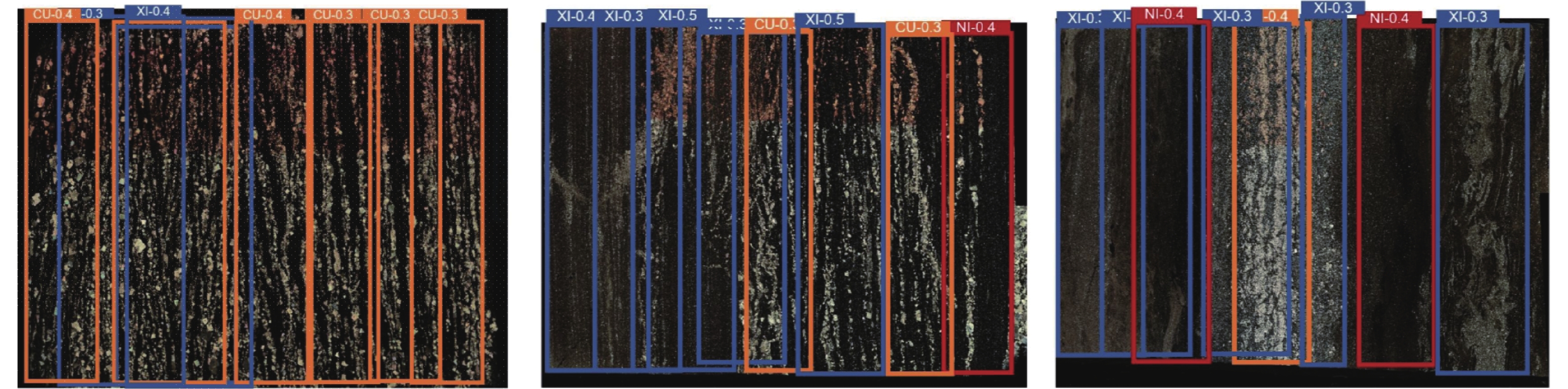
纹层类型的准确识别是光学薄片技术在油田勘探开发过程中的一个重要应用。在页岩储层改造过程中,由于页岩特有的薄层理构造与非均质性,准确识别地层中纹层类型,对选取储层改造位置和优化改造方案具有重要意义。光学大薄片相较于传统测井数据具有更加精确的岩性划分,相较于普通薄片具有更大尺度的纵向连续岩性变化规律特征,可提供厘米级别的储层信息,从而能够准确划分纹层类型,优选工程甜点。基于卷积神经网络(CNN)构建了纹层分类模型(简称CNN模型),利用纵向上连续的光学大薄片数据,CNN模型可以准确识别细砂质纹层、粉砂质纹层和泥质纹层,分类精度最高达73%,且分类准确率优于YOLOv5模型。研究结果表明,CNN模型能够有效实现纹层类型智能识别,且能够应对复杂背景和精细纹层特征,为页岩油气储层的精细化表征和开发提供了一种高效、精准的解决方案。
Abstract:The accurate recognition of lamination types is an important application field of optical thin section technology in the process of oilfield exploration and development. In the process of shale reservoir stimulation, due to the unique thin bedding structure and heterogeneity of shale, it is of great significance to accurately identify the lamination types in the formation for selecting the reservoir stimulation location and optimizing the stimulation plan. Compared with the well logging data, the large optical thin sections can achieve more accurate lithology division, and they have more obvious longitudinally continuous lithology variation characteristics than the ordinary thin sections, which can provide reservoir information at the centimeter level, so as to accurately classify the lamination types and optimize the engineering sweet spots. A lamination classification model (referred to as the CNN model) was constructed based on a convolutional neural network (CNN), and three types of lamination were classified and recognized by longitudinally continuous large optical thin section data. The results show that the CNN model can accurately identify fine sand lamination, silty sand lamination, and argillaceous lamination, and the classification accuracy can reach 73% and it is better than that of the YOLOv5 model. The results show that the CNN model can effectively realize intelligent lamination recognition and can deal with complex background and fine lamination features, which provides an efficient and accurate solution for the fine characterization and development of shale oil and gas.
-
Keywords:
- shale /
- lamination type /
- optical thin section /
- image classification /
- neural network /
- intelligent recognition
-
-
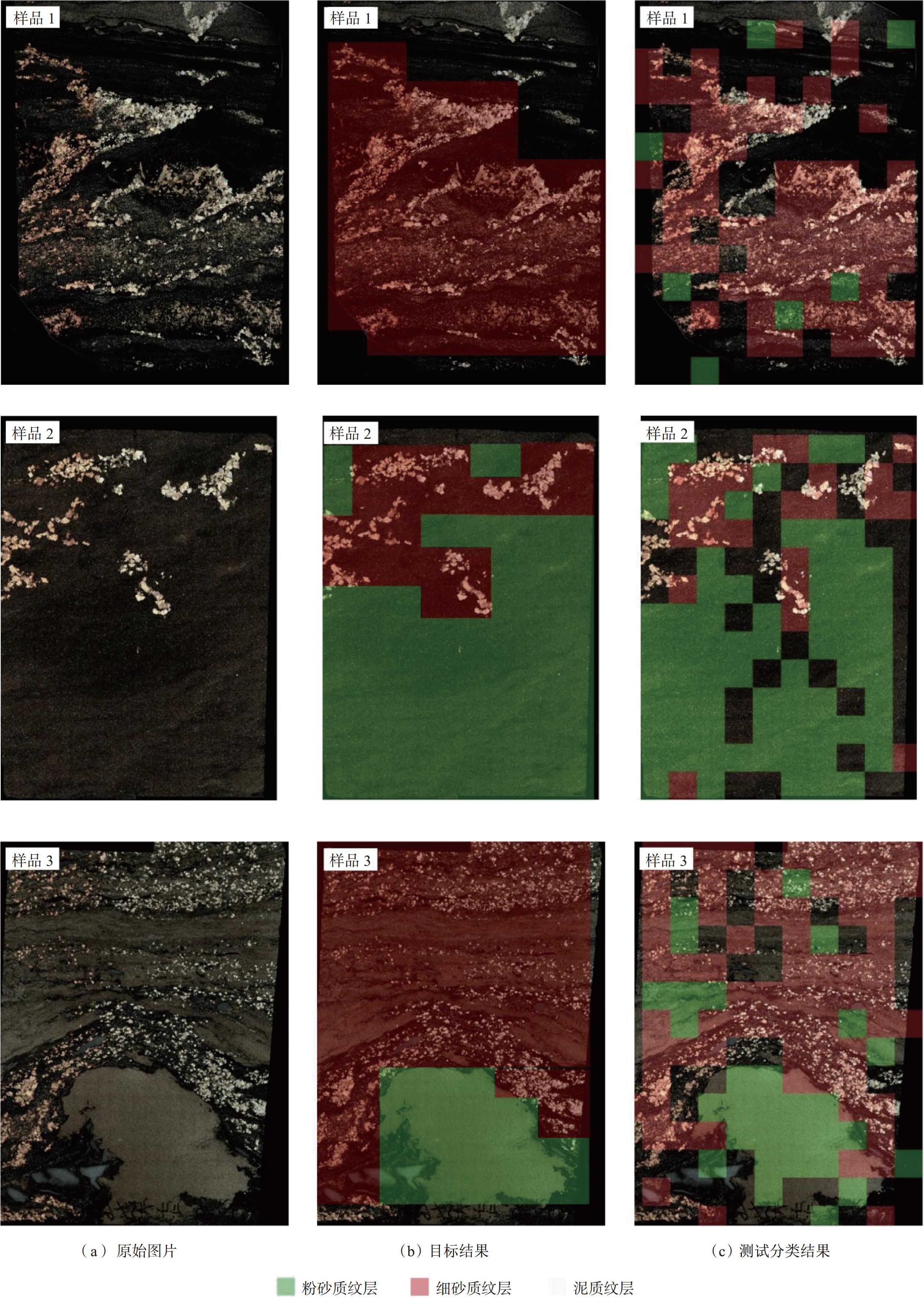
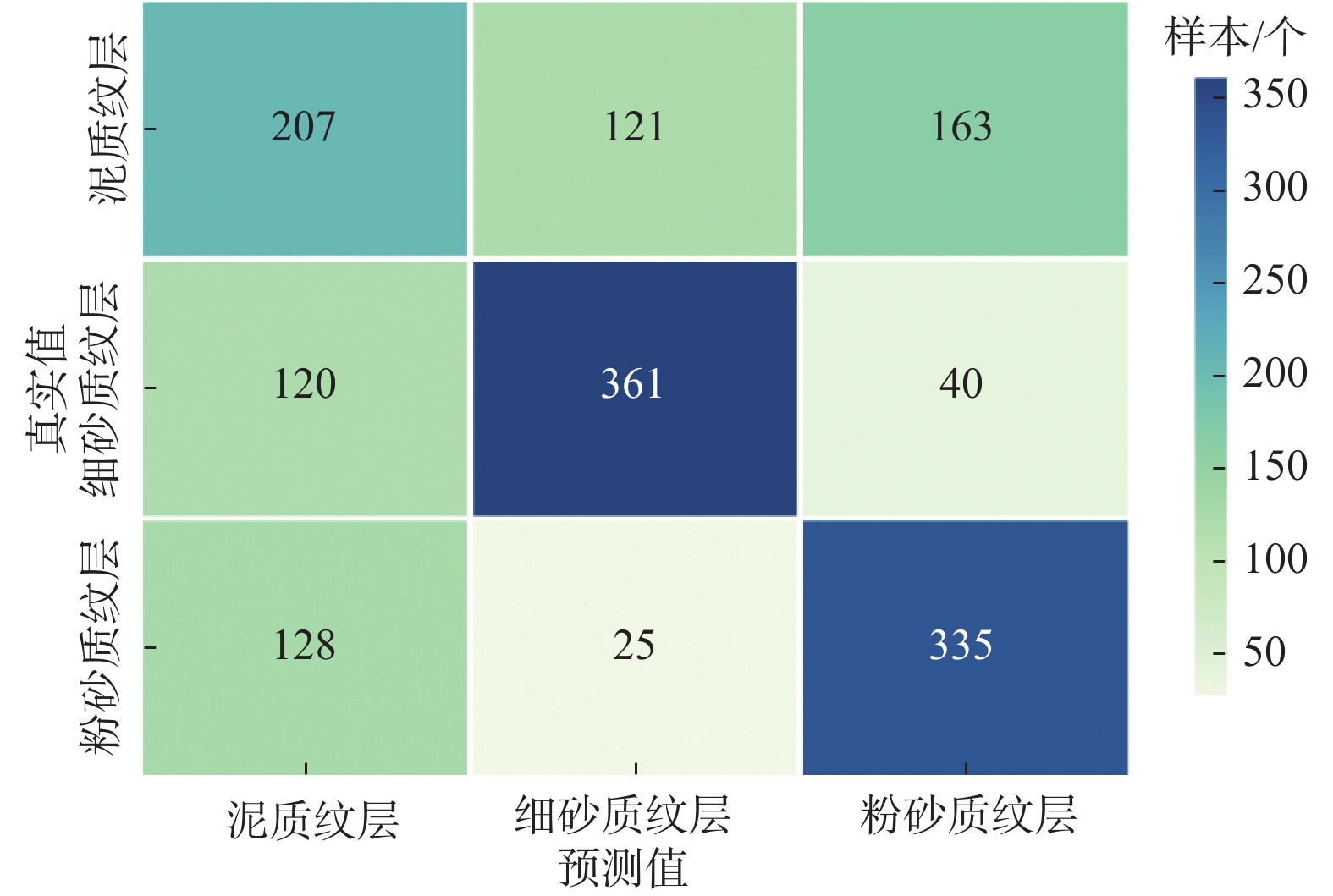
表 1 单井段CNN模型纹层分类效果
Table 1 Single-well segment lamination classification effects based on CNN model
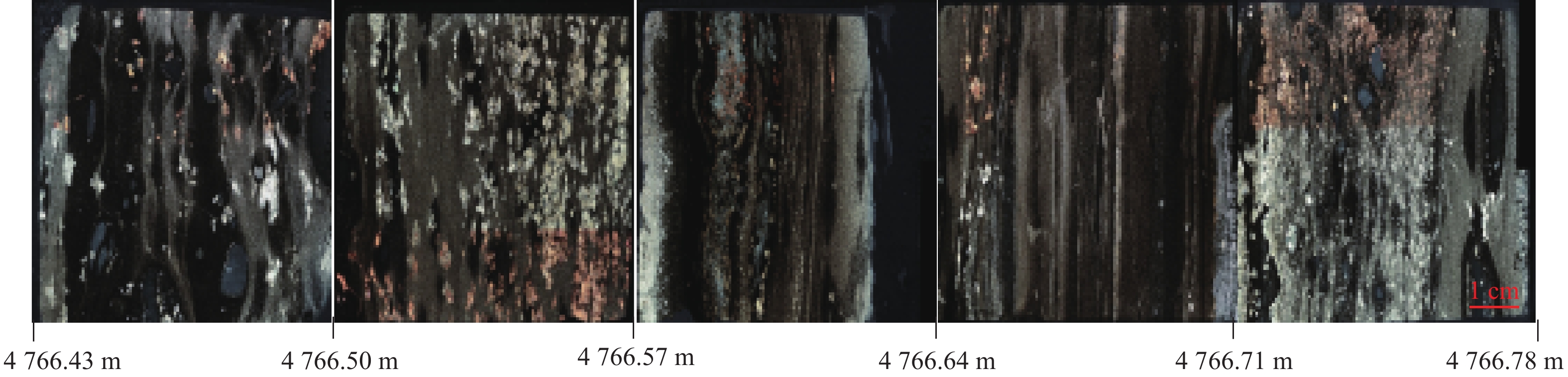
纹层类型 精度 召回率 F1值 泥质纹层 0.45 0.42 0.44 细砂质纹层 0.71 0.69 0.70 粉砂质纹层 0.62 0.69 0.65 表 2 4 669.94~4 670.37 m井段连续纹层识别结果
Table 2 Identification results of continuous lamination in well section of 4 669.94~4 670.37 m
序号 井段/m 纹层类型 准确率 1 4 669.94~4 669.96 细砂质 0.75 2 4 669.96~4 670.00 粉砂质 0.60 3 4 670.03~4 670.07 粉砂质 0.67 4 4 670.07~4 670.09 泥质 0.42 5 4 670.10~4 670.13 细砂质 0.73 6 4 670.13~4 670.18 粉砂质 0.61 7 4 670.21~4 670.27 粉砂质 0.68 8 4 670.31~4 670.34 粉砂质 0.66 9 4 670.34~4 670.37 泥质 0.47 表 3 多井段CNN模型纹层分类效果
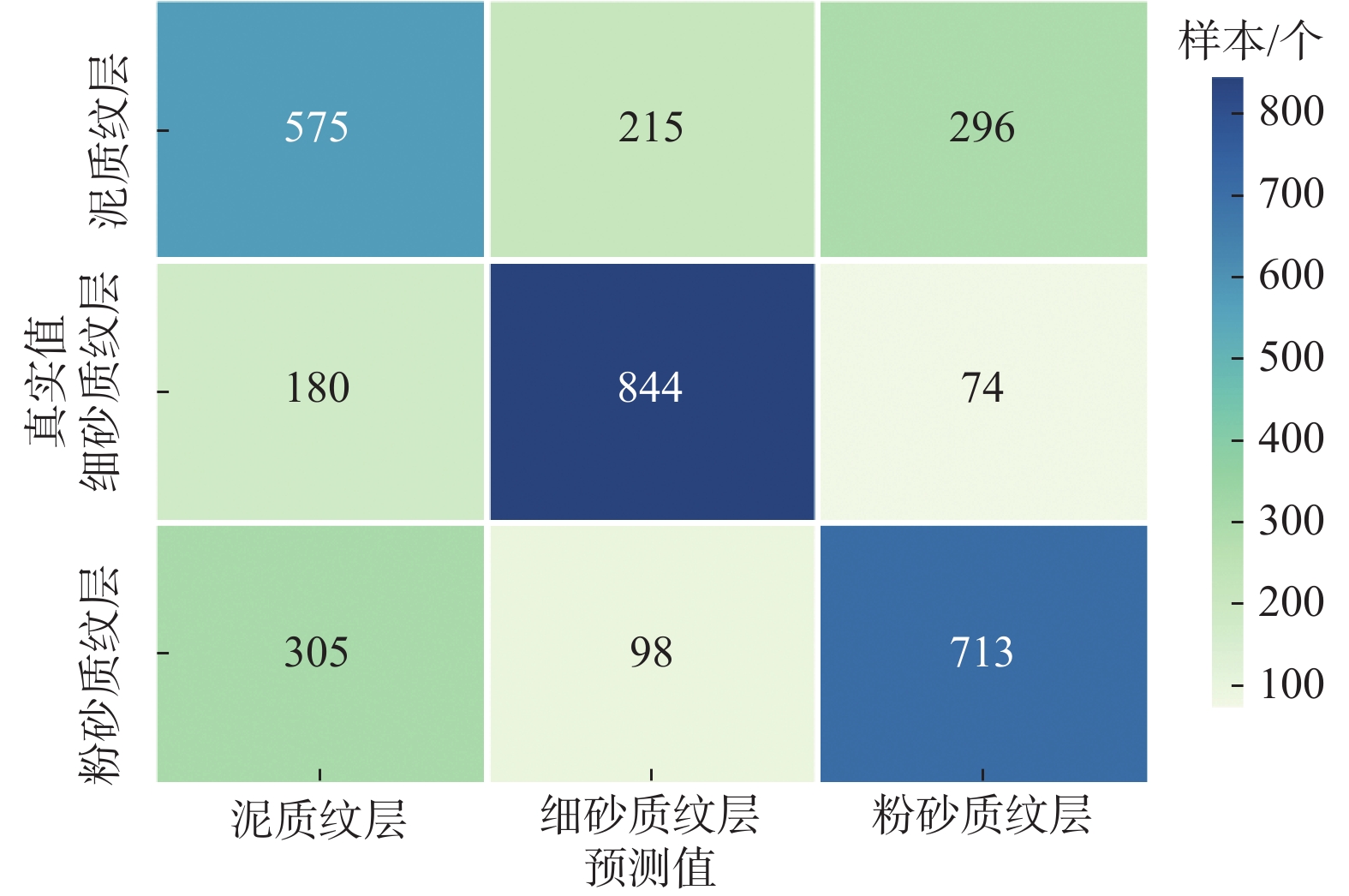
Table 3 Multi-well segment lamination classification effects
纹层类型 精度 召回率 F1值 泥质纹层 0.54 0.53 0.54 细砂质纹层 0.73 0.77 0.75 粉砂质纹层 0.66 0.64 0.65 表 4 4 711.14~4 712.40 m井段连续纹层识别结果
Table 4 Identification results of continuous lamination in well section of 4 711.14~4 712.40 m
序号 井段/m 纹层类型 准确率 1 4 711.14~4 711.16 粉砂质 0.68 2 4 711.16~4 711.20 细砂质 0.72 3 4 711.31~4 711.35 泥质 0.55 4 4 711.35~4 711.37 细砂质 0.77 5 4 711.68~4 711.73 粉砂质 0.73 6 4 711.90~4 711.91 粉砂质 0.71 7 4 711.91~4 711.93 粉砂质 0.68 8 4 711.93~4 711.95 泥质 0.66 9 4 711.95~4 711.96 粉砂质 0.76 10 4 712.02~4 712.09 泥质 0.68 11 4 712.21~4 712.27 粉砂质 0.72 12 4 712.33~4 712.40 泥质 0.62 -
[1] 石晓闪,刘大安,崔振东,等. 页岩气开采压裂技术分析与思考[J]. 天然气勘探与开发,2015,38(3):62–65. SHI Xiaoshan, LIU Da’an, CUI Zhendong, et al. Analysis and consideration of fracturing technology for shale gas exploitation[J]. Natural Gas Exploration and Development, 2015, 38(3): 62–65.
[2] 薛承瑾. 页岩气压裂技术现状及发展建议[J]. 石油钻探技术,2011,39(3):24–29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0890.2011.03.004 XUE Chengjin. Technical advance and development proposals of shale gas fracturing[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2011, 39(3): 24–29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0890.2011.03.004
[3] 赵文智,朱如凯,刘伟,等. 中国陆相页岩油勘探理论与技术进展[J]. 石油科学通报,2023,8(4):373–390. ZHAO Wenzhi, ZHU Rukai, LIU Wei, et al. Advances in theory and technology of non-marine shale oil exploration in China[J]. Petroleum Science Bulletin, 2023, 8(4): 373–390.
[4] 刘惠民,王敏生,李中超,等. 中国页岩油勘探开发面临的挑战与高效运营机制研究[J]. 石油钻探技术,2024,52(3):1–10. LIU Huimin, WANG Minsheng, LI Zhongchao, et al. Challenges and efficient operation mechanism of shale oil exploration and development in China[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2024, 52(3): 1–10.
[5] FAVERO V, FERRARI A, LALOUI L. On the hydro-mechanical behaviour of remoulded and natural Opalinus Clay shale[J]. Engineering Geology, 2016, 208: 128–135. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.04.030
[6] 金之钧,朱如凯,梁新平,等. 当前陆相页岩油勘探开发值得关注的几个问题[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2021,48(6):1276–1287. JIN Zhijun, ZHU Rukai, LIANG Xinping, et al. Several issues worthy of attention in current lacustrine shale oil exploration and development[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2021, 48(6): 1276–1287.
[7] 贾承造,王祖纲,姜林,等. 中国页岩油勘探开发研究进展与科学技术问题[J]. 世界石油工业,2024,31(4):1–11. JIA Chengzao, WANG Zugang, JIANG Lin, et al. Progress and key scientific and technological problems of shale oil exploration and development in China[J]. World Petroleum Industry, 2024, 31(4): 1–11.
[8] 李阳,曹小朋,赵清民,等. 济阳坳陷陆相断陷盆地页岩油开发的几点思考[J]. 石油钻探技术,2024,52(4):1–7. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2024074 LI Yang, CAO Xiaopeng, ZHAO Qingmin, et al. Thoughts on shale oil development in continental fault basin in Jiyang Depression[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2024, 52(4): 1–7. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2024074
[9] 胡月,陈雷,周昊,等. 海相页岩纹层特征及其对页岩储层发育的影响:以川南长宁地区龙马溪组为例[J]. 断块油气田,2021,28(2):145–150. HU Yue, CHEN Lei, ZHOU Hao, et al. Lamina characteristics of marine shale and its influence on shale reservoir development: a case study of Longmaxi Formation, Changning area, South Sichuan Basin[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2021, 28(2): 145–150.
[10] 周忠亚. 纹层型页岩油储层裂缝扩展机理及工艺对策[J]. 特种油气藏,2023,30(6):141–149. ZHOU Zhongya. Mechanism of fracture extension and process countermeasures in grain-type shale oil reservoirs[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2023, 30(6): 141–149.
[11] 熊敏,陈雷,陈鑫,等. 海相页岩纹层特征、成因机理及其页岩气意义[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2022,53(9):3490–3508. XIONG Min, CHEN Lei, CHEN Xin, et al. Characteristics, genetic mechanism of marine shale laminae and its significance of shale gas accumulation[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2022, 53(9): 3490–3508.
[12] 葸克来,李克,操应长,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组长73亚段富有机质页岩纹层组合与页岩油富集模式[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2020,47(6):1244–1255. XI Kelai, LI Ke, CAO Yingchang, et al. Laminae combination and shale oil enrichment patterns of Chang 73 sub-member organic-rich shales in the Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(6): 1244–1255.
[13] 唐洪明,唐 园,郑马嘉,等. 页岩纹层与破裂方式实验研究[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版),2022,44(4):51–61. TANG Hongming, TANG Yuan, ZHENG Majia, et al. An experimental study on lamina and fracture mode of shale[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition), 2022, 44(4): 51–61.
[14] BRITTENHAM M D. Geologic analysis of the Upper Jurassic Haynesville Shale in east Texas and west Louisiana: discussion[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2013, 97(3): 525–528. doi: 10.1306/01301211200
[15] BROADHEAD R F. Petrography and reservoir geology of Upper Devonian Shales, northern Ohio[J]. USGS Bulletin, 1993, 1909: 1–15.
[16] 贾文婷,牟建业,李小伟,等. 射孔参数对砂砾岩储层压裂的影响[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2024,46(1):97–105. JIA Wenting, MOU Jianye, LI Xiaowei, et al. Impact of perforation parameters on fracturing of glutenite reservoirs[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2024, 46(1): 97–105.
[17] 李国欣,刘国强,侯雨庭,等. 陆相页岩油有利岩相优选与压裂参数优化方法[J]. 石油学报,2021,42(11):1405–1416. doi: 10.7623/syxb202111001 LI Guoxin, LIU Guoqiang, HOU Yuting, et al. Optimization method of favorable lithofacies and fracturing parameter for continental shale oil[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2021, 42(11): 1405–1416. doi: 10.7623/syxb202111001
[18] 金智荣,黄 越,杜浩然,等. 页岩储层水平井密切割压裂射孔参数优化方法[J]. 石油机械,2023,51(6):89–96. JIN Zhirong, HUANG Yue, DU Haoran, et al. A perforating parameter optimization method for horizontal well multi-cluster fracturing in shale reservoirs[J]. China Petroleum Machinery, 2023, 51(6): 89–96.
[19] 韦世明,金衍,夏阳,等. 自发渗吸对页岩油储层压裂后闷井的影响[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2023,45(6):756–765. WEI Shiming, JIN Yan, XIA Yang, et al. Influence of spontaneous imbibition on post-fracturing well soaking in shale oil reservoirs[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2023, 45(6): 756–765.
[20] 陈思源,刘浩,金衍,等. 压裂支撑剂发展综述与展望[J]. 石油科学通报,2023,8(3):330–346. CHEN Siyuan, LIU Hao, JIN Yan, et al. Review and prospect of fracturing proppant development[J]. Petroleum Science Bulletin, 2023, 8(3): 330–346.
[21] 郭旭洋,金衍,黄雷,等. 页岩油气藏水平井井间干扰研究现状和讨论[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2021,43(3):348–367. GUO Xuyang, JIN Yan, HUANG Lei, et al. Research status and discussion of horizontal well interference in shale oil and gas reservoirs[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2021, 43(3): 348–367.
[22] 匡立春,刘合,任义丽,等. 人工智能在石油勘探开发领域的应用现状与发展趋势[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2021,48(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(21)60001-0 KUANG Lichun, LIU He, REN Yili, et al. Application and development trend of artificial intelligence in petroleum exploration and development[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2021, 48(1): 1–11. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(21)60001-0
[23] 蒋廷学,周珺,廖璐璐. 国内外智能压裂技术现状及发展趋势[J]. 石油钻探技术,2022,50(3):1–9. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2022065 JIANG Tingxue, ZHOU Jun, LIAO Lulu. Development status and future trends of intelligent fracturing technologies[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2022, 50(3): 1–9. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2022065
[24] 郭建春,张宇,曾凡辉,等. 非常规油气储层智能压裂技术研究进展与展望[J]. 天然气工业,2024,44(9):13–26. GUO Jianchun, ZHANG Yu, ZENG Fanhui, et al. Research progress and prospects of intelligent fracturing technology for unconventional reservoirs[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2024, 44(9): 13–26.
[25] 张世昆,陈作. 人工智能在压裂技术中的应用现状及前景展望[J]. 石油钻探技术,2023,51(1):69–77. ZHANG Shikun, CHEN Zuo. Status and prospect of artificial intelligence application in fracturing technology[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2023, 51(1): 69–77.
[26] 樊永东,庞惠文,金衍,等. 基于成像测井的孔缝智能分割与识别[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2022,44(4):500–505. FAN Yongdong, PANG Huiwen, JIN Yan, et al. Intelligent segmentation and recognition of pores and fractures based on imaging logging[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2022, 44(4): 500–505.
[27] PSZONKA J, GODLEWSKI P, FHEED A, et al. Identification and quantification of intergranular volume using SEM automated mineralogy[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2024, 162: 106708. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2024.106708
[28] GAO Yuan, YU Zixuan, CHEN Weiqiang, et al. Recognition of rock materials after high-temperature deterioration based on SEM images via deep learning[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2023, 25: 273–284. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2023.05.271
[29] WANG Mingyang, WANG Enzhi, LIU Xiaoli, et al. Scale-space effect and scale hybridization in image intelligent recognition of geological discontinuities on rock slopes[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2024, 16(4): 1315–1336. doi: 10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.08.015
[30] 边铁山. 基于SE-YOLOv5模型皮带异物检测算法研究[J]. 中国矿业,2024,33(7):127–134. BIAN Tieshan. Research on belt foreign object detection algorithm based on SE-YOLOv5 model[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2024, 33(7): 127–134.
[31] HAO Huizhen, JIANG Zhiwei, GE Shiping, et al. Siamese adversarial network for image classification of heavy mineral grains[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2022, 159: 105016.
[32] 曹蒙,王志章,李冰涛,等. 火成岩岩石薄片智能识别及分类方法[J]. 地质论评,2023,69(4):1581–1588. CAO Meng, WANG Zhizhang, LI Bingtao, et al. Intelligent identification and classification method for igneous rock thin sections[J]. Geological Review, 2023, 69(4): 1581–1588.
[33] SEO W, KIM Y, SIM H, et al. Classification of igneous rocks from petrographic thin section images using convolutional neural network[J]. Earth Science Informatics, 2022, 15(2): 1297–1307. doi: 10.1007/s12145-022-00808-5
[34] GAO Yanfang, CHEN Mian, PANG Huiwen. Experimental investigations on elastoplastic deformation and permeability evolution of terrestrial Karamay oil sands at high temperatures and pressures[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 190: 107124. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2020.107124
[35] 施振生,董大忠,王红岩,等. 含气页岩不同纹层及组合储集层特征差异性及其成因:以四川盆地下志留统龙马溪组一段典型井为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2020,47(4):829–840. doi: 10.11698/PED.2020.04.20 SHI Zhensheng, DONG Dazhong, WANG Hongyan, et al. Reservoir characteristics and genetic mechanisms of gas-bearing shales with different laminae and laminae combinations: a case study of member 1 of the Lower Silurian Longmaxi shale in Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(4): 829–840. doi: 10.11698/PED.2020.04.20
[36] WANG Chaofeng, WANG Congyue, WANG Lele, et al. Real-time tracking based on improved YOLOv5 detection in orchard environment for dragon fruit[J]. Journal of the ASABE, 2023, 66(5): 1109–1124. doi: 10.13031/ja.15643
[37] PARK J H, KIM J B, LEE S, et al. Hybrid MLP-CNN-based ground sink susceptibility prediction in urban area using underground pipe map[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2024, 245: 110031.
[38] KARIMPOULI S, TAHMASEBI P. Image-based velocity estimation of rock using convolutional neural networks[J]. Neural Networks, 2019, 111: 89–97. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2018.12.006
[39] VOULODIMOS A, DOULAMIS N, DOULAMIS A, et al. Deep learning for computer vision: a brief review[J]. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, 2018, 2018: 7068349.
[40] KIM W, KANEZAKI A, TANAKA M. Unsupervised learning of image segmentation based on differentiable feature clustering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 8055–8068. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.3011269



 下载:
下载: