The Application of Seismic while Drilling in High Temperature, High Pressure Reservoirs of the Yinggehai Basin
-
摘要:
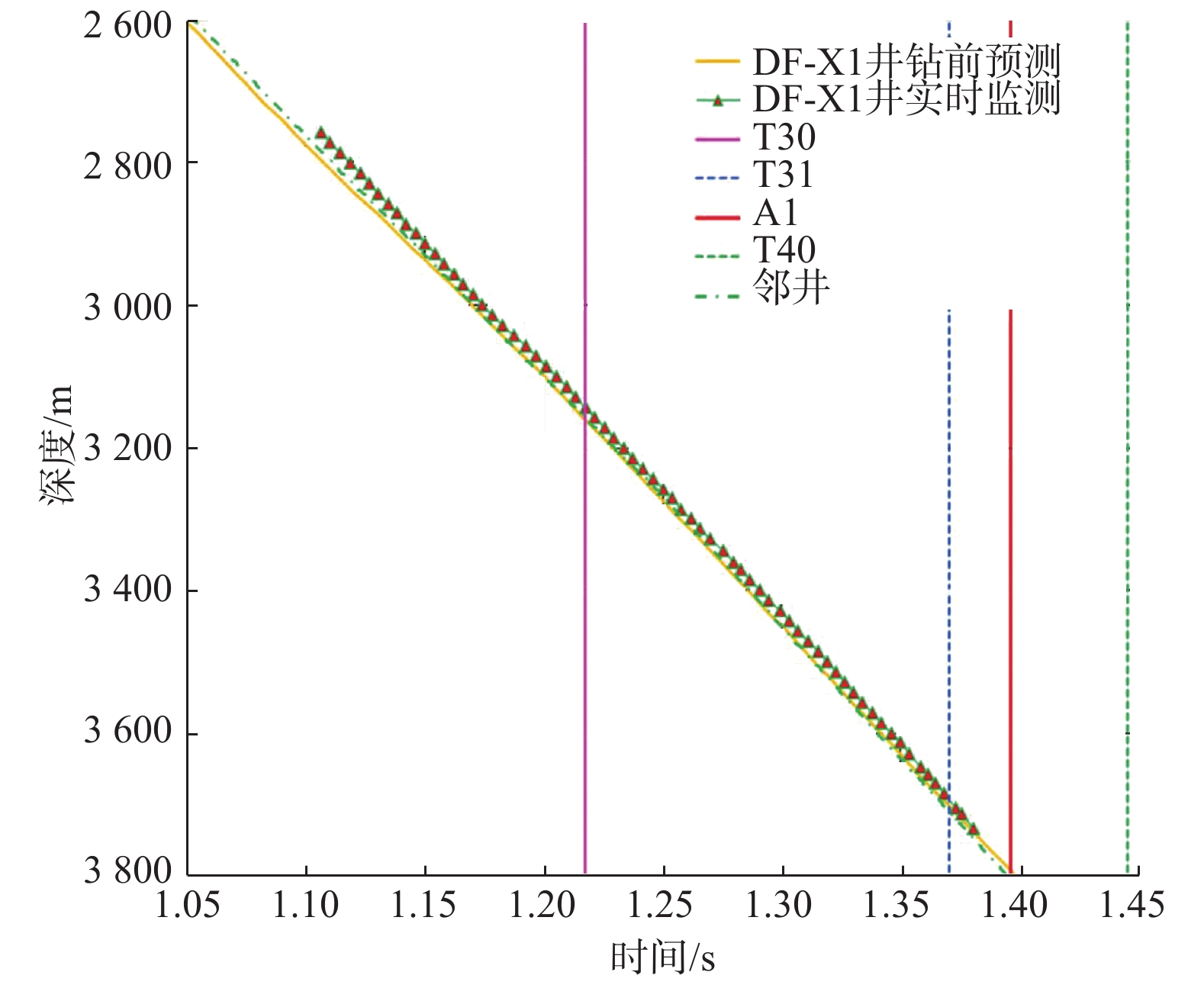
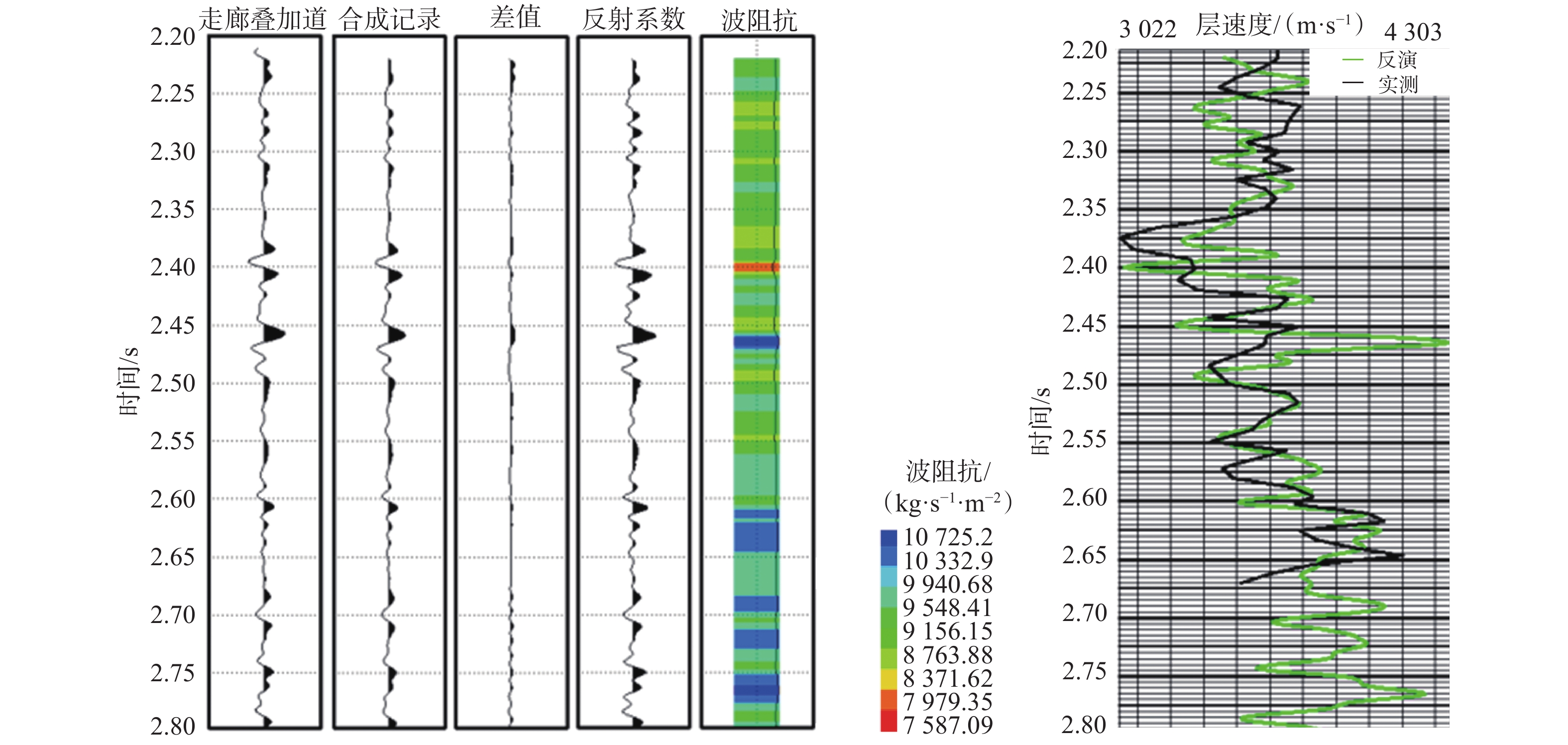
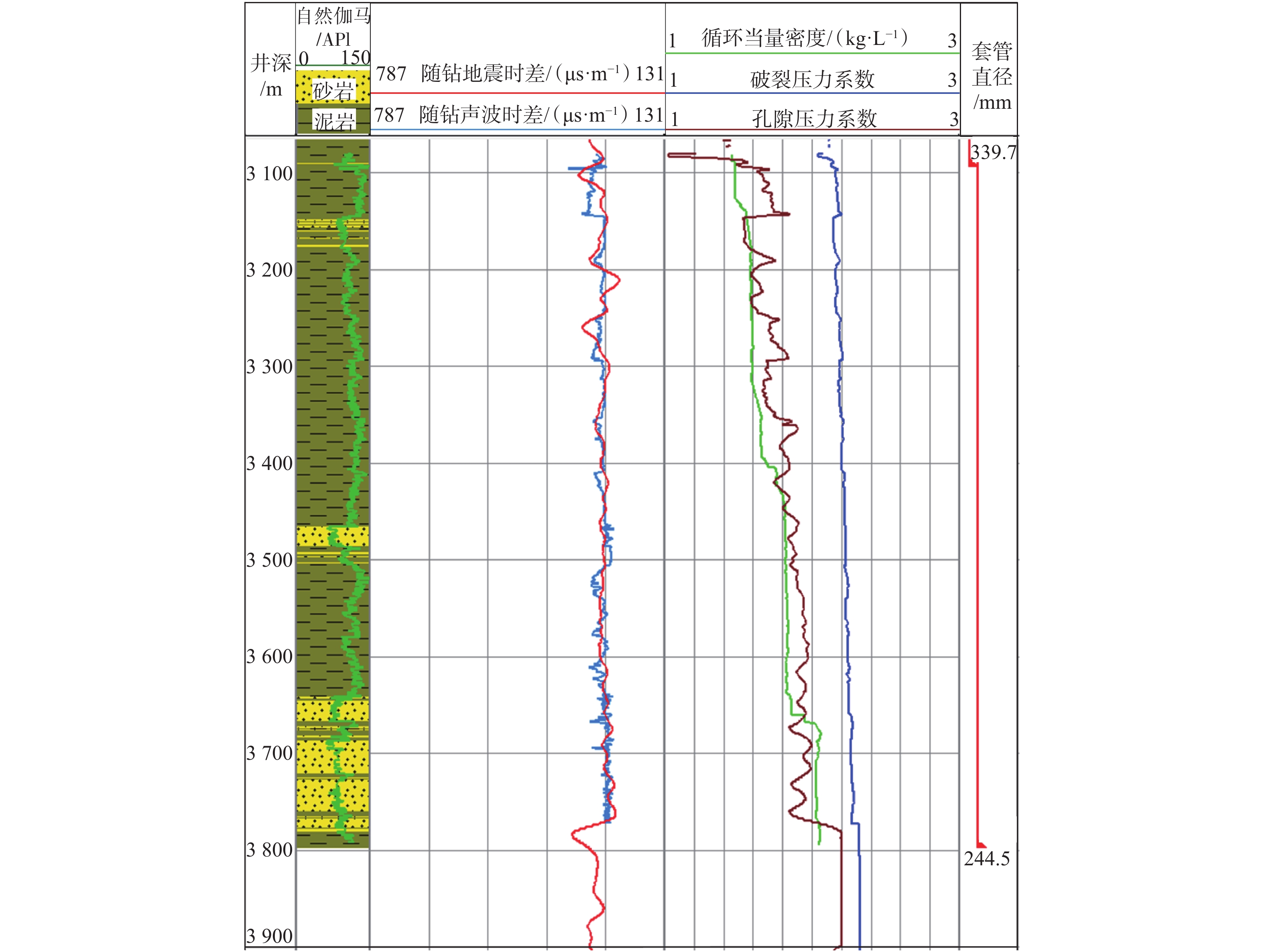
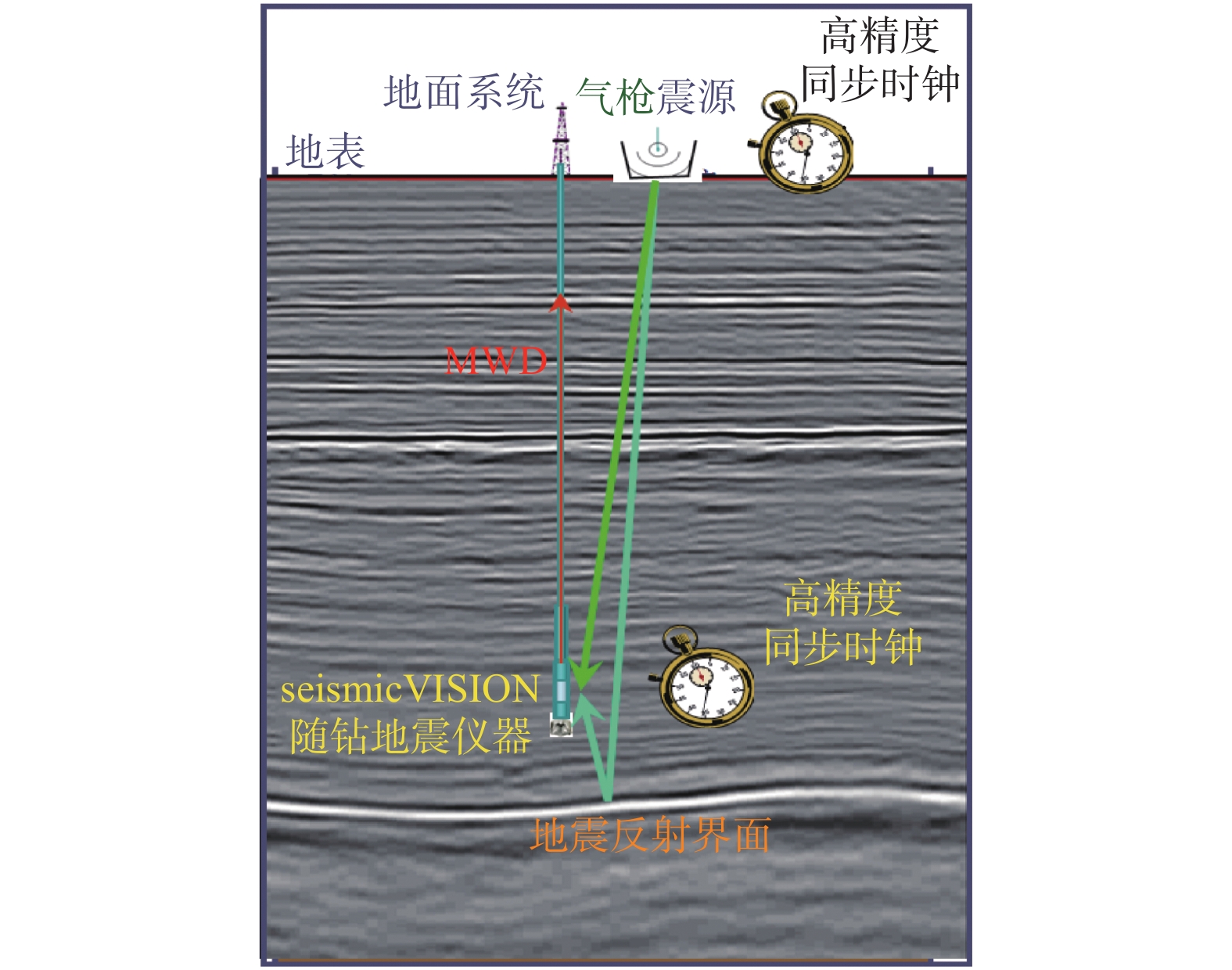
南海莺歌海盆地高温高压地层的钻井安全风险较高,为降低钻井风险,需要准确预测高压地层的压力和深度。为此,在预探井DF-X1井钻井过程中研究应用了随钻地震技术,利用随钻地震数据获得时深关系和地层层速度,实时更新钻头在地震剖面中的位置,确定钻头前方高压储层的深度和地层压力系数。在DF-X1井实钻过程中,应用随钻地震技术准确预测了高压储层A1砂体的地层孔隙压力系数、破裂压力系数和深度,高压储层A1砂体的预测深度与实钻深度相差仅6.00 m,确保了ϕ244.5 mm套管成功下到高压储层上部的泥岩中,确保了ϕ212.7 mm 井段的安全压力窗口;A1砂体孔隙压力系数和破裂压力系数的预测精度分别达到3.0%和1.0%,确保了该探井的顺利完钻。研究结果表明,随钻地震技术可以准确预测地层压力和高压储层深度,能有效降低钻井风险,提高作业效率。
Abstract:There are high temperature, high pressure (HTHP) formations in the Yinggehai Basin in the South China Sea, and they are considered high-risk for safety when penetrating the HTHP formations. In order to reduce the drilling risk, it is necessary to accurately predict the pressures and at each formation depth. For this reason, the seismic while drilling technology was applied in the pre-exploration Well DF-X1. The technology uses seismic data while drilling to obtain the time-depth relationship and the formation velocity, and it updates the bit position on the seismic profile in real time, and thus it determines the high pressure reservoir depth and formation pressure coefficient in front of the bit. During the actual drilling of Well DF-X1, the seismic while drilling technology was used to accurately predict the pore pressure coefficient, fracture pressure coefficient and depth of the high pressure reservoir A1 sand body. The predicted depth error of A1 sand body was only 6.00 m with the actually drilled depth, which ensured that the ϕ244.5 mm casing was run into the mudstone above the high pressure reservoir. By using seismic while drilling, the prediction accuracy of A1 sand body pore pressure coefficient achieved 3.0%, and the accuracy of formation fracture pressure coefficient up to 1.0%. Based on this, the drilling fluid density of the completion section was optimized to avoid the gas cut and lost circulation, kept the successful drilling of the well. The research results showed that the seismic while drilling technology could accurately predict the formation pressure along with the depth of the targeted high pressure reservoir, thus effectively reduce drilling risk and improving operation efficiency.
-
-
表 1 DF-X1井随钻地震各趟采集参数
Table 1 Parameters acquisition of each run in Well DF-X1 by seismic while drilling
采集次数 采集道数 起始深度/m 结束深度/m 井筒类型 道间距/m 1 22 2 767.06 3 067.20 套管 14.40 2 30 3 081.17 3 381.12 裸眼 14.40 3 44 3 369.60 3 771.22 裸眼 14.40 表 2 随钻地震地层深度实时预测结果
Table 2 Real-time formation depth prediction results of seismic while drilling
地震层位 随钻地震预测深度/m 实钻深度/m 误差/m T30 3 158.00 3 145.00 +13.00 T30_C 3 461.00 3 466.00 –5.00 T30_E 3 584.00 3 580.00 +4.00 T30_H 3 641.00 3 642.00 –1.00 T31 3 787.00 3 784.00 +3.00 A1砂顶 3 825.00 3 819.00 +6.00 -
[1] 郝芳,董伟良,邹华耀,等. 莺歌海盆地汇聚型超压流体流动及天然气晚期快速成藏[J]. 石油学报, 2003, 24(6): 7–12. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2003.06.002 HAO Fang, DONG Weiliang, ZOU Huayao, et al. Overpressure fluid flow and rapid accumulation of natural gas in Yinggehai Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2003, 24(6): 7–12. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2003.06.002
[2] 裴健翔,于俊峰,王立锋,等. 莺歌海盆地中深层天然气勘探的关键问题及对策[J]. 石油学报, 2011, 32(4): 573–579. doi: 10.7623/syxb201104003 PEI Jianxiang, YU Junfeng, WANG Lifeng, et al. Key challenges and strategies for the success of natural gas exploration in mid-deep strata of the Yinggehai Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2011, 32(4): 573–579. doi: 10.7623/syxb201104003
[3] 谢玉洪. 莺歌海高温超压盆地压力预测模式及成藏新认识[J]. 天然气工业, 2011, 31(12): 21–25. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2011.12.004 XIE Yuhong. Models of pressure prediction and new understandings of hydrocarbon accumulation in the Yinggehai Basin with high temperature and super high pressure[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2011, 31(12): 21–25. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2011.12.004
[4] 谢玉洪,张迎朝,李绪深,等. 莺歌海盆地高温超压气藏控藏要素与成藏模式[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(4): 601–609. doi: 10.7623/syxb201204009 XIE Yuhong, ZHANG Yingchao, LI Xushen, et al. Main controlling factors and formation models of natural gas reservoirs with high-temperature and overpressure in Yinggehai Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(4): 601–609. doi: 10.7623/syxb201204009
[5] 郝芳,刘建章,邹华耀,等. 莺歌海—琼东南盆地超压层系油气聚散机理浅析[J]. 地学前缘, 2015, 22(1): 169–180. HAO Fang, LIU Jianzhang, ZOU Huayao, et al. Mechanisms of natural gas accumulation and leakage in the overpressured sequences in the Yinggehai and Qiongdongnan Basins, offshore South China Sea[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2015, 22(1): 169–180.
[6] 张伙兰,裴健翔,张迎朝,等. 莺歌海盆地东方区中深层黄流组超压储集层特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2013, 40(3): 284–293. doi: 10.11698/PED.2013.03.04 ZHANG Huolan, PEI Jianxiang, ZHANG Yingchao, et al. Overpressure reservoirs in the mid-deep Huangliu Formation of the Dongfang Area, Yinggehai Basin, South China Sea[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2013, 40(3): 284–293. doi: 10.11698/PED.2013.03.04
[7] 杨红君,蔡军. 基于VSP的孔隙压力预测方法在莺歌海盆地的应用[J]. 中国海上油气, 2014, 26(4): 20–24. YANG Hongjun, CAI Jun. Applying a method to predict pore pressure based on VSP in Yinggehai Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2014, 26(4): 20–24.
[8] CAO Shunhua, XIE Yuhong, LIU Chang, et al. Multistage approach on pore pressure prediction: a case study in South China Sea[R]. SPE 103856, 2006.
[9] XIE Yuhong, CAI Jun, LING Xiazhen, et al. Ahead of bit pore pressure prediction using VSP: a case study in South China Sea[R]. SPE 130551, 2010.
[10] YANG H, CAI J, GUO S, et al. Predicting drilling target ahead of bit using VSP lookahead technique that help mitigate drilling risk in over pressure zone, a case example from South China Sea[R]. SPE 1653838, 2013.
[11] CAI J, CHENG Y F, CHEN M, et al. Deepwater exploration breakthrough with LWD technology in South China Sea[R]. SPE 176317, 2015.
[12] 蔡军,李文拓,刘鹏,等. 琼东南盆地深水区探井随钻压力监测技术与应用[J]. 天然气工业, 2015, 35(10): 99–105. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2015.10.013 CAI Jun, LI Wentuo, LIU Peng, et al. Research and application of while-drilling pressure-monitoring technology in exploration wells of deep water area, Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2015, 35(10): 99–105. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2015.10.013
[13] GAO Yongde, CHEN Ming, DU Chao, et al. Integrated real-time pressure monitoring enabled the success of drilling a HTHP offshore well: a casing study in Ledong Area of Yinggehai Basin, South China Sea[R]. IPTC 19313, 2019.
[14] GOUVEIA W P, SCALES J A. Bayesian seismic waveform inversion: parameter estimation and uncertainty analysis[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research (Solid Earth), 1998, 103(B2): 2759–2779. doi: 10.1029/97JB02933
[15] CONSTANT D W, BOURGOYNE A T Jr. Fracture-gradient prediction for offshore wells[J]. SPE Drilling Engineering, 1988, 3(2): 136–140. doi: 10.2118/15105-PA
[16] DUTTA N C. Geopressure prediction using seismic data: current status and the road ahead[J]. Geophysics, 2002, 67(6): 2012–2041. doi: 10.1190/1.1527101
[17] EATON B A. Fracture gradient prediction and its application in oilfield operations[J]. Journal of Petroleum Technology, 1969, 21(10): 1353–1360. doi: 10.2118/2163-PA
[18] FERTl W H. Abnormal formation pressure, implication to exploration, drilling and production of oil and gas resources[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1976: 392.
[19] ZAMORA M. New method predicts gradient fracture[J]. Petroleum Engineer International, 1989, 61(9): 38–47.
[20] EATON B A. The equation for geopressure prediction from well logs[R]. SPE 5544, 1975.
[21] FAN Xiangyu, GONG Ming, ZHANG Qiangui, et al. Prediction of the horizontal stress of the tight sandstone formation in eastern Sulige of China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2013, 113(1): 72–80.
[22] EATON B A, EATON T L. Fracture gradient prediction for the new generation[J]. World Oil, 1997, 218(10): 93–100.
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 刘长龙,赵鹏,方月月,吕鹏,阚亮,苏坡. 基于二次交联的有机复合交联调剖体系研究与应用. 当代化工. 2023(10): 2352-2356 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 刘大为,乔梦月. 复合型交联剂调剖溶液性能评价. 化学工程师. 2018(08): 75-77+74 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 梁守成,吕鑫,陈冠中,李强,李丽霞. 一种新型二次交联凝胶体系的合成与应用. 科学技术与工程. 2017(04): 189-193+202 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 魏开鹏,杨欢,斯容,方群,刘学全. 红河油田水平井置胶成坝技术. 石油钻探技术. 2017(02): 81-86 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 顾宏,汪小平,杨开. 海外河油田注水提高采收率关键技术试验与应用. 化学工程与装备. 2016(10): 131-133 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(6)



 下载:
下载: