Oil Recovery Enhancement by Composite Flooding Technology for Gasi N1–N21 Ultra-High-Salinity Reservoir in Qinghai Oilfield
-
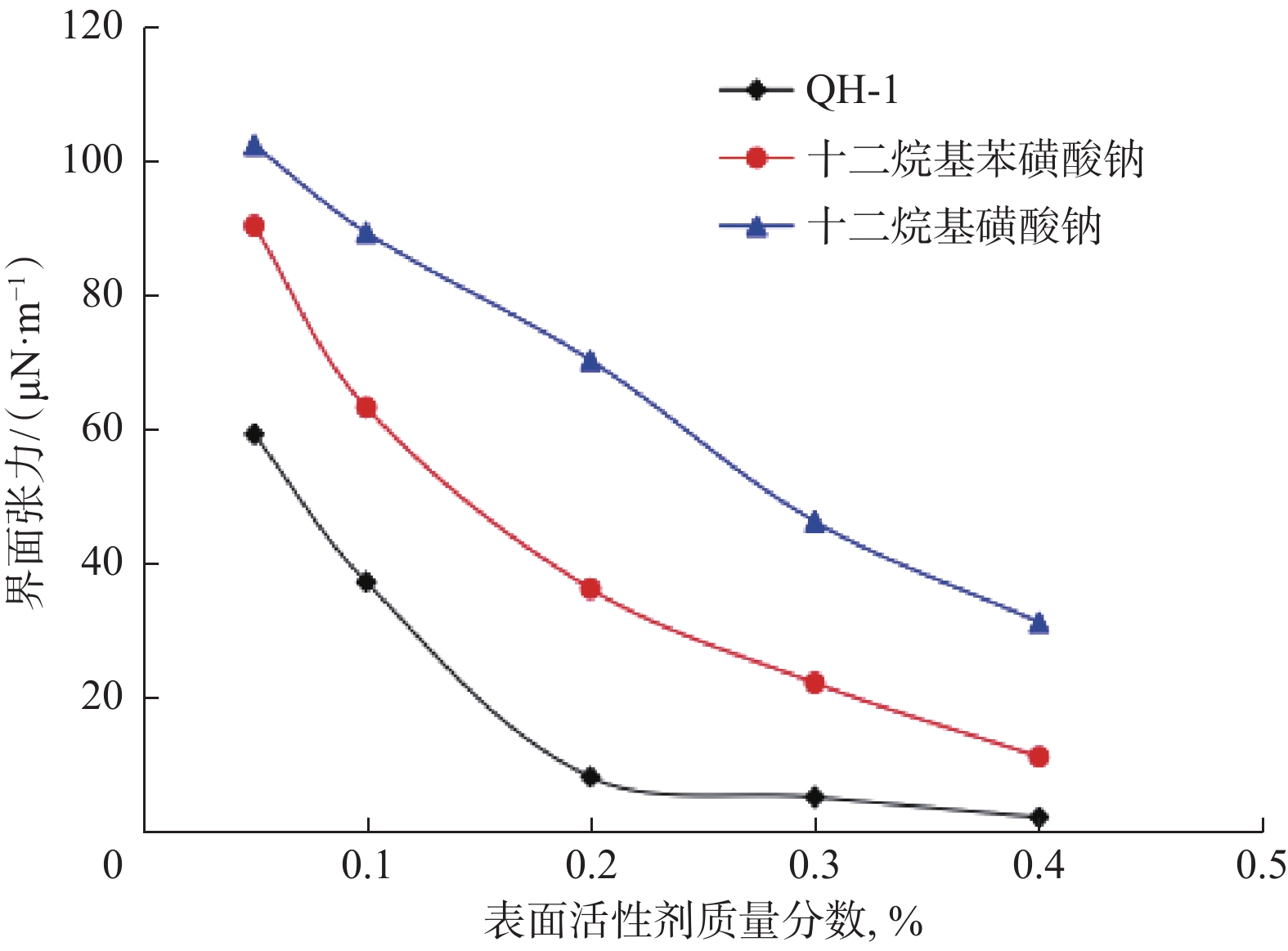
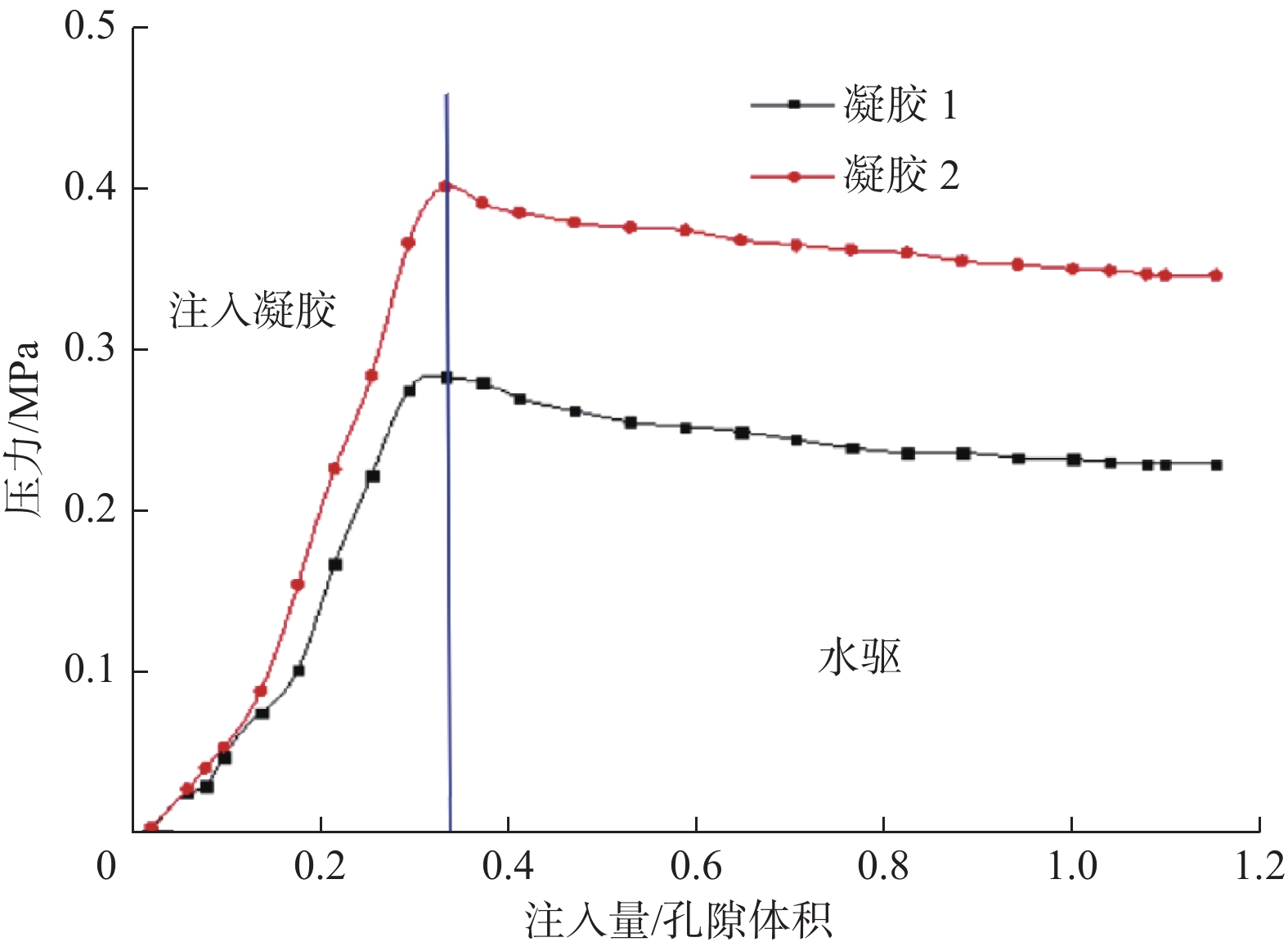
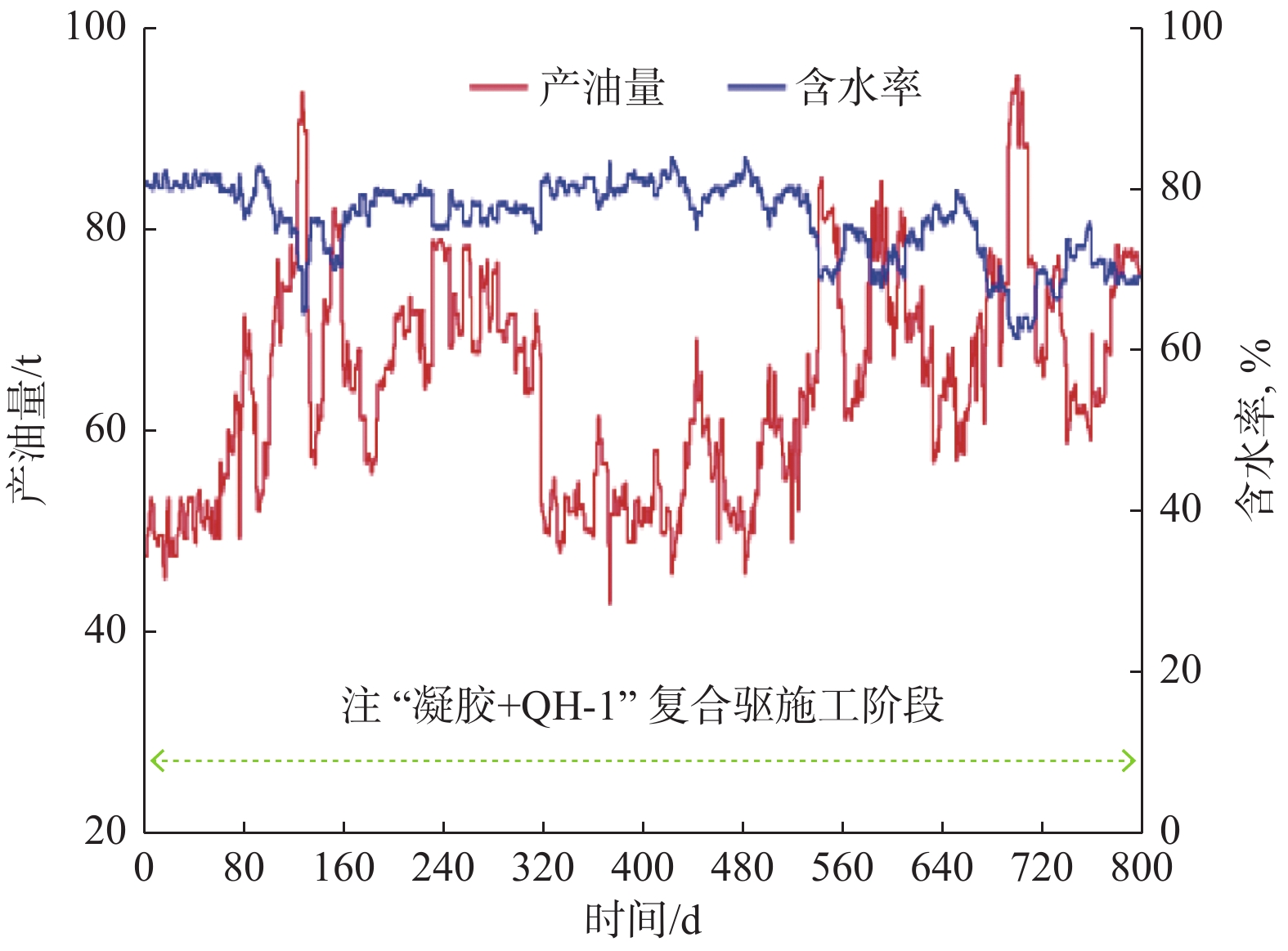
摘要: 青海油田尕斯N1–N21油藏的地层水矿化度和钙镁离子含量超高,进行凝胶与表面活性剂复合驱,常规凝胶易脱水破胶,长期稳定性差,同时常规表面活性剂易与地层水中的钙镁离子发生反应产生沉淀。针对前一问题,合成了适用于尕斯N1–N21油藏的抗高盐有机凝胶,配方为0.3%~0.4%聚合物+0.2%~0.3%交联剂+0.1%~0.2%稳定剂,该体系在68 ℃条件下初凝时间大于70 h,成胶后凝胶黏度大于1.0×104 mPa∙s;优选了抗高盐表面活性剂QH-1,评价了界面张力和驱油效果,发现质量分数0.4%的QH-1溶液可提高采收率18.72%。室内试验结果表明,交替注入抗高盐有机凝胶和QH-1能有效遏制水的无效循环,提高中低渗区域的驱油效率,优化的“凝胶+QH-1”复合驱可提高采收率27.6%以上。该复合驱在尕斯N1–N21油藏9口注水井进行了应用,应用后对应油井的平均含水率由80%降至70%,增产油量2.41×104 t。研究结果表明,“凝胶+QH-1”复合驱提高采收率技术对青海油田尕斯N1–N21超高盐油藏增油降水具有很好的效果,具有推广价值。Abstract: The salinity and the content of calcium and magnesium ions are ultra-high in the formation water of Gasi N1–N21 reservoir in Qinghai Oilfield. While using gel and surfactant composite flooding, conventional gels are prone to dehydrate and break, showing poor long-term stability. Meanwhile, conventional surfactants are easy to react with the calcium and magnesium ions in formation water to cause precipitation. In view of this, a high-salinity-resistant organogel suitable for Gasi N1–N21 reservoir was developed, which consisted of polymer (0.3%–0.4%) + crosslinking agent (0.2%–0.3%) + stabilizer (0.1%–0.2%). The initial setting time of the system was longer than 70 h at 68 ℃, and the viscosity after gelling was greater than 1.0×104 mPa·s. What's more, a high-salinity-resistant surfactant QH-1 was optimized, and the interfacial tension and oil displacement effect were evaluated, witha finding that the QH-1 solution with a mass fraction of 0.4% could enhance the oil recovery by 18.72%. The laboratory test results indicated that alternate injection of the high-salinity-resistant organogel and QH-1 could effectively curb the ineffective water circulation and improve the oil displacement efficiency in the low and medium permeability areas. Notably, the optimized “gel + QH-1” composite flooding was capable of enhancing oil recovery by more than 27.6%. The composite flooding was applied to 9 water-injection wells in Gasi N1–N21 reservoir. As a result, the average water cut of these oil wells decreased from 80% to 70%, and the oil production increased by 2.41 × 104 t. The research results show that the oil recovery enhancement by “gel + QH-1” composite flooding is effective in enhancing oil production and decreasing water cut in Gasi N1–N21 ultra-high-salinity reservoir, so it is worthy of promotion and application.
-
-
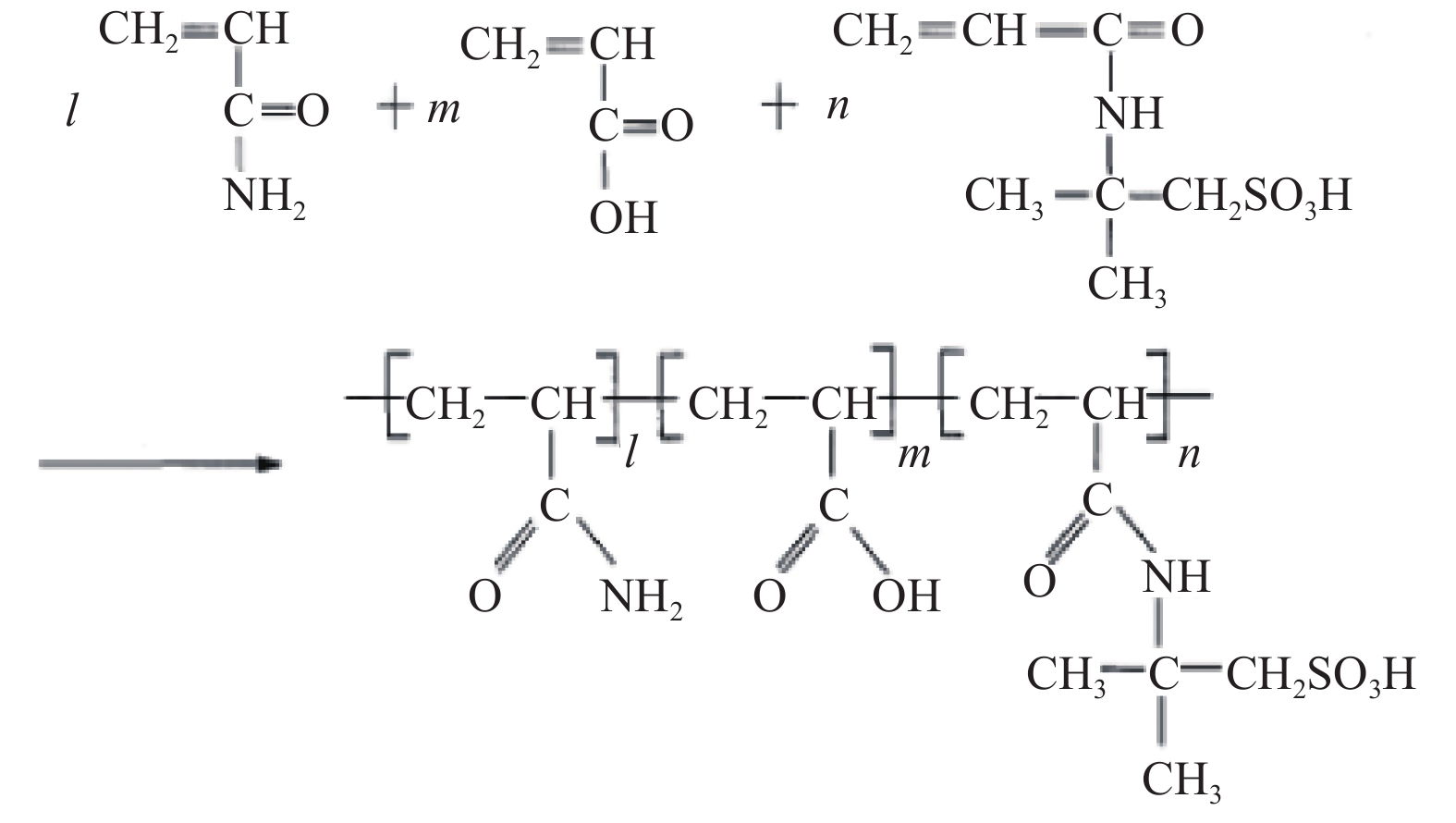
表 1 抗高盐有机凝胶68 ℃下的性能
Table 1 Performance of high-salinity-resistant organogels at 68 ℃
聚合物
质量分数,%交联剂
质量分数,%稳定剂
质量分数,%表观黏度/
(mPa∙s)初凝时间/h 0.2 0.1 0.05 1 500 180 0.2 0.10 2 500 150 0.3 0.20 3 200 130 0.3 0.1 0.05 4 000 125 0.2 0.10 8 200 100 0.3 0.20 10 300 80 0.4 0.1 0.05 8 400 105 0.2 0.10 11 200 90 0.3 0.20 13 000 75 表 2 抗高盐有机凝胶封堵性能试验结果
Table 2 Test results of plugging performance of high-salinity-resistant organogels
凝胶 渗透率/mD 压力梯度/(MPa∙m–1) 注入凝胶 水驱 1 391 3.20 3.84 1 050 0.68 2.86 5 103 0.30 4.14 2 420 4.48 5.02 1 120 1.20 6.67 5 260 0.48 8.31 表 3 抗高盐有机凝胶转向效果试验结果
Table 3 Test results of steering effect of high-salinity-resistant organogels
凝胶 渗透率/mD 含油饱和度,% 采收率,% 水驱 注凝胶 1 356 62.8 5.6 21.7 987 66.5 32.2 57.0 4 981 71.2 45.1 55.7 2 398 63.6 6.1 23.0 1 056 67.1 33.1 59.4 5 138 73.4 48.3 59.6 表 4 耐高盐表面活性剂QH-1岩心驱油的试验结果
Table 4 Core displacement test results of high-salinity-resistant surfactant QH-1
岩心渗透率/
mDQH-1质量
分数,%水驱采收
率,%QH-1驱采
收率,%365 0.1 25.50 6.12 342 0.2 27.68 12.47 381 0.3 26.72 15.11 357 0.4 25.55 18.72 表 5 “凝胶+QH-1”复合驱岩心驱替试验结果
Table 5 Core displacement test results of "Gel +QH-1" composite flooding
凝胶与QH-1组合形式 渗透率/mD 含油饱和度,% 采收率,% 水驱 “凝胶+ QH-1”复合驱 0.10 PV凝胶+0.20 PV表面活性剂 463 64.3 30.5 58.1 1 635 67.5 36.5 66.8 0.10 PV凝胶0.25 PV表面活性剂 568 62.1 29.7 59.2 1 890 70.4 37.5 68.7 0.10 PV凝胶+0.30 PV表面活性剂 324 61.3 28.5 61.2 1 500 72.1 35.2 69.5 注:1)凝胶配方为0.4%耐高盐聚合物+0.2%交联剂+0.1%稳定剂;表面活性剂为0.3%QH-1。 -
[1] 梁丹,吕鑫,蒋珊珊,等. 渤海油田分级组合深部调剖技术[J]. 石油钻探技术,2015,43(2):104–109. LIANG Dan, LYU Xin, JIANG Shanshan, et al. The technology of classified combination of deep profile control in the Bohai Oilfield[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2015, 43(2): 104–109.
[2] 张贵清,孙磊,夏烨,等. 耐贮存改性酚醛树脂交联剂的合成及性能评价[J]. 石油钻探技术,2017,45(6):99–104. ZHANG Guiqing, SUN Lei, XIA Ye, et al. Synthesis and property evaluation of storable modified phenolic resin cross-linking agent[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2017, 45(6): 99–104.
[3] 付国强,王克亮. 水驱后凝胶与表活剂交替注入驱油效果[J]. 当代化工,2016,45(3):495–497. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0460.2016.03.020 FU Guoqiang, WANG Keliang. Oil displacement effect of alternative injection of gel and surfactant after water flooding[J]. Contemporary Chemical Industry, 2016, 45(3): 495–497. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0460.2016.03.020
[4] 石延辉,王帅,张绍辉. 调剖+表活剂驱油综合治理多裂缝非均质复杂油藏[J]. 石油工业技术监督,2018,34(6):40–42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1346.2018.06.012 SHI Yanhui, WANG Shuai, ZHANG Shaohui. Comprehensive control of multi-fractured heterogeneous complex reservoirs by profile control and surfactant flooding[J]. Technology Supervision in Petroleum Industry, 2018, 34(6): 40–42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1346.2018.06.012
[5] 白宝君,周佳,印鸣飞. 聚丙烯酰胺类聚合物凝胶改善水驱波及技术现状及展望[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2015,42(4):481–487. BAI Baojun, ZHOU Jia, YIN Mingfei. A comprehensive review of polyacrylamide polymer gels for conformance control[J]. Petroleum Exloration and Development, 2015, 42(4): 481–487.
[6] 张兵,蒲春生,于浩然,等. 裂缝性油藏多段塞凝胶调剖技术研究与应用[J]. 油田化学,2016,33(1):46–50. ZHANG Bing, PU Chunsheng, YU Haoran, et al. Research and application of multi-slug gel profile control technology in fractured reservoirs[J]. Oilfield Chemistry, 2016, 33(1): 46–50.
[7] 宋官龙. 适合低渗高盐油藏的表面活性剂复配体系及性能研究[J]. 油田化学,2016,33(1):99–102. SONG Guanlong. Performance evaluation of mixed surfactants for EOR in high salinity and low permeability reservoirs[J]. Oilfield Chemistry, 2016, 33(1): 99–102.
[8] 陈斌,曹小华,周亮,等. 适用于高温高盐低渗砂岩油藏的表面活性剂驱油体系[J]. 钻采工艺,2021,44(3):87–91. CHEN Bin, CAO Xiaohua, ZHOU Liang, et al. Surfactant flooding system for high temperature and high salinity of low permeability sandstone reservoirs[J]. Drilling & Production Technology, 2021, 44(3): 87–91.
[9] 于萌,铁磊磊,李翔,等. 海上油田剖面调整用分散共聚物颗粒体系的研制[J]. 石油钻探技术,2020,48(2):118–122. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2020019 YU Meng, TIE Leilei, LI Xiang, et al. Development of dispersed copolymer particle system for profile control in offshore oilfield[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2020, 48(2): 118–122. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2020019
[10] 卢祥国,王树霞,王荣建,等. 深部液流转向剂与油藏适应性研究:以大庆喇嘛甸油田为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2011,38(5):576–582. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(11)60056-6 LU Xiangguo, WANG Shuxia, WANG Rongjian, et al. Adaptability of a deep profile control agent to reservoirs: taking the Lamadian Oilfield in Daqing as an example[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2011, 38(5): 576–582. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(11)60056-6
[11] 王洋,韩国彤,葛际江,等. 表面活性剂提高碳酸盐岩油藏采收率进展[J]. 油田化学,2015,32(2):301–306,316. WANG Yang, HAN Guotong, GE Jijiang, et al. Research progress of enhanced oil recovery with surfactants in carbonate reservoirs[J]. Oilfield Chemistry, 2015, 32(2): 301–306,316.
[12] 潘斌林. APEC(Na)降低油水界面张力影响因素研究[J]. 油田化学,2014,31(1):95–98. PAN Binlin. Influencing factors of APEC(Na) on reducing interfacial tension[J]. Oilfield Chemistry, 2014, 31(1): 95–98.
[13] LIU Yifei, DAI Caili, WANG Kai, et al. New insights into the hydroquinone (HQ)-hexamethylenetetramine (HMTA) gel system for water shut-off treatment in high temperature reservoirs[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2016, 35: 20–28. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2015.09.032
[14] 张绍东,付继彤,姚军,等. 重质石油磺酸盐化学驱方案设计方法研究及应用[J]. 石油大学学报(自然科学版),2002,26(4):48–50. ZHANG Shaodong, FU Jitong, YAO Jun, et al. Design and application of chemical displacement pilot with weighted petroleum sulfonate[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum(Edition of Natural Science), 2002, 26(4): 48–50.
[15] 张永强,赫文秀. 阳离子碳氟与阴离子碳氢表面活性剂复配体系的性质[J]. 精细石油化工,2014,31(3):63–67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9384.2014.03.015 ZHANG Yongqiang, HE Wenxiu. Properties of mixed system of fluorocarbon cationic surfactant and hydrocarbon anionic surfac-tant[J]. Speciality Petrochemicals, 2014, 31(3): 63–67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9384.2014.03.015



 下载:
下载: