Experimental Study on Rock Crack Characteristics of PDC Cutter in the Process of Rock Breaking
-
摘要:
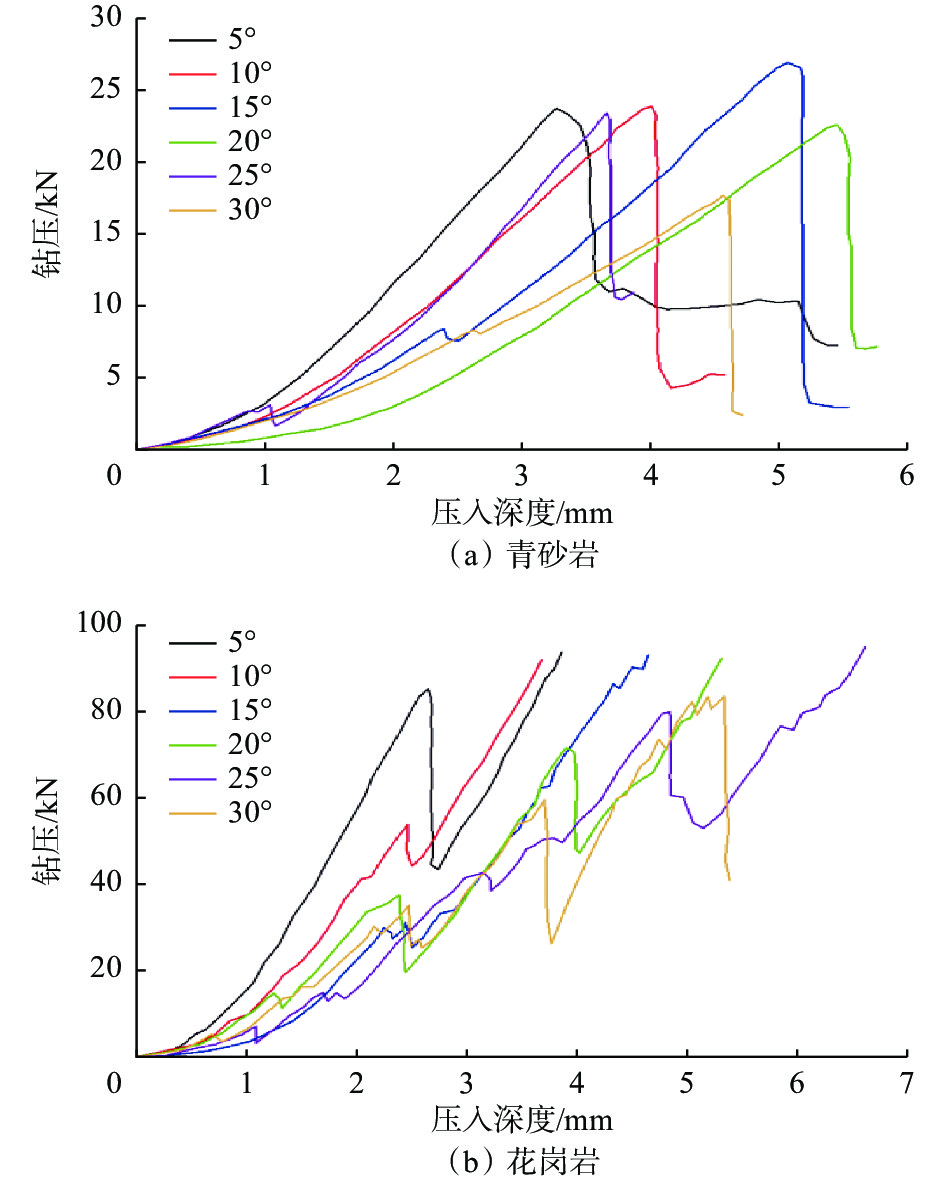
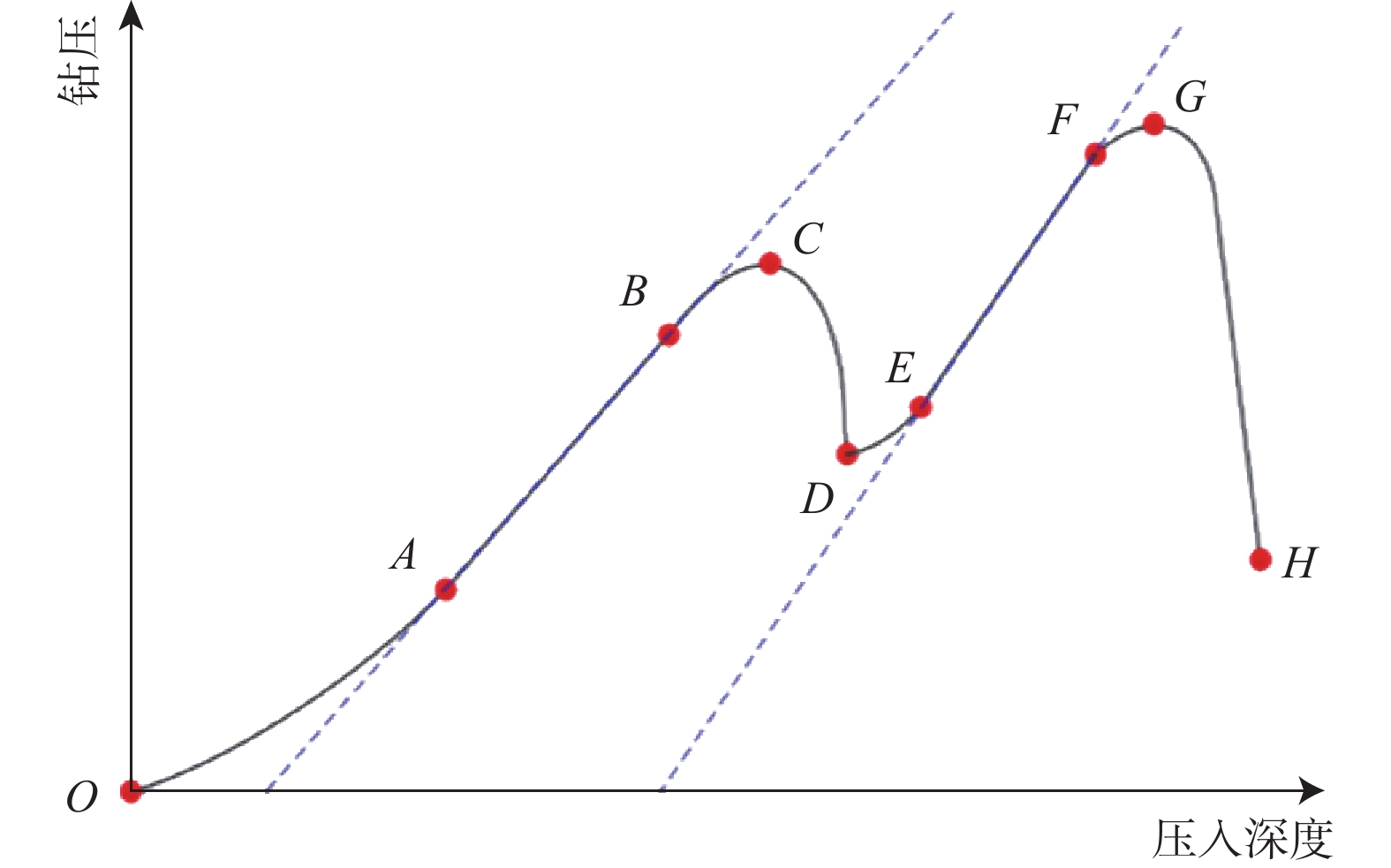
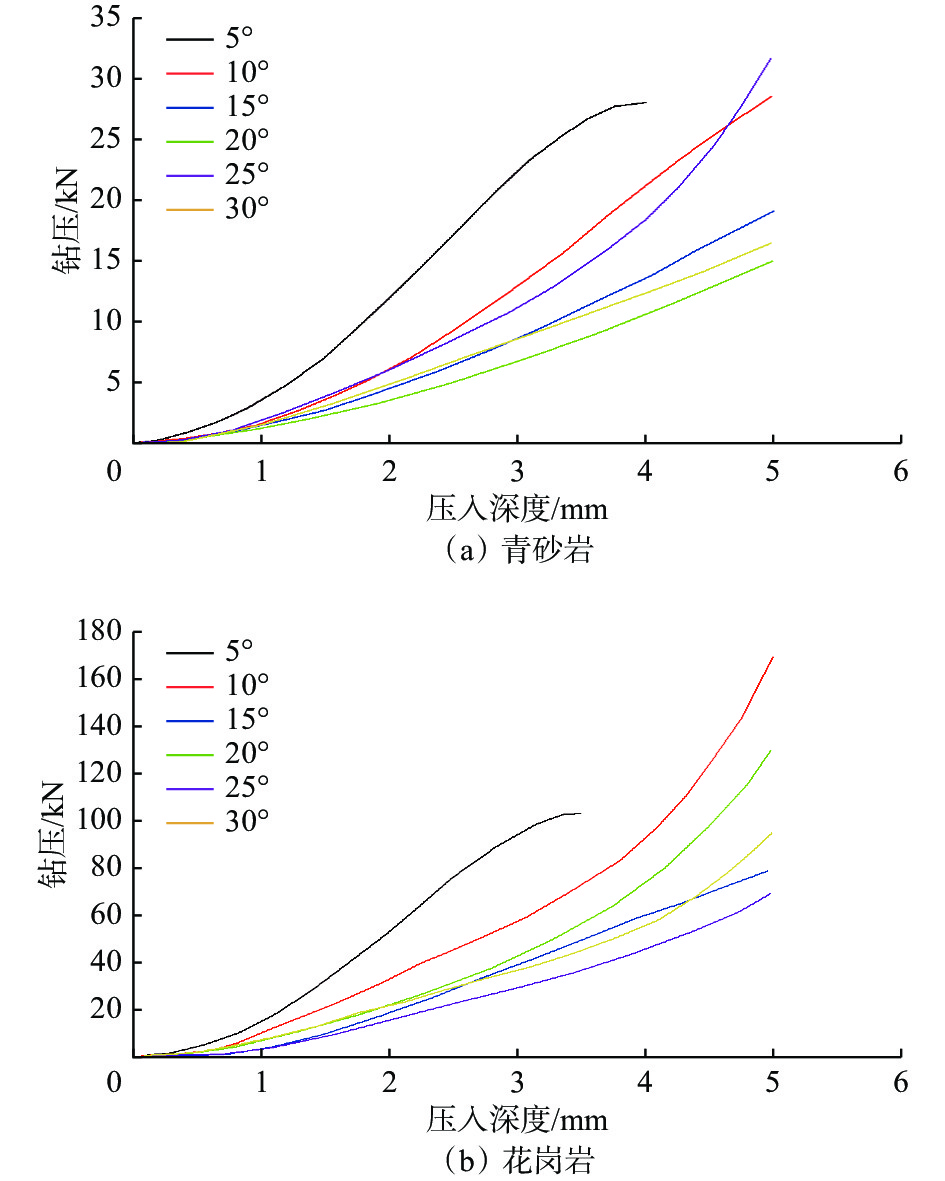
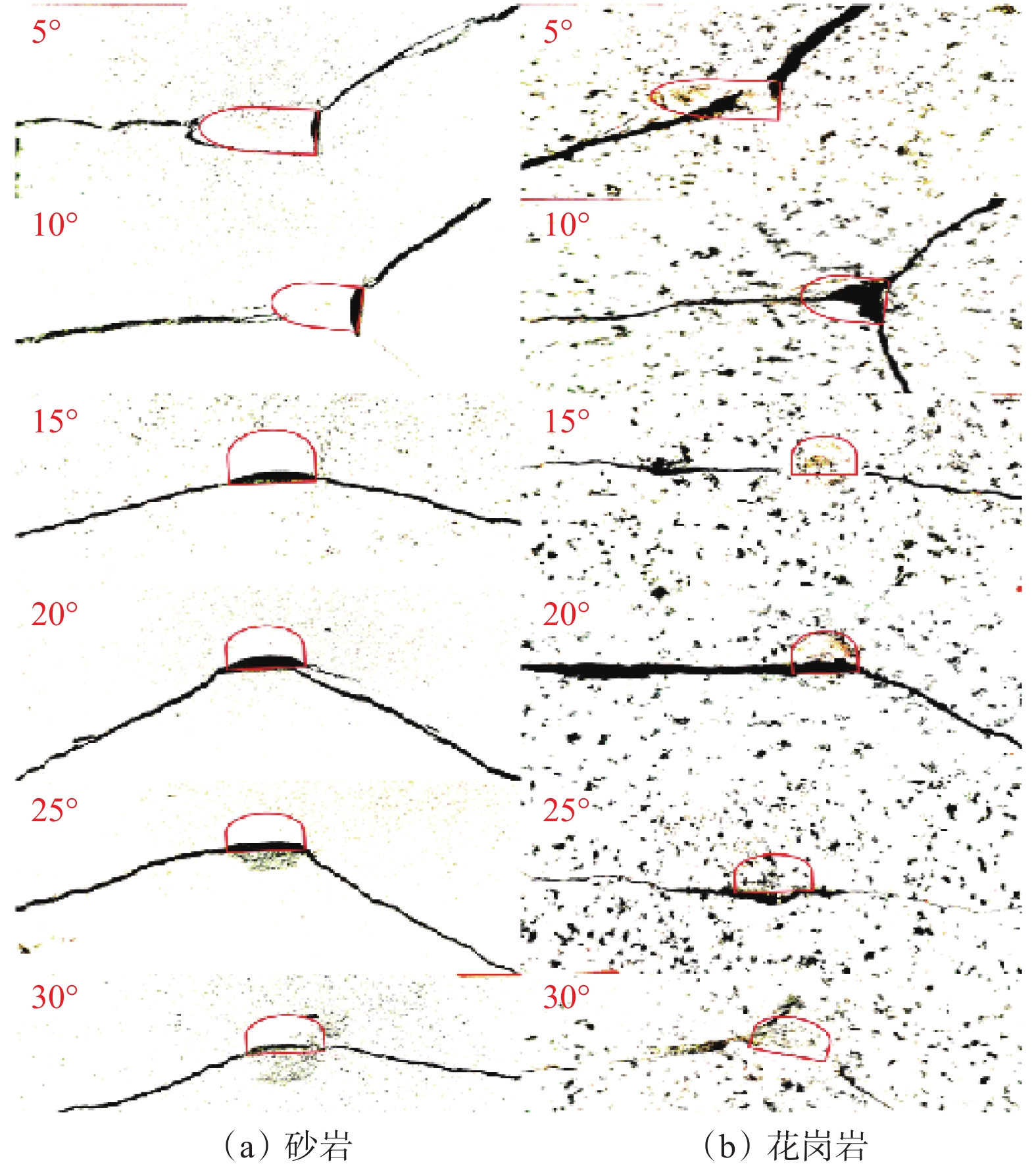
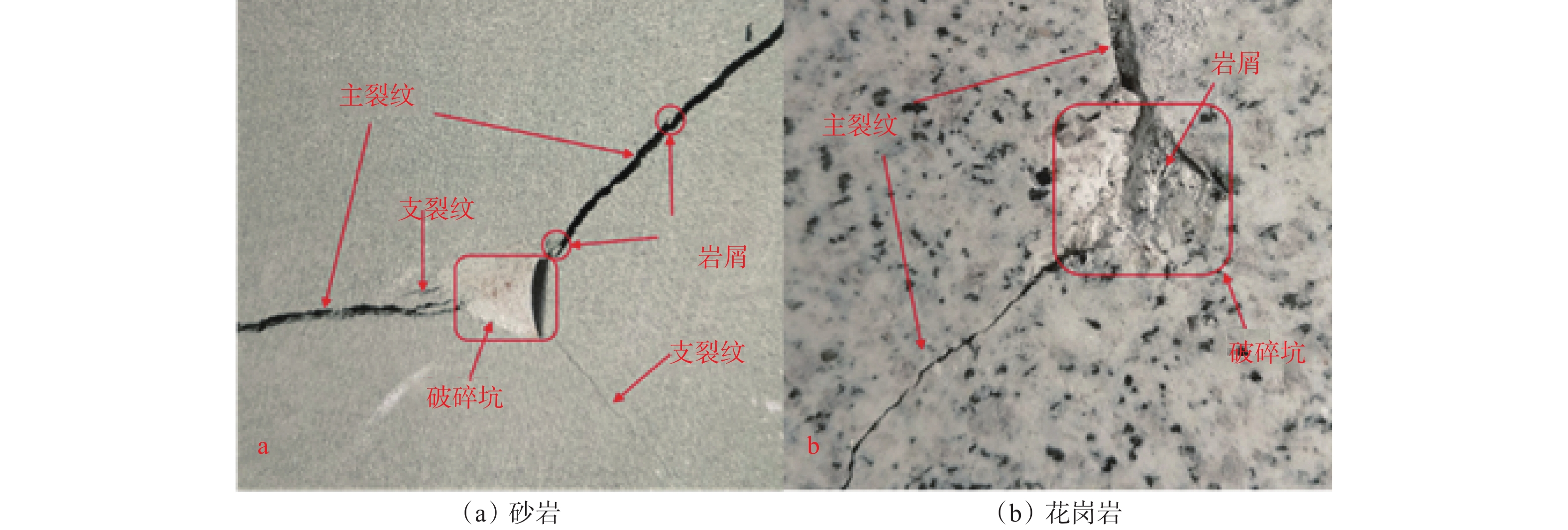
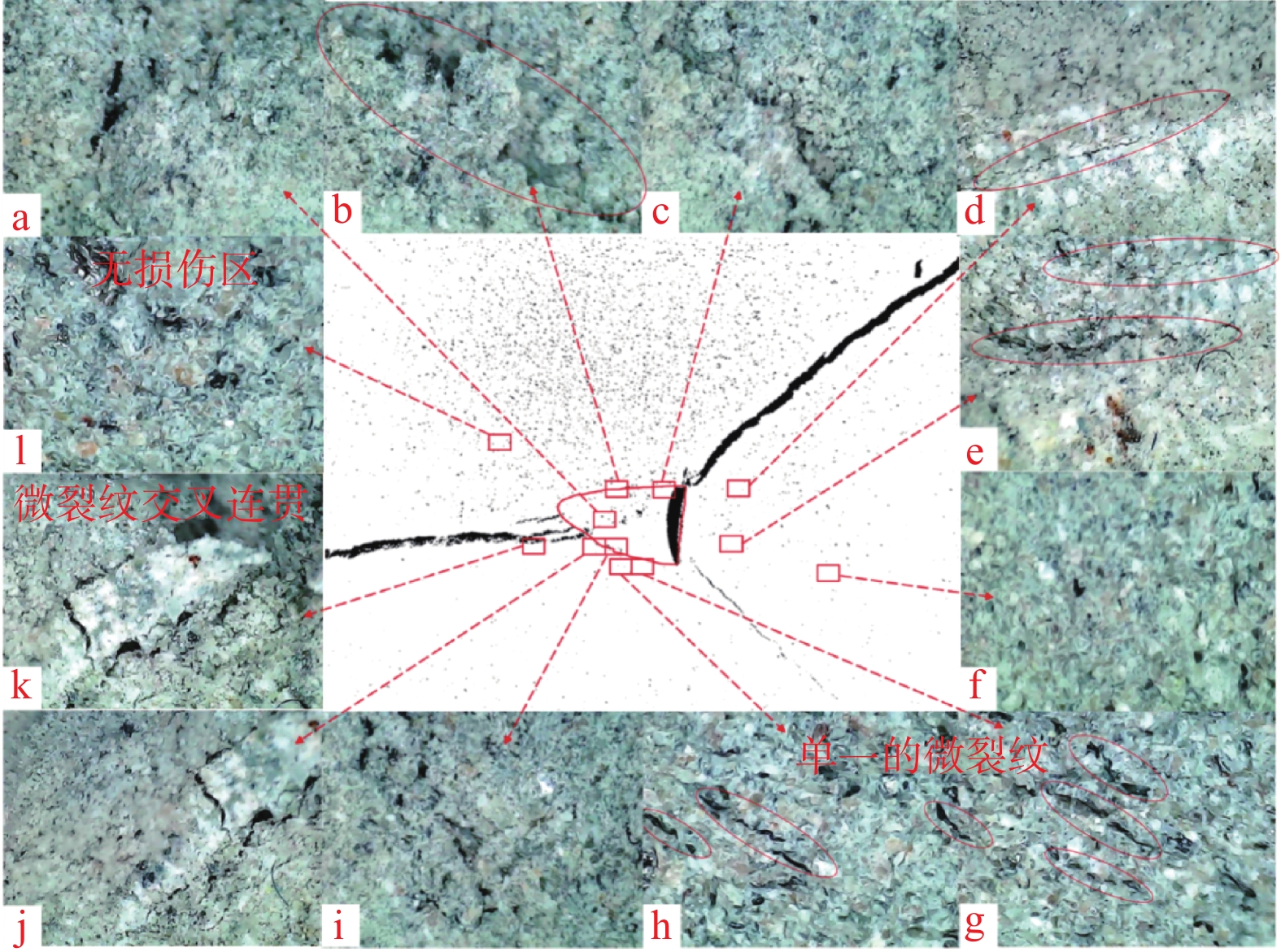
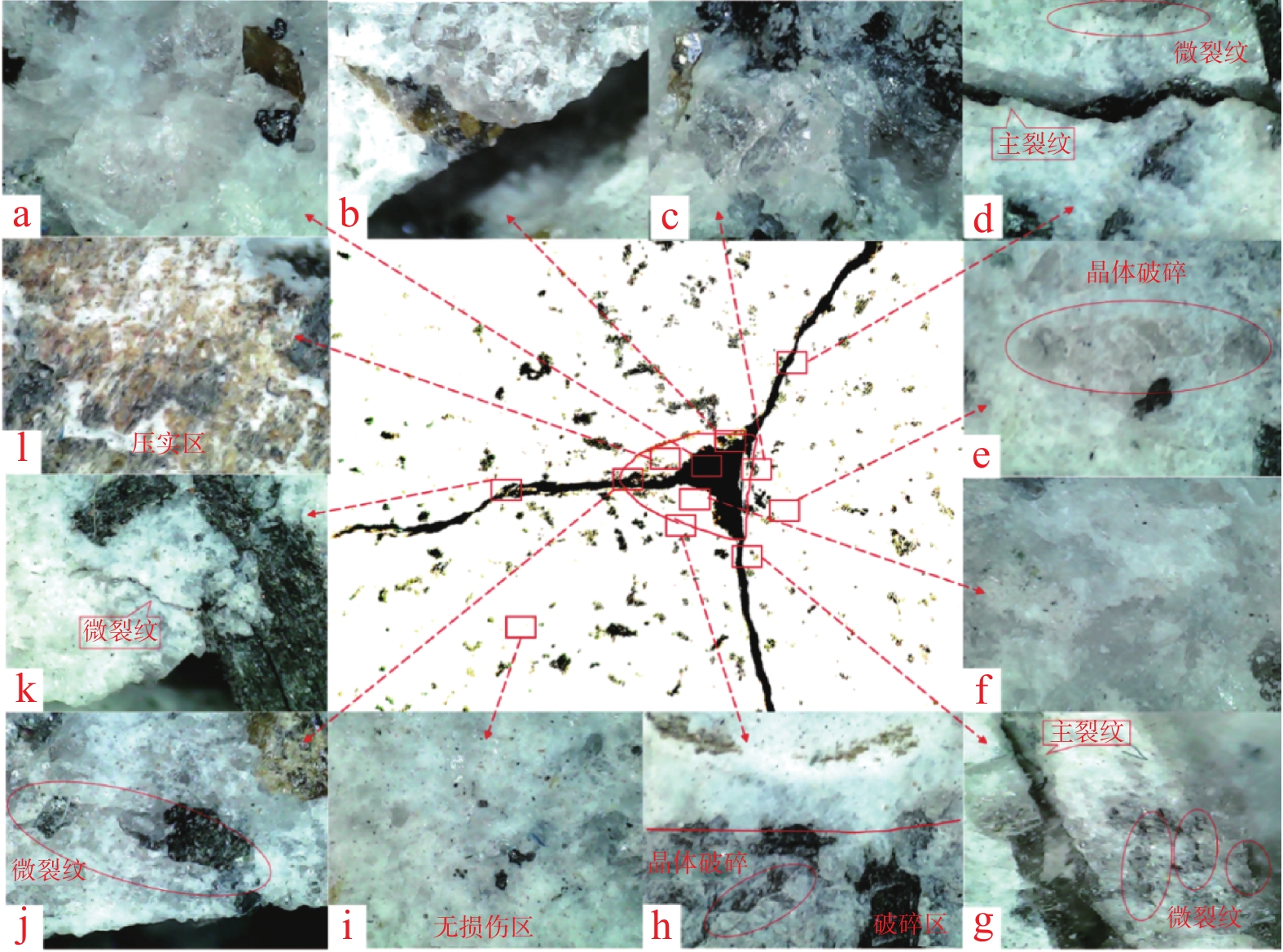
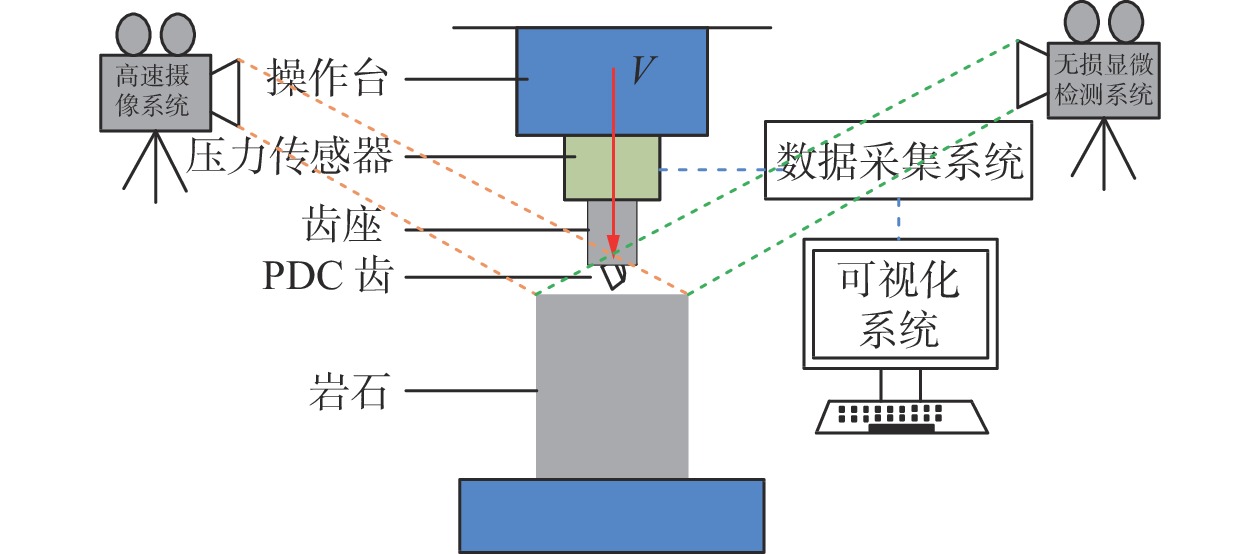
PDC齿是PDC钻头的重要破岩单元,其破岩过程包含压入和旋转切削,但现有研究忽略了压入过程的岩石损伤。为了研究PDC齿压入岩石的能力和探究岩石损伤机理,为PDC钻头的参数选择提供理论依据,采用室内试验方法研究了不同前倾角PDC齿压入青砂岩、花岗岩的破岩过程,采用岩石无损显微检测技术分析了岩石宏观及细观的裂纹。研究表明,砂岩的破碎方式为细小砂粒和黏结物的脱落,花岗岩的破碎方式为晶体的脆性破碎。岩石受载后会先在岩石内部薄弱地方萌生出单一的微裂纹,微裂纹连贯扩展形成主裂纹,主裂纹持续扩展形成宏观可见的裂纹;主裂纹附近为薄弱区域,其内部包含很多尚未成形的微裂纹;接触区域的齿尖处为应力集中区,主裂纹沿此开裂。岩石损伤过程随着前倾角的变化而变化,20°前倾角PDC齿压入青砂岩的能力最强,25°前倾角PDC齿压入花岗岩的能力最强;压入深度小于4 mm时,5°前倾角PDC齿压入岩石的能力最差。研究结果对于揭示岩石的细观与宏观损伤机理、建立PDC钻头破岩的评价方法和优化PDC钻头的设计参数及工作参数等具有重要作用。
Abstract:Polycrystalline diamond compact (PDC) cutters are an important rock-breaking unit of PDC bits, which include indentation and rotary cutting in rock breaking process. However, existing studies ignore the rock damage during indentation. The objective of this paper is to investigate the indentation ability of PDC cutters into the rock and explore the mechanisms of rock damage. This study aims to provide a theoretical basis for the parameter selection of PDC bits. The rock-breaking process of PDC cutters with different rake angles pressed into blue sandstone and granite was studied by laboratory test methods. Macroscopic and mesoscopic cracks in the rock were analyzed using non-destructive microscopic detection technology. The study found that the crushing of sandstone was caused by the falling off between fine sand particles and the binder, and the crushing of granite was manifested as the brittle fracture of crystals. After the rock was loaded, a single micro-crack would first appear in the weak part of the rock, and the micro-crack would continuously expand to form a main crack. The main crack would continue to expand to form a macroscopic and visible crack. The part near the main crack would become a weak area containing many micro-cracks that have not yet formed. The cutter tip in the contact area was the stress concentration area, and the main crack was developed along this area. The process of rock damage varies with the rake angle. The ability of PDC cutter with a rake angle of 20° to press into blue sandstone is the strongest, and the ability of PDC cutter with a rake angle of 25° to press into granite is the strongest. PDC cutter with a rake angle of 5° and an indentation depth of 4 mm had the worst ability to press into the rock. The research results are of great significance for revealing the mesoscopic and macroscopic damage mechanisms of rock, establishing the evaluation method of PDC bits for rock breaking, and selecting and optimizing the design and working parameters of PDC bits.
-
Keywords:
- PDC cutter /
- rock breaking mechanism /
- crack /
- macroscopic damage /
- mesoscopic damage
-
-
表 1 试验岩样主要的物理力学性质参数
Table 1 Main property parameters of rocks
岩性 抗压强度/MPa 弹性模量/GPa 泊松比 抗拉强度/MPa 黏聚力/MPa 内摩擦角/(°) 密度/(g·cm−3) 青砂岩 25.54 4.05 0.30 1.63 18.64 40.69 2.23 花岗岩 148.45 11.81 0.25 3.34 26.28 56.68 2.66 -
[1] 胡素云,李建忠,王铜山,等. 中国石油油气资源潜力分析与勘探选区思考[J]. 石油试验地质,2020,42(5):813–823. HU Suyun, LI Jianzhong, WANG Tongshan, et al. CNPC oil and gas resource potential and exploration target selection[J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment, 2020, 42(5): 813–823.
[2] 周长所,杨进,幸雪松,等. 基于机械比能理论的渤海深层钻井参数优化[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2021,43(6):693–697. doi: 10.13639/j.odpt.2021.06.001 ZHOU Changsuo, YANG Jin, XING Xuesong, et al. Optimizing drilling parameters of deep formations in the Bohai Basin based on mechanical specific energy theory[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2021, 43(6): 693–697. doi: 10.13639/j.odpt.2021.06.001
[3] 曾义金. 中国石化深层超深层油气井固井技术新进展与发展建议[J]. 石油钻探技术,2023,51(4):66–73. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2023035 ZENG Yijin. Novel advancements and development suggestions of cementing technologies for deep and ultra-deep wells of Sinopec[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2023, 51(4): 66–73. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2023035
[4] 闫睿昶,陈新勇,汝大军,等. 巴彦河套新区深井钻完井关键技术[J]. 石油钻 采工艺,2022,44(1):15–19. doi: 10.13639/j.odpt.2022.01.003 YAN Ruichang, CHEN Xinyong, RU Dajun, et al. Key technologies for deep well drilling and completion in Bayan Hetao New Area[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2022, 44(1): 15–19. doi: 10.13639/j.odpt.2022.01.003
[5] 何立成,唐波. 准噶尔盆地超深井钻井技术现状与发展建议[J]. 石油钻探技术,2022,50(5):1–8. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2022092 HE Licheng, TANG Bo. The up to date technologies of ultra-deep well drilling in Junggar basin and suggestions for further improvements[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2022, 50(5): 1–8. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2022092
[6] 兰凯,董成林,李光泉,等. 威荣深层页岩气田水平段安全提速技术对策[J]. 断块油气田,2023,30(3):505–510. doi: 10.6056/dkyqt202303019 LAN Kai,DONG Chenglin,LI Guangquan,et al. Technical strategy to enhance drilling speed safely of horizontal section for deep shale gas field in Weiyuan-Rongchang Block[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2023, 30(3): 505–510. doi: 10.6056/dkyqt202303019
[7] 黄安龙. PDC齿破岩过程岩石损伤演化模拟与试验研究[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学, 2022. HUANG Anlong. Simulation and experimental study of rock damage evolution on PDC bit[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University, 2022
[8] DENG Rong, HUANG Anlong, AN Mei. Study on the tooth load of the biconical-profiled single cone bit[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2021, 54(12): 6235–6248.
[9] 张富晓,黄志强,周已. PDC钻头切削齿失效分析[J]. 石油矿场机械,2015,44(9):44–49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3482.2015.09.011 ZHANG Fuxiao, HUANG Zhiqiang, ZHOU Yi. Failure analysis of PDC bit cutter[J]. Oil Field Equipment, 2015, 44(9): 44–49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3482.2015.09.011
[10] 袁军,邹德永,刘笑傲. 切向导入式旋流喷嘴辅助PDC钻头破岩实验[J]. 断块油气田,2016,23(4):528–532. doi: 10.6056/dkyqt201604026 YUAN Jun, ZOU Deyong, LIU Xiao′ao. Rock-breaking by tangential import swirl nozzle assisted PDC bit in abrasive formation[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2016, 23(4): 528–532. doi: 10.6056/dkyqt201604026
[11] 冯雨润. PDC齿作用下的岩石损伤规律研究[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学, 2018. FENG Yurun. Study on rock damage law under PDC teeth[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University, 2018
[12] DAI Xianwei, HUANG Zhongwei, WU Xiaoguang, et al. Failure analysis of high-temperature granite under the joint action of cutting and liquid nitrogen jet impingement[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2021, 54(12): 6249-6264.
[13] DAI Xianwei, HUANG Zhongwei, ZOU Wenchao, et al. Failure characteristics of rocks subjected to PDC cutter indentation[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2021, 207: 108992.
[14] 刘伟吉. 井底岩石塑脆性破碎机理及其影响因素研究[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学, 2017. LIU Weiji. The ductile-brittle failure mechanism and its influence factors investigation of bottom hole rock[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University, 2017
[15] CHENG Zhen, SHENG Mao, LI Gensheng, et al. Cracks imaging in linear cutting tests with a PDC cutter: Characteristics and development sequence of cracks in the rock[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2019, 179: 1151–1158. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2019.04.053
[16] 祝效华,刘伟吉. 单齿高频扭转冲击切削的破岩及提速机理[J]. 石油学报,2017,38(5):578–586. ZHU Xiaohua, LIU Weiji. The rock breaking and ROP rising mechanism for single-tooth high-frequency torsional impact cutting[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2017, 38(5): 578–586.
[17] 刘伟吉,曾义金,祝效华,等. 单齿复合冲击切削破岩机制及其与扭转冲击的对比[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版),2020,44(3):74–80. LIU Weiji, ZENG Yijin, ZHU Xiaohua, et al. Mechanism of rock breaking under composite and torsional impact cutting[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum(Edition of Natural Science), 2020, 44(3): 74–80.
[18] JAIME M C, ZHOU Yaneng, LIN J S, et al. Finite element modeling of rock cutting and its fragmentation process[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2015, 80: 137–146. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2015.09.004
[19] KAREKAL S. Modeling rock chipping process in linear drag cutting mode[R]. ISRM-EUROCK-2012-035, 2012.
[20] 吴泽兵,席凯凯,赵海超,等. 仿生 PDC 齿旋转破岩时的温度场和破岩特性模拟研究 [J]. 石油钻探技术,2022,50(2):71–77. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2021114 WU Zebing, XI Kaikai, ZHAO Haichao, et al. Simulation study on temperature field and rock breaking characteristics of the bionic PDC cutter in rotating state[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2022, 50(2): 71–77. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2021114
[21] 刘笑傲,邹德永,王庆,等. 基于离散元法的砾岩地层三棱齿切削破岩数值模拟[J]. 特种油气藏,2022,29(4):149–155. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2022.04.021 LIU Xiaoao, ZOU Deyong, WANG Qing, et al. Numerical simulation of rock breaking by triangular prismatic cutter in conglomerate formation based on discrete element method[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2022, 29(4): 149–155. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2022.04.021
[22] 杨迎新,高翔,陈红,等. PDC钻头岩石可钻性测定与分级新方法研究[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,2019,15(3):811–819. YANG Yinxin, GAO Xiang, CHEN Hong, et al. A new method for measuring and grading of PDC bit rock drillability[J]. Chinese Jour-nal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2019, 15(3): 811–819.
[23] 蒋廷学,王海涛. 中国石化页岩油水平井分段压裂技术现状与发展建议[J]. 石油钻探技术,2021,49(4):14–21. JIANG Tingxue, WANG Haitao. The current status and development suggestions for Sinopec's staged fracturing technologies of horizontal shale oil wells[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2021, 49(4): 14–21.
[24] DZ/T 0276.18—2015. 岩石物理力学性质试验规程: 第18部分: 岩石单轴抗压强度试验[S]. DZ/T 0276.18—2015. Specification for testing physical and mechanical properties of rock: part 18: uniaxial compressive strength test of rock[S].
[25] DZ/T 0276.19—2015. 岩石物理力学性质试验规程: 第19部分: 岩石单轴压缩变形试验[S]. DZ/T 0276.19—2015. Specification for testing physical and mechanical properties of rock: part 19: rock deformation test under uniaxial compression[S].
[26] DZ/T 0276.21—2015. 岩石物理力学性质试验规程: 第21部分: 岩石抗拉强度试验[S]. DZ/T 0276.21—2015. Specification for testing physical and mechanical properties of rock: part 21: tensile strength test of rock[S].
[27] DAI Xianwei, HUANG Zhongwei, SHI Huaizhong, et al. Rock failure analysis based on the cutting force in the single PDC cutter tests[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 194: 107339. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2020.107339
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 陈安星,魏群,郭丰,谢正正. PDC钻头前角对岩石钻孔过程影响研究. 当代化工研究. 2024(18): 60-63 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陈霖,贺育贤,马海云,张慧,庞合善,陈伟林,易先中. 基于热应力PDC钻头胎体断裂失效分析及试验研究. 机床与液压. 2024(20): 26-34 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: