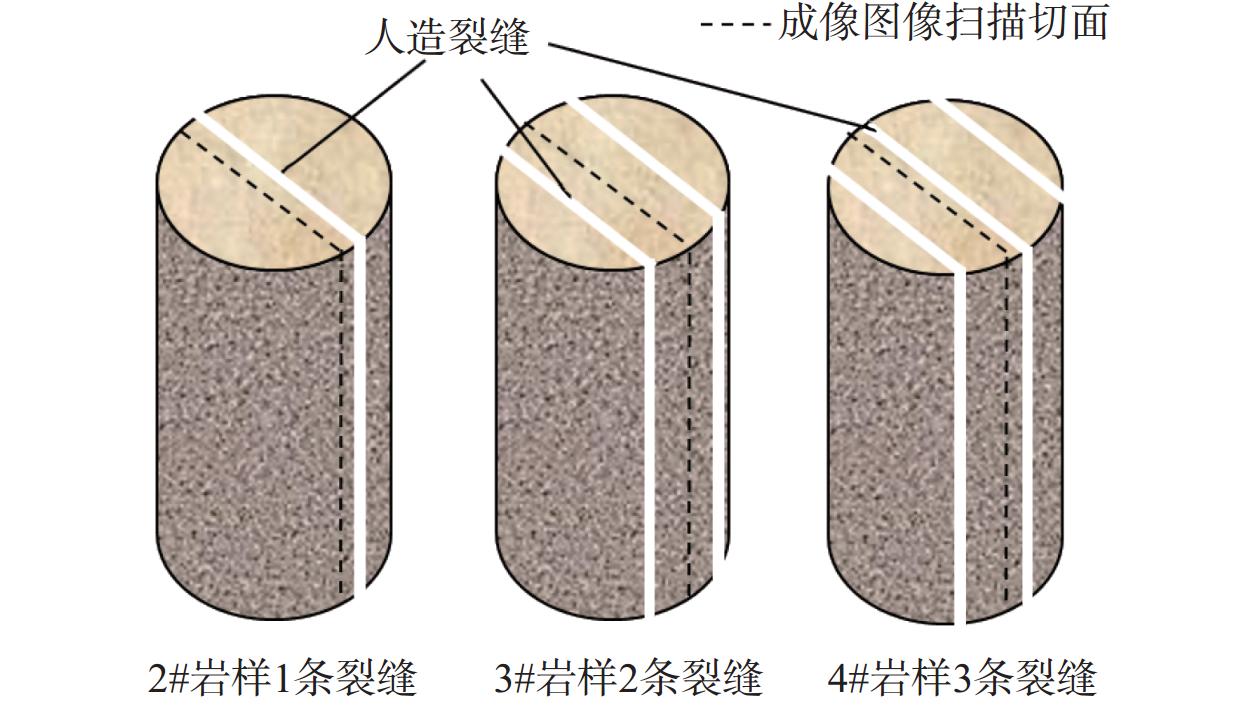
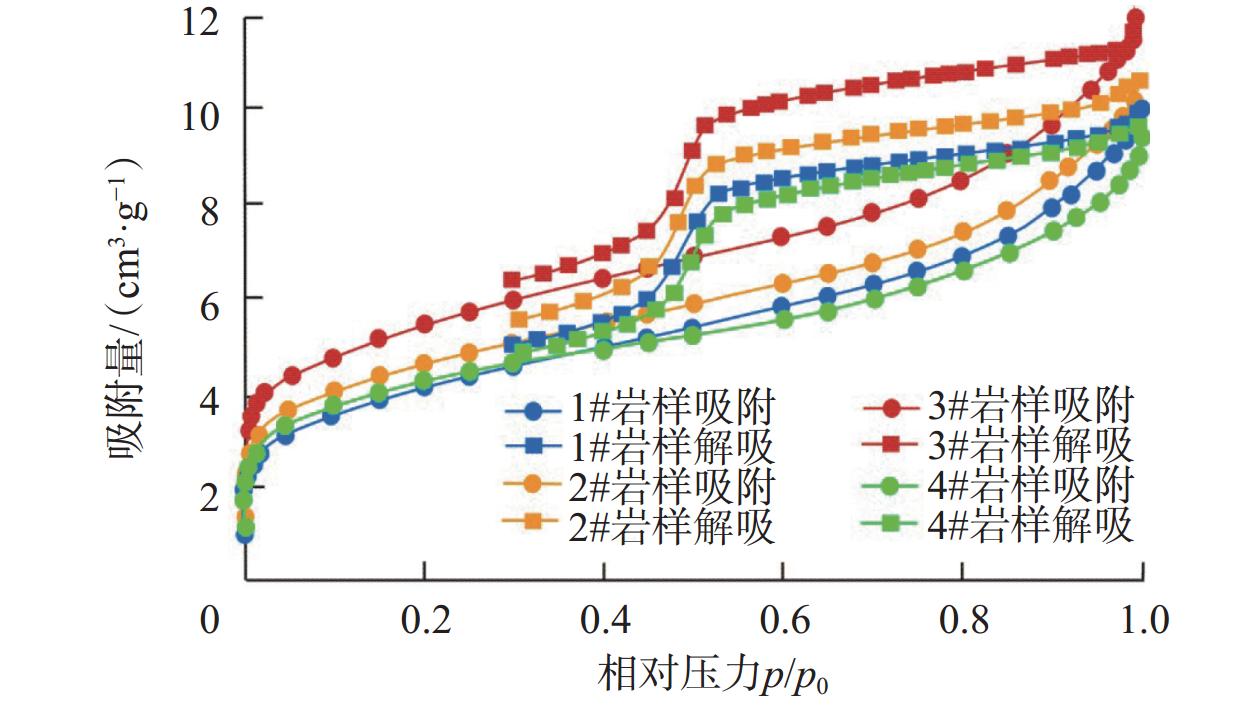
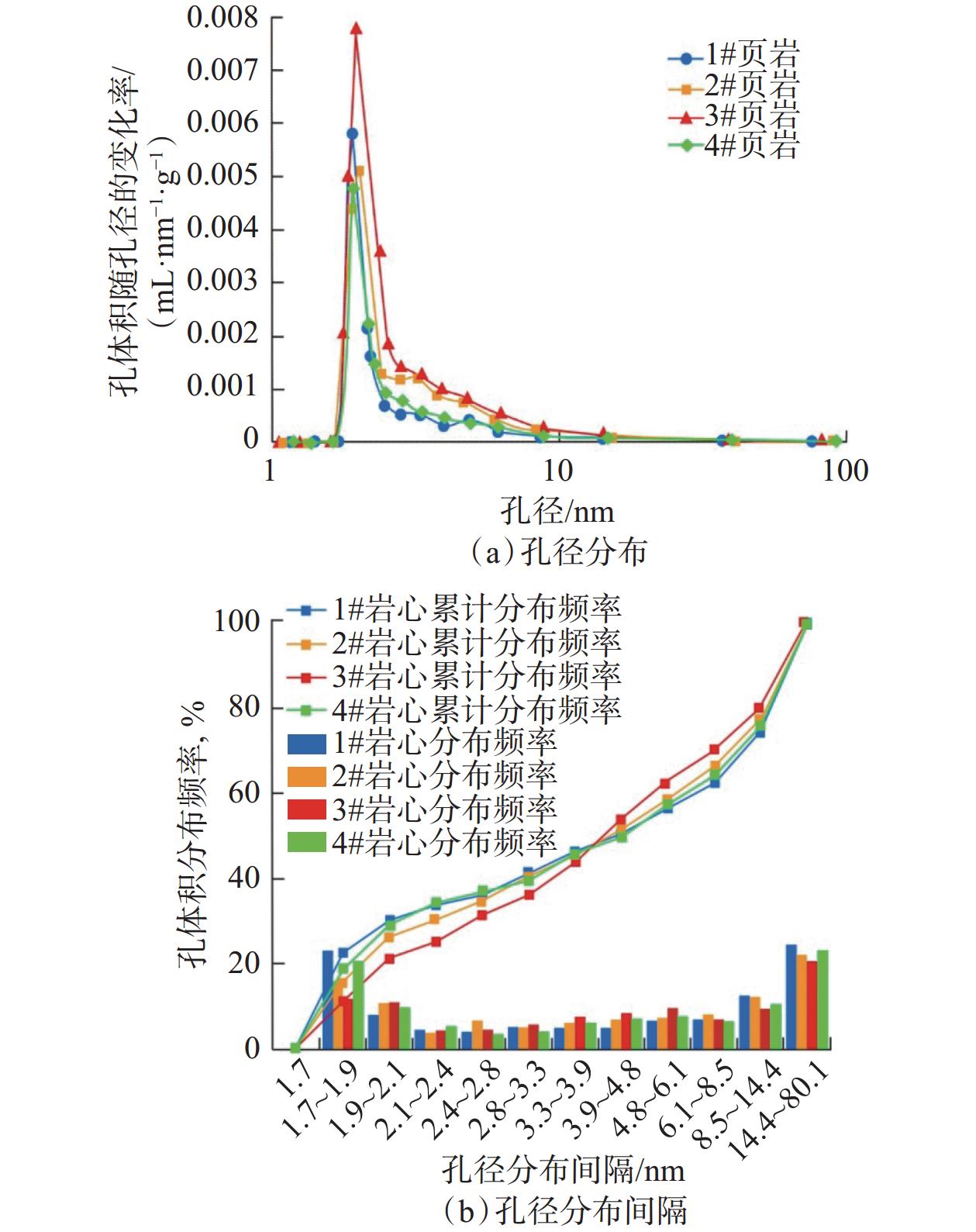
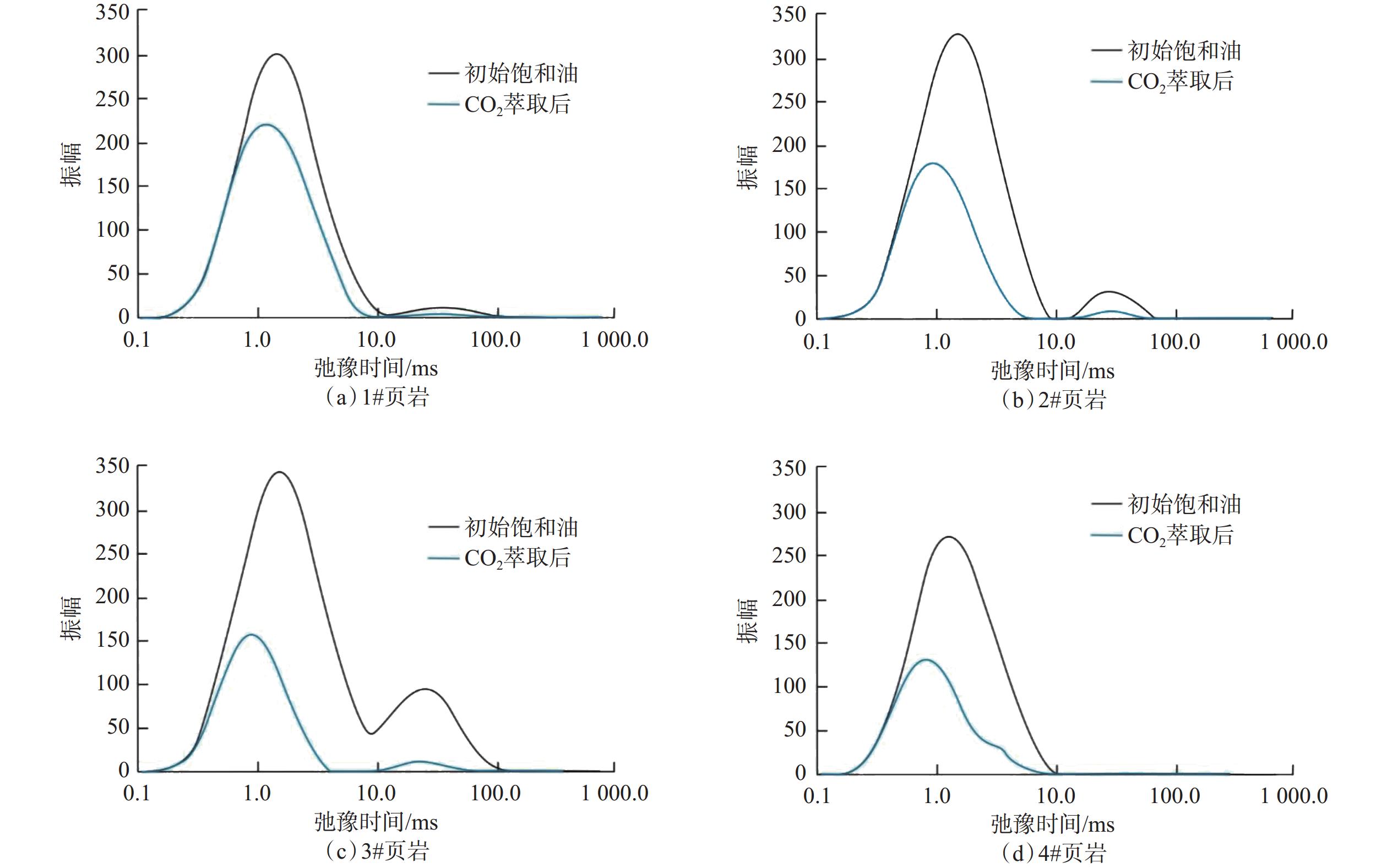
Evaluation of Shale Oil Extraction by Supercritical CO2 and Analysis of Influencing Factors
-
摘要:
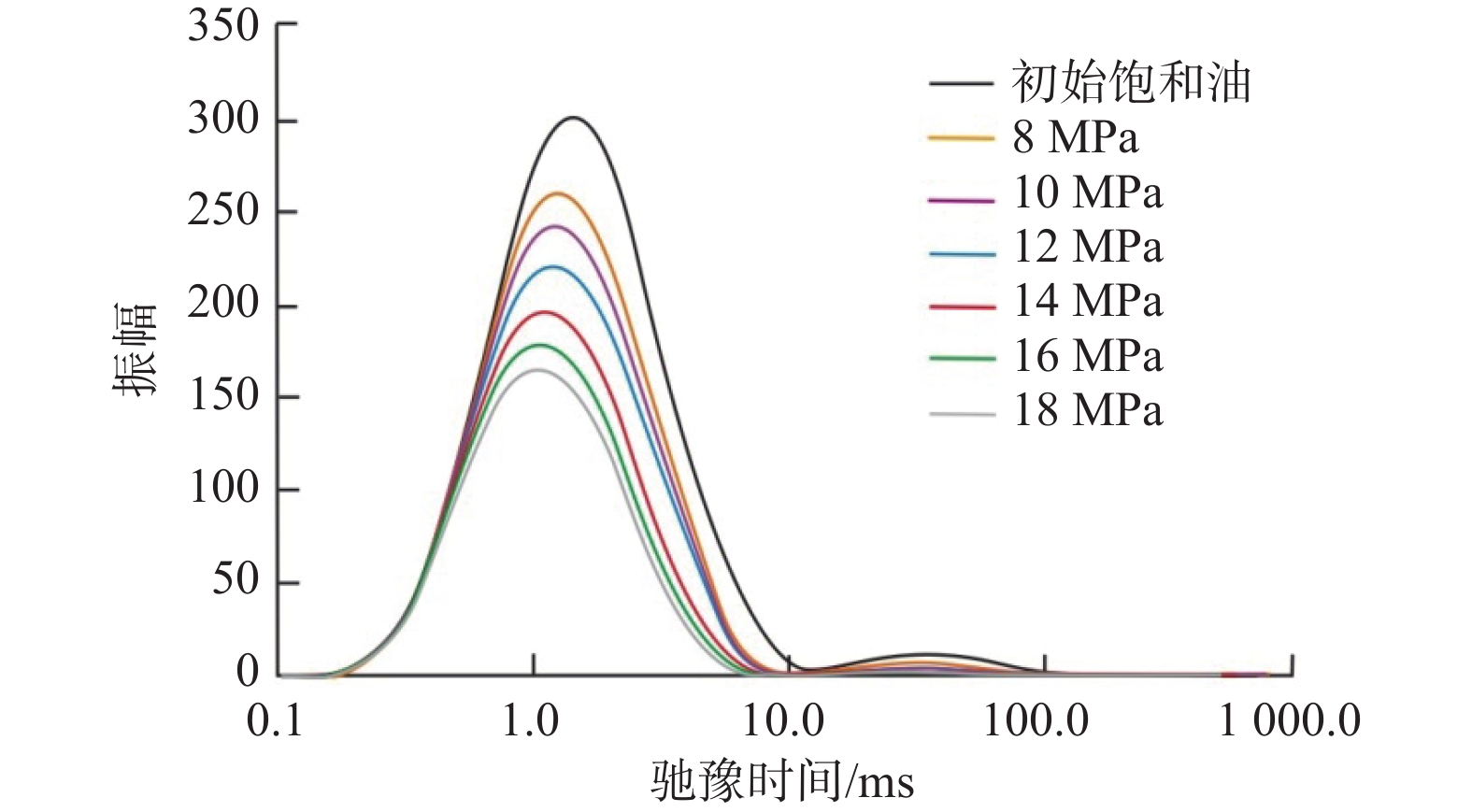
为明确裂缝及压力对超临界CO2萃取页岩油的影响机理,在获取试验用页岩岩样孔径分布、比表面积和孔体积的基础上,进行了超临界CO2岩样萃取试验,采用改进的磁悬浮天平高压吸附仪,实时测定了高温高压下页岩岩样质量的变化;并结合页岩核磁共振T2谱,精确测定了超临界CO2对页岩油的萃取效率,明确了萃取过程中页岩孔隙动用特征及动用孔径下限。试验结果表明,目标储层页岩中介孔(孔径2~50 nm)发育程度最高,占总孔隙体积和总比表面积的69.72%和73.47%;而大孔(孔径>50 nm)发育程度最差,仅占总孔隙体积和总比表面积的4.45%和10.77%。原油主要赋存于孔径1.4~120.0 nm的小孔径孔隙中,CO2对大孔径(>86 nm)孔隙中原油的萃取效果高于小孔径(≤86 nm)孔隙;裂缝能够增大CO2与基质中页岩油的接触面积,加快油气传质速度,提高基质动用深度,降低页岩油渗流阻力和孔隙动用下限。然而,CO2萃取效率除与裂缝数量相关外,还受基质渗透率及裂缝−基质连通特征的影响。CO2动用孔隙孔径下限随注入压力升高而降低,由8 MPa时的6.54 nm减小至18 MPa的3.27 nm。研究成果可为注CO2提高页岩油采收率提供借鉴。
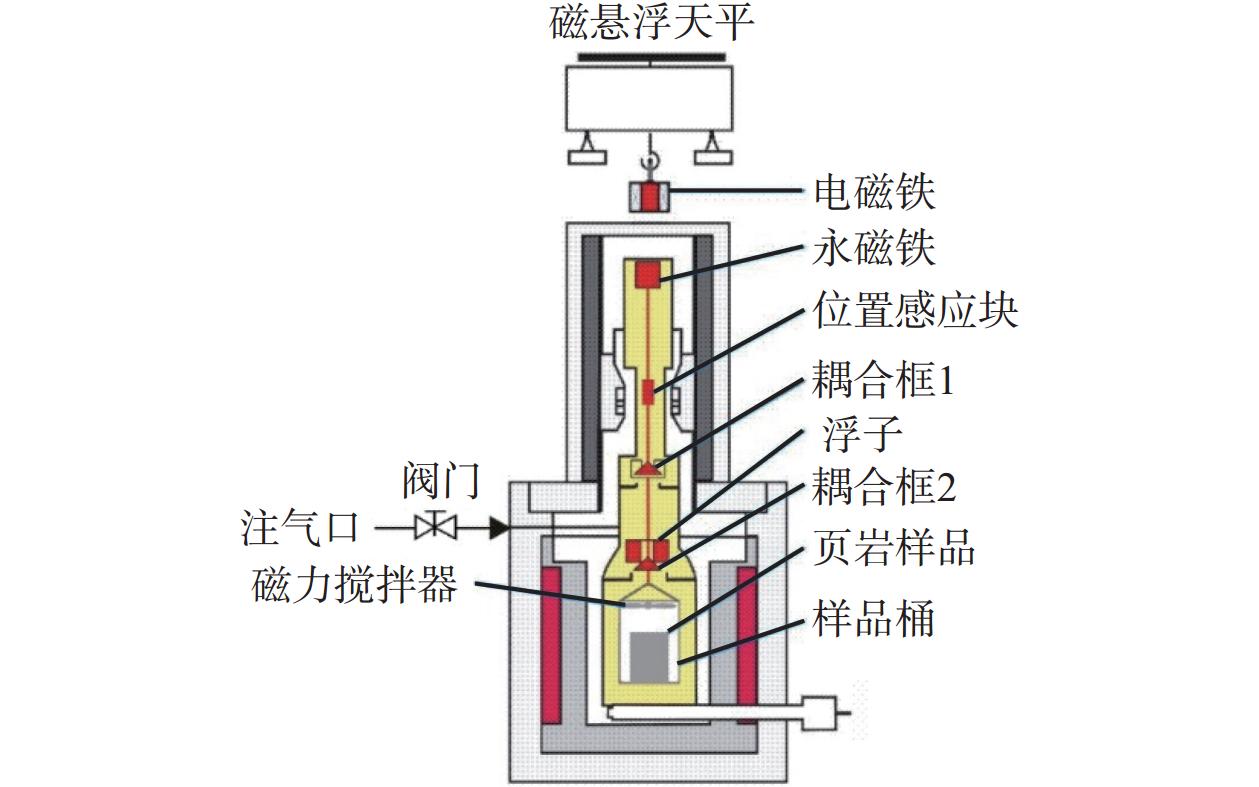
Abstract:To define the influence mechanism of fractures and pressure on the extraction of shale oil by supercritical CO2, the core extraction experiment by supercritical CO2 was conducted on the basis of identifying the pore size distribution, specific surface area, and pore volume of experimental shales. The improved magnetic suspension balance high pressure adsorption instrument was used to measure the shale mass change under high temperature and pressure in real time. Combined with the nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) T2 spectrum of shale, the extraction efficiency of shale oil by supercritical CO2 was accurately measured, and the producing characteristics of shale pores and the lower limit of producing pore size in the extraction process were defined. The experimental results show that the target reservoir shale mesopore (pore size of 2~50 nm) is the most developed, accounting for 69.72% and 73.47% of the total pore volume and total specific surface area. However, macropores (>50 nm) are the least developed, accounting for only 4.45% and 10.77% of the total pore volume and total specific surface area. The crude oil mainly exists in the pores with a small pore size of 1.4~120 nm. The extraction effect of CO2 on the crude oil in the pores with large pore size (>86 nm) is better than that in the pores with small pore size (≤86 nm). Fractures can increase the contact area between CO2 and shale oil in the matrix, accelerate the mass transfer rate of oil and gas, improve the depth of matrix production, and reduce the shale oil seepage resistance and the lower limit of pore production. However, the CO2 extraction efficiency is not only related to the number of fractures but also affected by matrix permeability and fracture-matrix connectivity. The lower limit of pore size for CO2 production decreases with the increase in injection pressure from 6.54 nm at 8 MPa to 3.27 nm at 18 MPa. The research findings provide a reference for enhancing the recovery rate of shale oil by injecting CO2.
-
Keywords:
- shale oil /
- fractures /
- CO2 /
- injection pressure /
- NMR /
- extraction efficiency /
- weighing method
-
-
表 1 试验用页岩岩样的基本物性参数
Table 1 Basic physical parameters of experimental shale samples
岩样编号 孔隙度,% 渗透率/mD 有机碳含量,% 热成熟度,% 矿物组分及含量,% 石英 钠长石 方解石 白云石 黄铁矿 黏土矿物 1# 5.62 0.004 47 3.52 2.31 26.3 4.5 9.4 3.4 2.7 53.7 2# 6.38 0.006 56 3.18 2.04 41.7 4.4 15.1 3.1 4.8 30.9 3# 6.15 0.007 52 4.22 2.27 37.2 4.1 11.4 2.7 3.5 41.1 4# 5.62 0.003 81 3.06 2.14 29.7 5.7 8.6 4.2 3.3 48.5 表 2 低温氮气吸附试验测得页岩岩样的孔隙结构参数
Table 2 Measurement of pore structure parameters of experimental shale samples by low temperature nitrogen adsorption experiment
样品编号 BJH孔体积/(μL·g−1) 平均
孔径/nm不同孔径孔隙体积占
总孔隙体积的比例,%BET比表面积/
(m2·g−1)不同孔径孔隙比表面积占
总孔隙比表面积的比例,%<2 nm 2~50 nm >50 nm <2 nm 2~50 nm >50 nm 1 22.47 6.26 30.92 63.42 5.67 1.44 18.81 69.38 11.81 2 26.98 6.34 20.54 74.48 4.98 2.05 14.92 72.03 13.05 3 29.79 7.28 24.34 72.64 3.03 2.93 12.64 79.97 7.39 4 24.64 6.05 27.52 68.35 4.13 1.76 16.71 72.48 10.81 均值 25.97 6.48 25.83 69.72 4.45 2.05 15.77 73.47 10.77 表 3 采用实时称重法和NMR法计算CO2萃取效率的对比
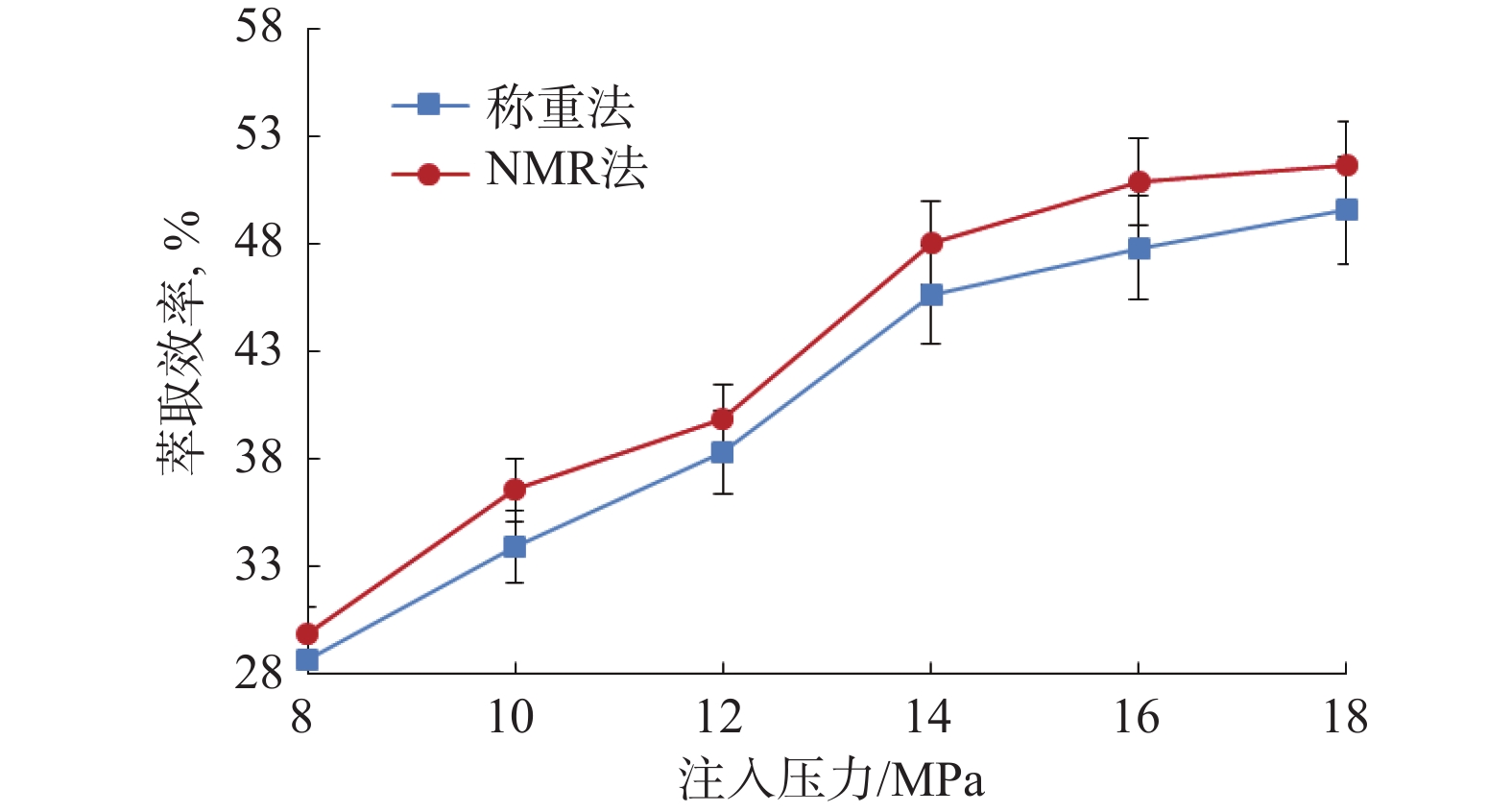
Table 3 Calculation of CO2 extraction efficiency by real-time weighing method and NMR method
岩心编号 岩心质量/g 饱和原油量/mL CO2萃取效率,% 萃取前 萃取后 实时称重法 NMR法 1# 61.86 61.65 0.57 37.00 39.89 2# 56.59 56.20 0.66 58.68 60.43 3# 60.10 59.58 0.71 73.04 74.29 4# 58.46 58.09 0.61 60.43 61.65 -
[1] 董岩,肖佃师,彭寿昌,等. 页岩油层系储集层微观孔隙非均质性及控制因素:以吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组为例[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报,2021,40(1):115–123. DONG Yan, XIAO Dianshi, PENG Shouchang, et al. Heterogeneity of microscopic pores in shale oil reservoir and its controlling factors: taking the Lucaogou Formation in the Jimusar Sag as an example[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2021, 40(1): 115–123.
[2] 卢双舫,李俊乾,张鹏飞,等. 页岩油储集层微观孔喉分类与分级评价[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2018,45(3):436–444. doi: 10.11698/PED.2018.03.08 LU Shuangfang, LI Junqian, ZHANG Pengfei, et al. Classification of microscopic pore-throats and the grading evaluation on shale oil reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(3): 436–444. doi: 10.11698/PED.2018.03.08
[3] 屈海清. 鄂尔多斯盆地页岩气的开发[J]. 化工设计通讯,2019,45(7):264–265. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6490.2019.07.172 QU Haiqing. Shale gas development in Ordos Basin[J]. Chemical Engineering Design Communications, 2019, 45(7): 264–265. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6490.2019.07.172
[4] 王晓雯. 致密油藏储层敏感性评价及主控因素研究[J]. 特种油气藏,2021,28(1):103–110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2021.01.015 WANG Xiaowen. Study on reservoir sensitivity evaluation and key control factors of tight oil reservoirs[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2021, 28(1): 103–110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2021.01.015
[5] MA Quanzheng, YANG Shenglai, LYU Daoping, et al. Experimental investigation on the influence factors and oil production distribution in different pore sizes during CO2 huff-n-puff in an ultra-high-pressure tight oil reservoir[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2019, 178: 1155–1163. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2019.04.012
[6] 胡伟,吕成远,王锐,等. 水驱转CO2混相驱渗流机理及传质特征[J]. 石油学报,2018,39(2):201–207. doi: 10.7623/syxb201802008 HU Wei, LYU Chengyuan, WANG Rui, et al. Porous flow mechanisms and mass transfer characteristics of CO2 miscible flooding after water flooding[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2018, 39(2): 201–207. doi: 10.7623/syxb201802008
[7] 李凤霞,王海波,周彤,等. 页岩油储层裂缝对CO2吞吐效果的影响及孔隙动用特征[J]. 石油钻探技术,2022,50(2):38–44. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2022006 LI Fengxia, WANG Haibo, ZHOU Tong, et al. The influence of fractures in shale oil reservoirs on CO2 huff and puff and its pore production characteristics[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2022, 50(2): 38–44. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2022006
[8] GAMADI T D, SHENG J J, SOLIMAN M Y, et al. An experimental study of cyclic CO2 injection to improve shale oil recovery[R]. SPE 169142, 2014.
[9] LI Lei, SU Yuliang, HAO Yongmao, et al. A comparative study of CO2 and N2 huff-n-puff EOR performance in shale oil production [J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2019, 181: 106174. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2019.06.038
[10] 李二党,韩作为,高祥瑞,等. 不同注气介质驱替致密油藏微观孔隙动用特征研究[J]. 石油钻探技术,2020,48(5):85–91. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2020078 LI Erdang, HAN Zuowei, GAO Xiangrui, et al. Research on the microscopic pore producing characteristics of tight reservoirs displaced by different gas injection media[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2020, 48(5): 85–91. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2020078
[11] LI Lei, SHENG J J. Numerical analysis of cyclic CH4 injection in liquid-rich shale reservoirs based on the experiments using different-diameter shale cores and crude oil[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2017, 39: 1–14. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2017.01.017
[12] ABEDINI A, TORABI F. Oil recovery performance of immiscible and miscible CO2 huff-and-puff processes[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2014, 28(2): 774–784.
[13] YU Haiyang, XU Hang, FU Wenrui, et al. Extraction of shale oil with supercritical CO2: effects of number of fractures and injection pressure[J]. Fuel, 2021, 285: 118977. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.118977
[14] 刘永. 基于核磁共振流态分析的页岩微纳米孔隙类型划分方法[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2018. LIU Yong. A study of shale pore size classification by using low field nuclear magnetic resonance fluid typing method[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2018.
[15] 岳长涛,李术元,许心怡,等. 宜宾地区页岩微孔特征及吸附解吸特性研究[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版),2018,40(5):84–94. YUE Changtao, LI Shuyuan, XU Xinyi, et al. Micropore characteristics and adsorption and desorption properties of shales in the Yibin region[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University(Science & Technology Edition), 2018, 40(5): 84–94.
[16] 肖立志,罗嗣慧,龙志豪. 井场核磁共振技术及其应用的发展历程与展望[J]. 石油钻探技术,2023,51(4):140–148. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2023034 XIAO Lizhi, LUO Sihui, LONG Zhihao. The course of development and the future of wellsite NMR technologies and their applications[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2023, 51(4): 140–148. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2023034
[17] LYU Chaohui, NING Zhengfu, WANG Qing, et al. Application of NMR T2 to pore size distribution and movable fluid distribution in tight sandstones[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2018, 32(2): 1395–1405.
[18] 姚艳斌,刘大锰. 基于核磁共振弛豫谱技术的页岩储层物性与流体特征研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2018,43(1):181–189. YAO Yanbin, LIU Dameng. Petrophysical properties and fluids transportation in gas shale: a NMR relaxation spectrum analysis method[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2018, 43(1): 181–189.
[19] 郎东江,伦增珉,吕成远,等. 页岩油注二氧化碳提高采收率影响因素核磁共振实验[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2021,48(3):603–612. doi: 10.11698/PED.2021.03.15 LANG Dongjiang, LUN Zengmin, LYU Chengyuan, et al. Nuclear magnetic resonance experimental study of CO2 injection to enhance shale oil recovery[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2021, 48(3): 603–612. doi: 10.11698/PED.2021.03.15
[20] 黄兴,李响,张益,等. 页岩油储集层二氧化碳吞吐纳米孔隙原油微观动用特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2022,49(3):557–564. doi: 10.11698/PED.20210582 HUANG Xing, LI Xiang, ZHANG Yi, et al. Microscopic production characteristics of crude oil in nano-pores of shale oil reservoirs during CO2 huff and puff[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2022, 49(3): 557–564. doi: 10.11698/PED.20210582
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 刘献博,薛亮,刘敏,王智明,张峥,邵天宇. 连续波钻井液脉冲发生器压力波波形优化研究. 石油机械. 2020(12): 44-51 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)



 下载:
下载: