High-Efficiency Anti-Sloughing Drilling Fluid Technology for Tanuma Shale of East Baghdad Oilfield in Iraq
-
摘要:
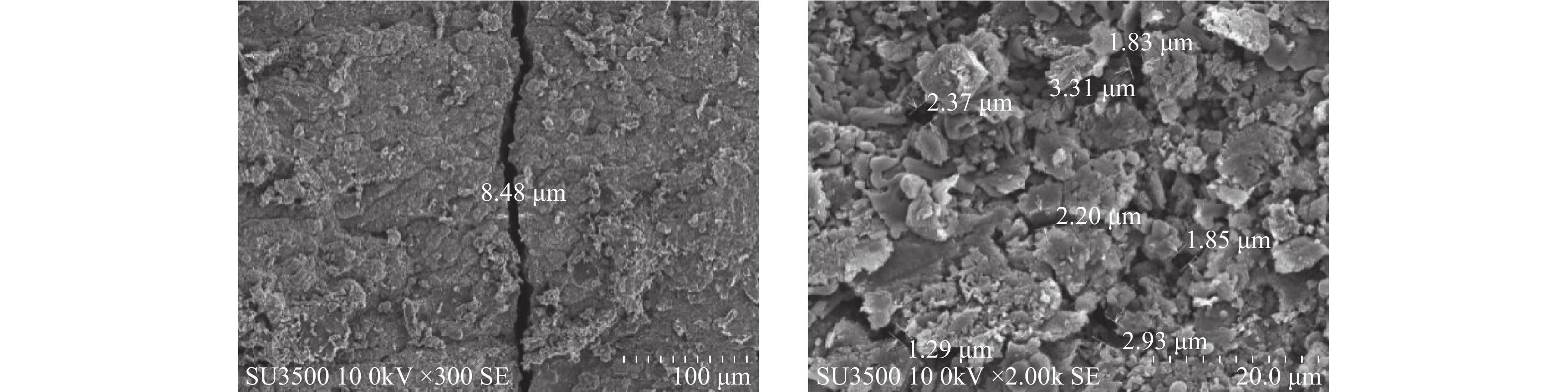
伊拉克东巴油田South-2区块采用水平井开发Khasib组储层,但该区块首口以Khasib组为目的层的水平井在钻井过程中,因Tanuma组泥页岩多次发生坍塌卡钻,导致井眼报废。研究Tanuma组矿物组成、孔缝发育情况和水化膨胀特性发现,该组泥页岩具有黏土矿物含量高、水敏性较强、宏观层理发育明显、微观孔缝发育度高和水化膨胀速率快等特点,导致钻井过程中因黏土矿物快速水化膨胀而发生井眼失稳问题。基于此,通过室内试验,优选了封堵剂N-Seal及抑制剂U-HIB,对氯化钾聚磺钻井液的配方进行了优化,形成了高效防塌钻井液。室内试验发现,高效防塌钻井液具有良好的流变性、较强的封堵和抑制能力,能够满足Tanuma组泥页岩井段高效封堵的要求。该防塌钻井液在South-2区块3口水平井进行了现场试验,均成功钻穿Tanuma组泥页岩层段,顺利钻至设计井深,未出现坍塌掉块等井眼失稳问题。室内研究与现场试验结果表明,高效防塌钻井液能够有效解决Tanuma组泥页岩坍塌的技术难题,为实现Khasib组储层的有效开发提供技术支撑。
Abstract:East Baghdad Oilfield in Iraq employs horizontal wells to develop reservoirs of the Khasib Formation in the South-2 block. However, in the drilling of the first horizontal well in the block with the Khasib Formation as the target, repeated sloughing and sticking happened drilling through the shale formation of Tanuma, which resulted in borehole abandonment. Researches on formation mineral composition, pore-fracture development, and hydration swelling characteristics show that the Tanuma shale features high clay mineral content, strong water sensitivity, evident macro bedding development, high micro pore and fracture development, and fast hydration swelling rate. As a result, wellbore instability occurs due to the rapid hydration swelling of clay minerals during drilling. Through laboratory evaluation, a high-efficiency anti-sloughing drilling fluid system was developed, by selecting N-Seal plugging agent and U-HIB inhibitor and optimizing the formula of the KCl/polysulfonate drilling fluid system. The evaluation demonstrated that the drilling fluid system with good rheologic characteristics presented strong plugging and inhibition performances, which met the requirements of high-efficiency plugging of Tanuma shale. In field tests of the drilling fluid in three horizontal wells of the South-2 block, Tanuma shale was drilled through without any wellbore instability issues. Laboratory evaluation and field tests show that the application of proposed drilling fluid system can effectively eliminate the technical difficulties of borehole instability in drilling through Tanuma shale, and provide support for the effective development of reservoirs in the Khasib Formation.
-
Keywords:
- horizontal well /
- shale /
- hole stabilization /
- anti-sloughing drilling fluid /
- East Baghdad Oilfield
-
-
表 1 Tanuma组泥页岩矿物组成分析结果
Table 1 Mineral composition analysis of Tanuma shale
井深/m 矿物含量,% 石英 方解石 黄铁矿 铁白云石 黏土 2 388 1.19 11.49 10.64 40.08 36.60 2 389 6.57 10.26 10.33 21.31 51.53 2 390 5.83 11.66 12.92 27.93 41.66 表 2 6种封堵剂的性能评价试验结果
Table 2 Performance evaluation of six plugging agents
试验流体配方 瞬时滤失量/
mL静滤失速率/
(mL·min−0.5)累计滤失量/
mL基浆 2.69 18.10 35.2 基浆+2%FT-1 0.23 8.69 21.3 基浆+2%NSI 0.30 16.36 26.6 基浆+2%N-JC 0.45 15.37 29.1 基浆+2%N-CaCO3 0.12 7.33 13.2 基浆+2%N-Seal 0.13 6.01 10.2 基浆+2%N-Polymer 0.19 8.33 17.6 表 3 高效防塌钻井液和氯化钾聚磺钻井液流变性试验结果
Table 3 Rheology test of high-efficiency anti-sloughing drilling fluid and KCl/polysulfonate drilling fluid
密度/
(kg·L−1)钻井液 六速旋转黏度计读数 静切力/Pa 塑性黏度/
(mPa·s)动切力/Pa API滤失量/mL ϕ600 ϕ300 ϕ200 ϕ100 ϕ6 ϕ3 1.55 氯化钾聚磺 82 54 40 25 5 4 2.0/5.5 28 13.0 2.6 高效防塌 85 55 42 26 5 4 2.5/5.0 30 12.5 2.4 1.60 氯化钾聚磺 83 53 40 25 5 4 2.0/4.5 30 11.5 2.6 高效防塌 88 56 44 27 5 4 2.0/4.5 32 12.0 2.0 1.65 氯化钾聚磺 86 56 40 25 5 4 2.0/4.5 30 13.0 2.4 高效防塌 90 57 41 25 5 4 2.0/4.5 33 12.0 2.2 表 4 高效防塌钻井液在3口水平井中的试验效果
Table 4 Field test of high-efficiency anti-sloughing drilling fluid in three horizontal wells
井号 泥页岩
井段/m纯钻进
时间/h平均机械
钻速/(m·h−1)起钻复杂
时间/hEBSK-5-5H 2 510~2 625 51.76 2.22 6.2 EBSK-2-2H 2 492~2 608 61.00 1.90 3.2 EBSK-3-3H 2 540~2 653 62.18 1.82 6.8 -
[1] 程远方,张锋,王京印,等. 泥页岩井壁坍塌周期分析[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版),2007,31(1):63–66. CHENG Yuanfang, ZHANG Feng, WANG Jingyin, et al. Analysis of borehole collapse cycling time for shale[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2007, 31(1): 63–66.
[2] 南旭. 关于页岩气井井壁失稳机理及其油基钻井液技术探究[J]. 化工管理,2020(17):96–97. NAN Xu. Study on wellbore instability mechanism of shale gas well and oil based drilling fluid technology[J]. Chemical Management, 2020(17): 96–97.
[3] 袁华玉,程远方,王伟,等. 长水平段钻井泥岩井壁坍塌周期分析[J]. 科学技术与工程,2017,17(3):183–189. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2017.03.028 YUAN Huayu, CHENG Yuanfang, WANG Wei, et al. Analysis on time-dependent wellbore collapse for long horizontal well in shale formation[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2017, 17(3): 183–189. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2017.03.028
[4] 李辉. 白油基油包水钻井液在JHW00421井水平段的应用[J]. 新疆石油天然气,2020,16(2):38–42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2677.2020.02.009 LI Hui. The application of invert white oil based drilling fluid in horizontal section of Well JHW00421[J]. Xinjiang Oil & Gas, 2020, 16(2): 38–42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2677.2020.02.009
[5] SY/T 5163—2018 沉积岩中黏土矿物和常见非黏土矿物X射线衍射分析方法[S]. SY/T 5163—2018 Analysis method for clay minerals and ordinary non-clay minerals in sedimentary rocks by the X-ray diffraction[S].
[6] 王倩,王刚,蒋宏伟,等. 泥页岩井壁稳定耦合研究[J]. 断块油气田,2012,19(4):517–521. WANG Qian, WANG Gang, JIANG Hongwei, et al. Study on shale wellbore stability coupling[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2012, 19(4): 517–521.
[7] 张伟国,狄明利,卢运虎,等. 南海西江油田古近系泥页岩地层防塌钻井液技术[J]. 石油钻探技术,2019,47(6):40–47. ZHANG Weiguo, DI Mingli, LU Yunhu, et al. Anti-sloughing drilling fluid technology for the Paleogene shale stratum of the Xijiang Oilfield in the South China Sea[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2019, 47(6): 40–47.
[8] 梁利喜,丁乙,刘向君,等. 硬脆性泥页岩井壁稳定渗流–力化耦合研究[J]. 特种油气藏,2016,23(2):140–143. LIANG Lixi, DING Yi, LIU Xiangjun, et al. Seepage-mechanochemistry coupling of wellbore stability in hard-brittle shale[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2016, 23(2): 140–143.
[9] 蔚宝华,邓金根,闫伟. 层理性泥页岩地层井壁坍塌控制方法研究[J]. 石油钻探技术,2010,38(1):56–59. YU Baohua, DENG Jingen, YAN Wei. Borehole sloughing control in shale formations[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2010, 38(1): 56–59.
[10] 姚新珠,时天钟,于兴东,等. 泥页岩井壁失稳原因及对策分析[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2001,18(3):38–41. YAO Xinzhu, SHI Tianzhong, YU Xingdong, et al. Shale wellbore failure and precautionary measures[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2001, 18(3): 38–41.
[11] 樊泽霞,高锦屏,郭东荣. 泥页岩水化作用综合评价[J]. 石油钻探技术,1999,27(6):26–27. FAN Zexia, GAO Jinping, GUO Dongrong. Comprehensive evaluation of mud shale hydration[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 1999, 27(6): 26–27.
[12] SY/T 5162—1997 岩石样品扫描电子显微镜分析方法[S]. SY/T 5162—1997 Analytical method of rock sample by scanning electron microscope[S].
[13] 王建华,鄢捷年,苏山林. 硬脆性泥页岩井壁稳定评价新方法[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2006,28(2):28–30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7393.2006.02.009 WANG Jianhua, YAN Jienian, SU Shanlin. New method for evaluating borehole stability in brittle shale[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2006, 28(2): 28–30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7393.2006.02.009
[14] 刘厚彬,韩旭,张俊,等. 川西低渗透气藏气体钻井井壁稳定性评价方法[J]. 石油钻探技术,2019,47(1):25–31. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2019004 LIU Houbin, HAN Xu, ZHANG Jun, et al. Wellbore stability evaluation during gas drilling through low permeability gas reservoirs in Western Sichuan[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2019, 47(1): 25–31. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2019004
[15] 丁乙,梁利喜,刘向君,等. 温度和化学耦合作用对泥页岩地层井壁稳定性的影响[J]. 断块油气田,2016,23(5):663–667. doi: 10.6056/dkyqt201605027 DING Yi, LIANG Lixi, LIU Xiangjun, et al. Influence of temperature and chemical on wellbore stability in clay shale formation[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2016, 23(5): 663–667. doi: 10.6056/dkyqt201605027
[16] 邓媛,何世明,邓祥华,等. 力化耦合作用下的层理性页岩气水平井井壁失稳研究[J]. 石油钻探技术,2020,48(1):26–33. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2020010 DENG Yuan, HE Shiming, DENG Xianghua, et al. Study on wellbore instability of bedded shale gas horizontal wells under chemo-mechanical coupling[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2020, 48(1): 26–33. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2020010
[17] 燕松兵,刘付臣,杨振周,等. 大庆致密油井页岩井壁稳定性实验研究[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2020,37(2):140–147. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2020.02.002 YAN Songbing, LIU Fuchen, YANG Zhenzhou, et al. Experimentalstudy on shale borehole wall stability of tight oil wells in Daqing Oilfield[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2020, 37(2): 140–147. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2020.02.002
[18] 赵凯,樊勇杰,于波,等. 硬脆性泥页岩井壁稳定研究进展[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2016,38(3):277–285. doi: 10.13639/j.odpt.2016.03.001 ZHAO Kai, FAN Yongjie, YU Bo, et al. Research progress of wellbore stability in hard brittle shale[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2016, 38(3): 277–285. doi: 10.13639/j.odpt.2016.03.001
[19] 刘厚彬,崔帅,孟英峰,等. 深层脆性页岩水平井井壁崩落失稳研究[J]. 断块油气田,2021,28(3):323–328. LIU Houbin, CUI Shuai, MENG Yingfeng, et al. Study on wellbore caving and instability of horizontal well in deep brittle shale[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2021, 28(3): 323–328.
[20] 韩正波,刘厚彬,张靖涛,等. 深层脆性页岩力学性能及井壁稳定性研究[J]. 特种油气藏,2020,27(5):167–174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2020.05.026 HAN Zhengbo, LIU Houbin, ZHANG Jingtao, et al. Research on the mechanical properties and borehole stability of deep brittle shale[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2020, 27(5): 167–174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2020.05.026
[21] SY/T 5613—2000 泥页岩理化性能试验方法[S]. SY/T 5613—2000 Methods for testing shale physics and chemistry properties[S].
[22] 金军斌. 塔里木盆地顺北区块超深井火成岩钻井液技术[J]. 石油钻探技术,2016,44(6):17–23. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.201606003 JIN Junbin. Drilling fluid technology for igneous rocks in ultra-deep wells in the Shunbei Area, Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2016, 44(6): 17–23. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.201606003
[23] 黄维安,牛晓,沈青云,等. 塔河油田深侧钻井防塌钻井液技术[J]. 石油钻探技术,2016,44(2):51–57. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.201602009 HUANG Weian, NIU Xiao, SHEN Qingyun, et al. Anti-sloughing drilling fluid technology for deep sidetracking wells in the Tahe Oilfield[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2016, 44(2): 51–57. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.201602009
[24] 刘锋报,邵海波,周志世,等. 哈拉哈塘油田硬脆性泥页岩井壁失稳机理及对策[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2015,32(1):38–41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2015.01.10 LIU Fengbao, SHAO Haibo, ZHOU Zhishi, et al. Mechanism and strategy to deal with borehole instability of hard and brittle shales in Halahatang Oilfield[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2015, 32(1): 38–41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2015.01.10
[25] 陈修平,李双贵,于洋,等. 顺北油气田碳酸盐岩破碎性地层防塌钻井液技术[J]. 石油钻探技术,2020,48(2):12–16. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2020005 CHEN Xiuping, LI Shuanggui, YU Yang, et al. Anti-collapse drilling fluid technology for broken carbonate formation in Shunbei Oil and Gas Field[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2020, 48(2): 12–16. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2020005
[26] 林常茂,张永青,刘超,等. 新型井壁稳定剂DLF-50的研制与应用[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2015,32(4):17–20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2015.04.005 LIN Changmao, ZHANG Yongqing, LIU Chao, et al. Development and application of the new shale stabilizer DLF-50[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2015, 32(4): 17–20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2015.04.005
[27] 卢震,黄贤斌,孙金声,等. 水基钻井液用耐高温纳米聚合物封堵剂的研制[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2020,42(5):587–591. doi: 10.13639/j.odpt.2020.05.011 LU Zhen, HUANG Xianbin, SUN Jinsheng, et al. Development of the nano-polymer plugging agent with high temperature tolerance for water-based drilling fluid[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2020, 42(5): 587–591. doi: 10.13639/j.odpt.2020.05.011
[28] 廖奉武,李坤豫,胡靖,等. 钻井液封堵剂高温高压封堵性能评价方法[J]. 科学技术与工程,2019,19(29):90–95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2019.29.015 LIAO Fengwu, LI Kunyu, HU Jing, et al. Evaluation method for HTHP plugging property of drilling fluid plugging agent[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2019, 19(29): 90–95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2019.29.015
[29] 林永学,甄剑武. 威远区块深层页岩气水平井水基钻井液技术[J]. 石油钻探技术,2019,47(2):21–27. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2019022 LIN Yongxue, ZHEN Jianwu. Water based drilling fluid technology for deep shale gas horizontal wells in Block Weiyuan[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2019, 47(2): 21–27. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2019022
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 穆瑞东,王琦,张莹辉. 超高密度复合盐水钻井液流变性调控及应用. 辽宁化工. 2023(02): 302-305 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 邱艺,马天寿,陈颖杰,杨赟,邓昌松. 泥质粉砂储层欠平衡水平井井壁稳定性演化规律. 中南大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(03): 967-983 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 徐声驰,刘锐,孟鑫,刘博文,孙志高,付基友,翟晓鹏,张军. 基于井眼坍塌角度和坍塌深度预测模型的泥岩水平段井壁稳定性评价方法. 石油钻采工艺. 2023(02): 136-142 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 刘送永,徐保龙,秦立学,孟庆皓,李洪盛. 煤矿巷道掘进长距离快速超前钻探工艺策略及配套机具研究. 煤炭科学技术. 2023(S2): 229-239 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 何立成,唐波. 准噶尔盆地超深井钻井技术现状与发展建议. 石油钻探技术. 2022(05): 1-8 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: