Development and Applications of a Compound Axial and Torsional Impact Drilling Tool
-
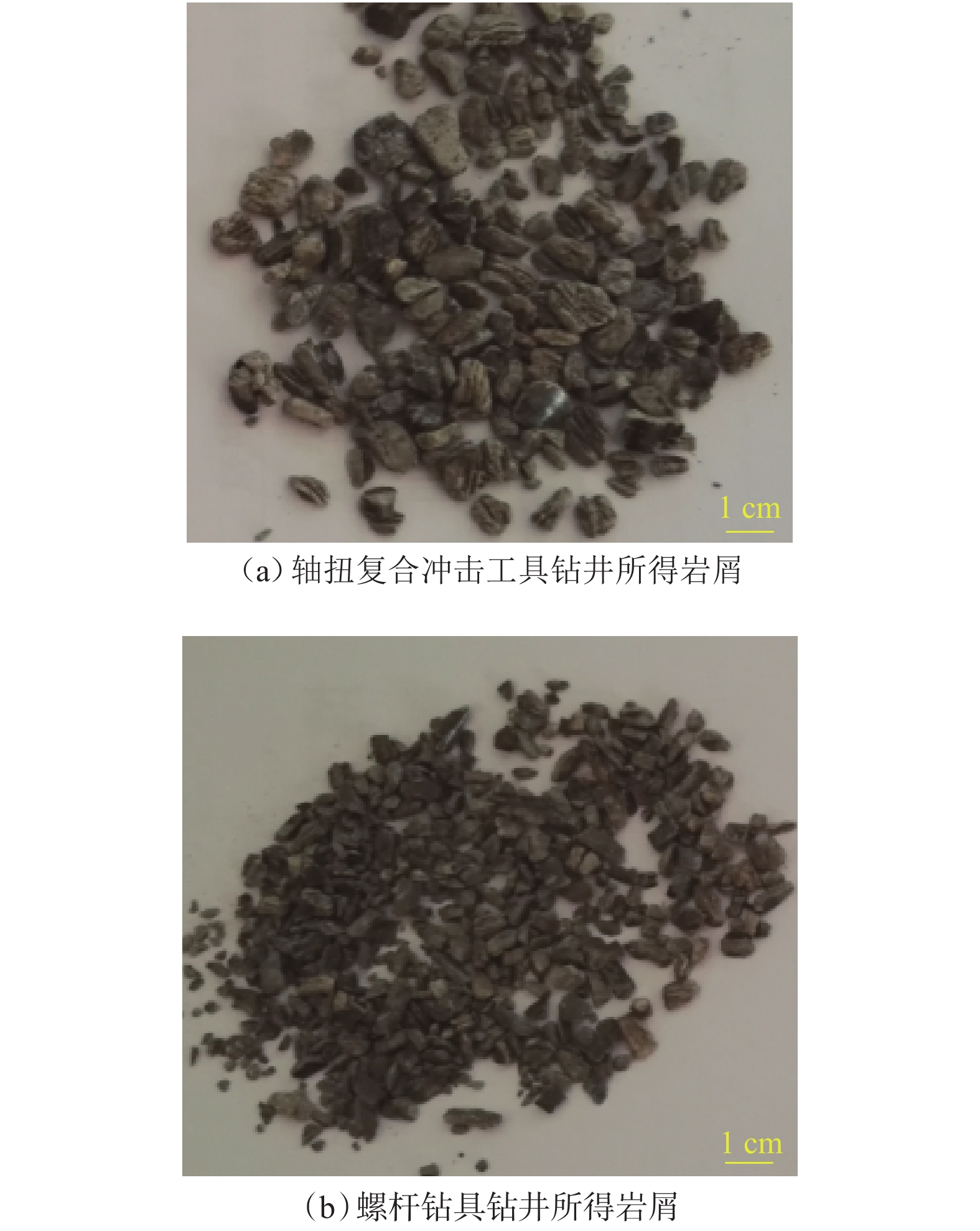
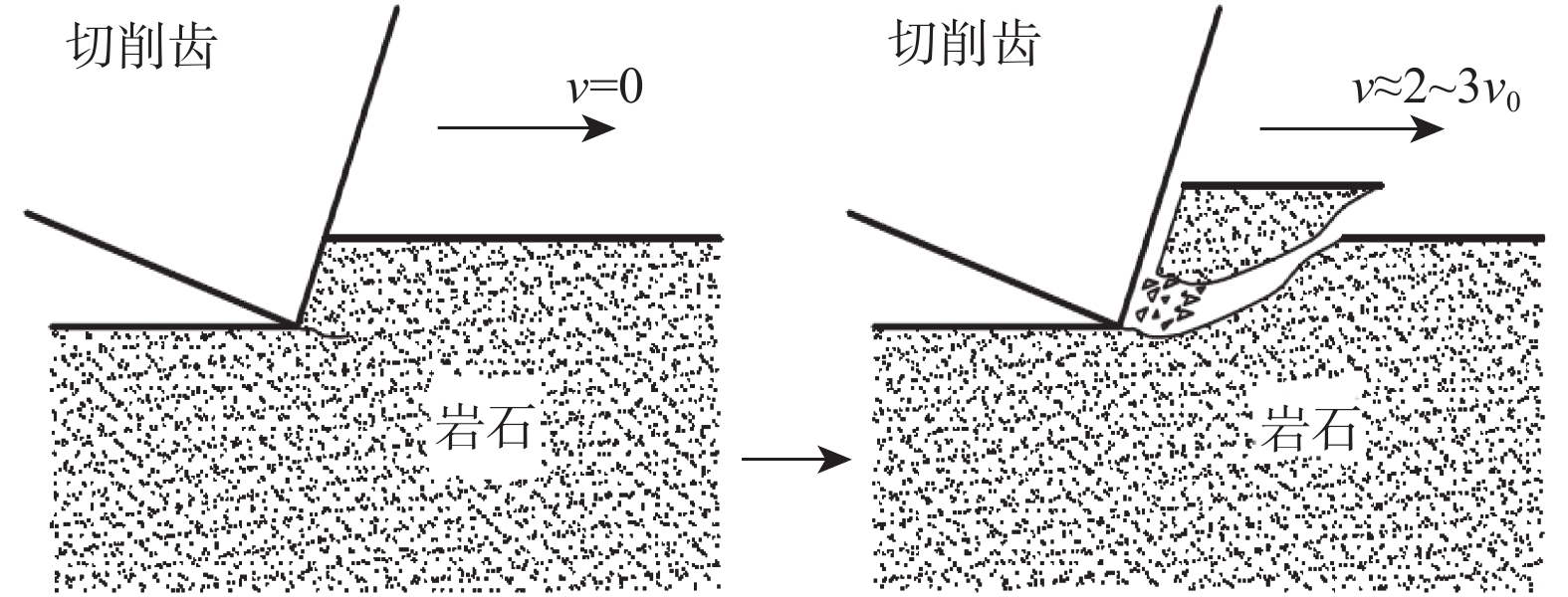
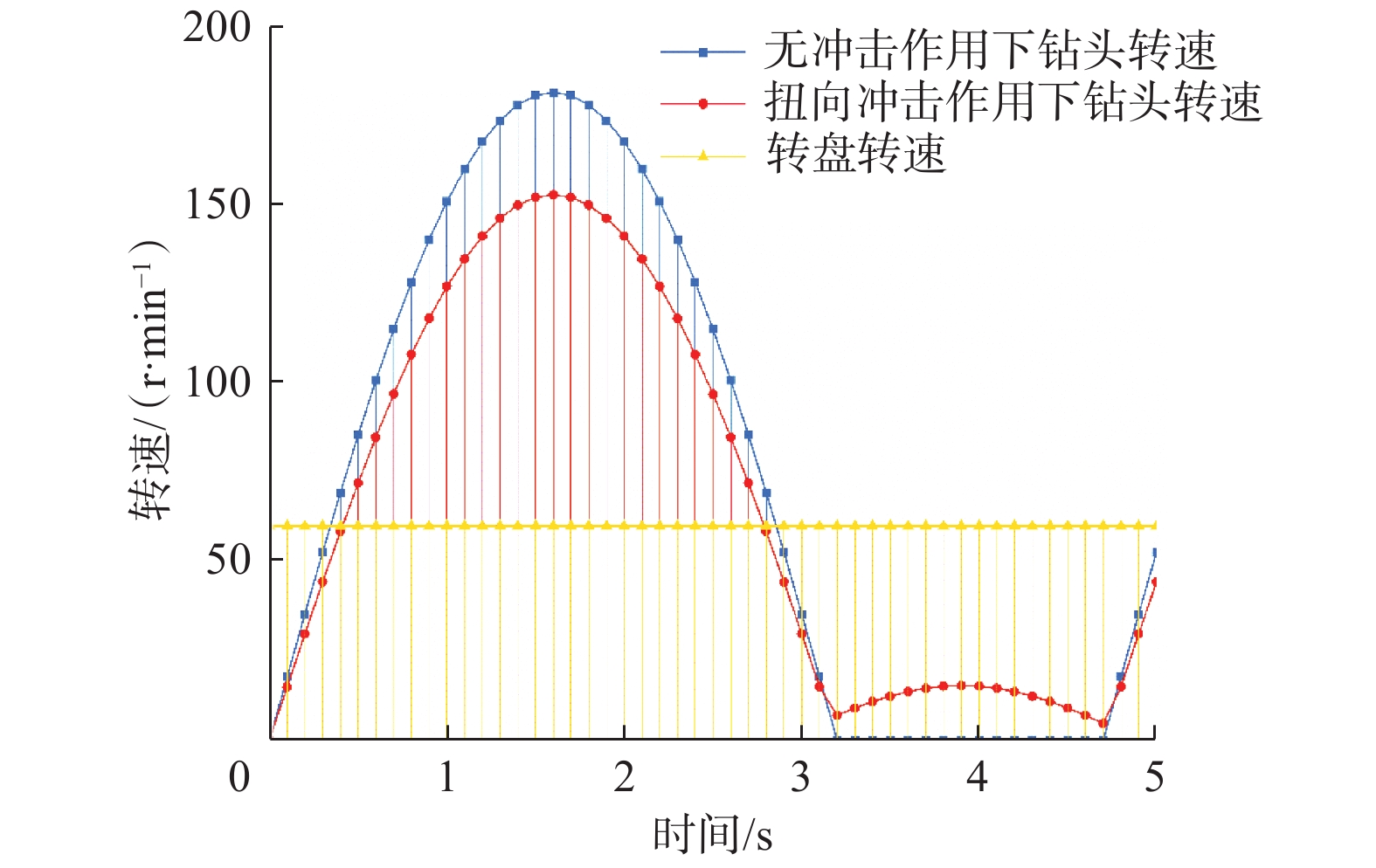
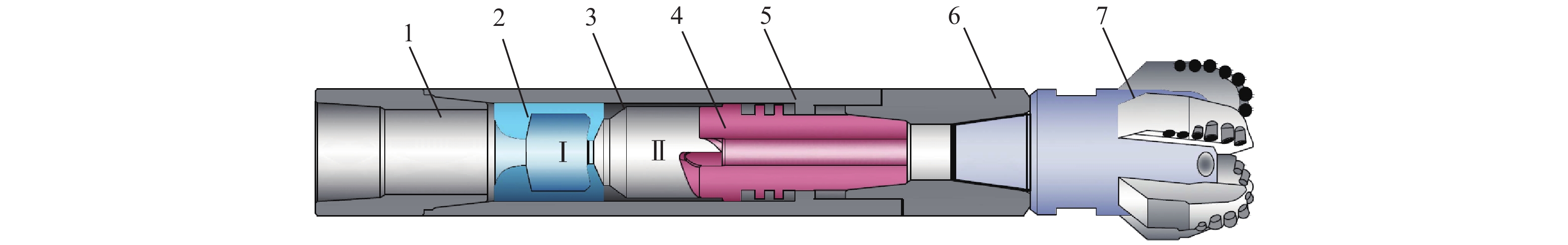
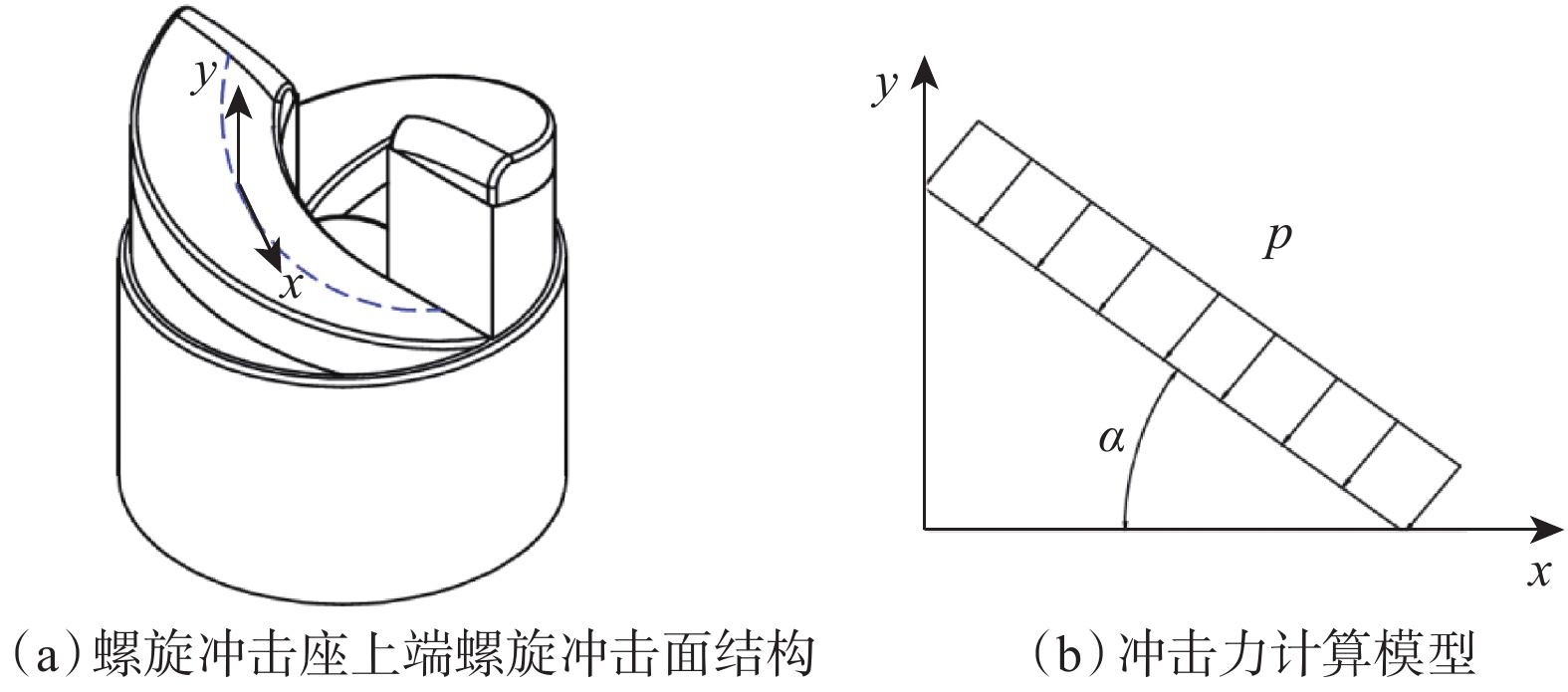
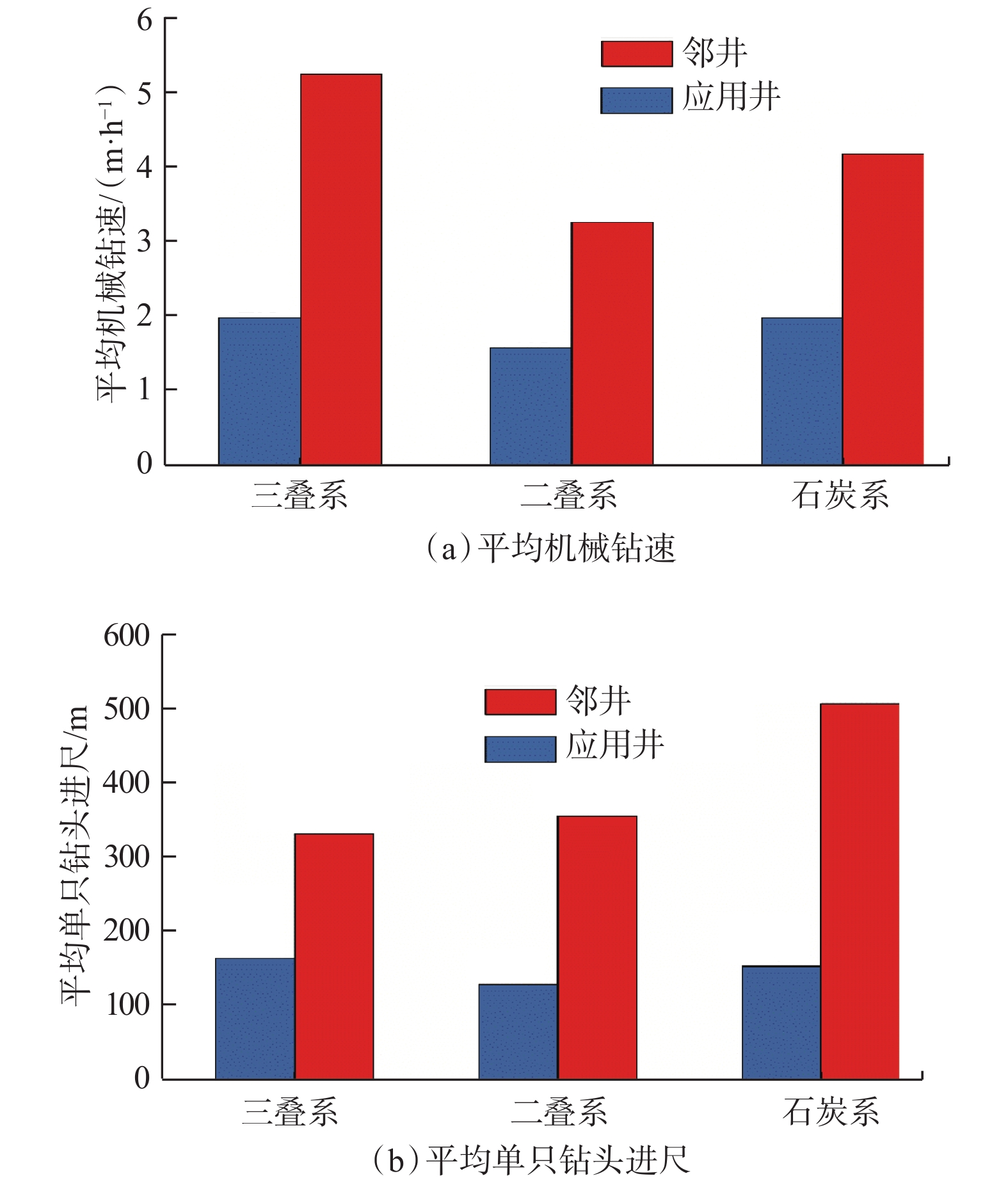
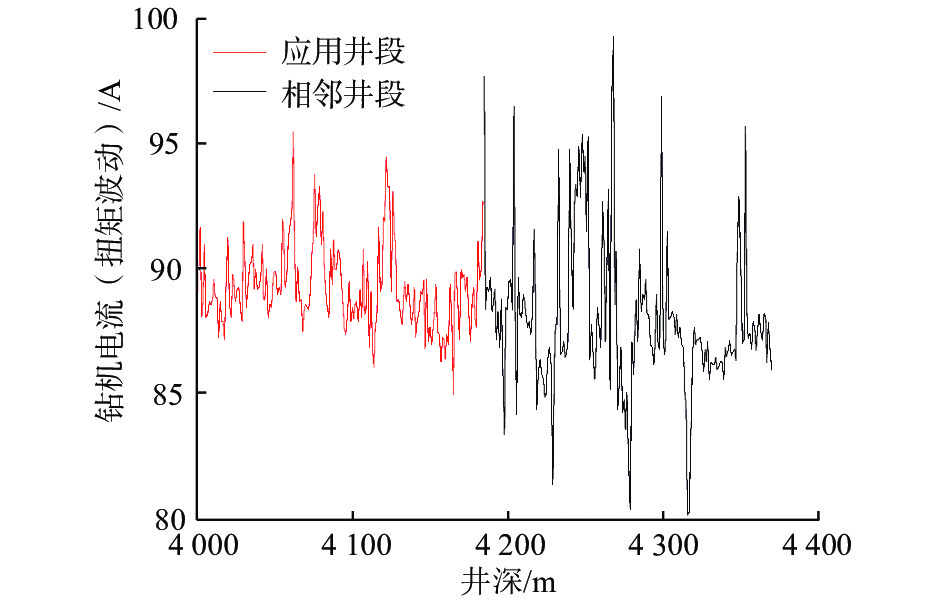
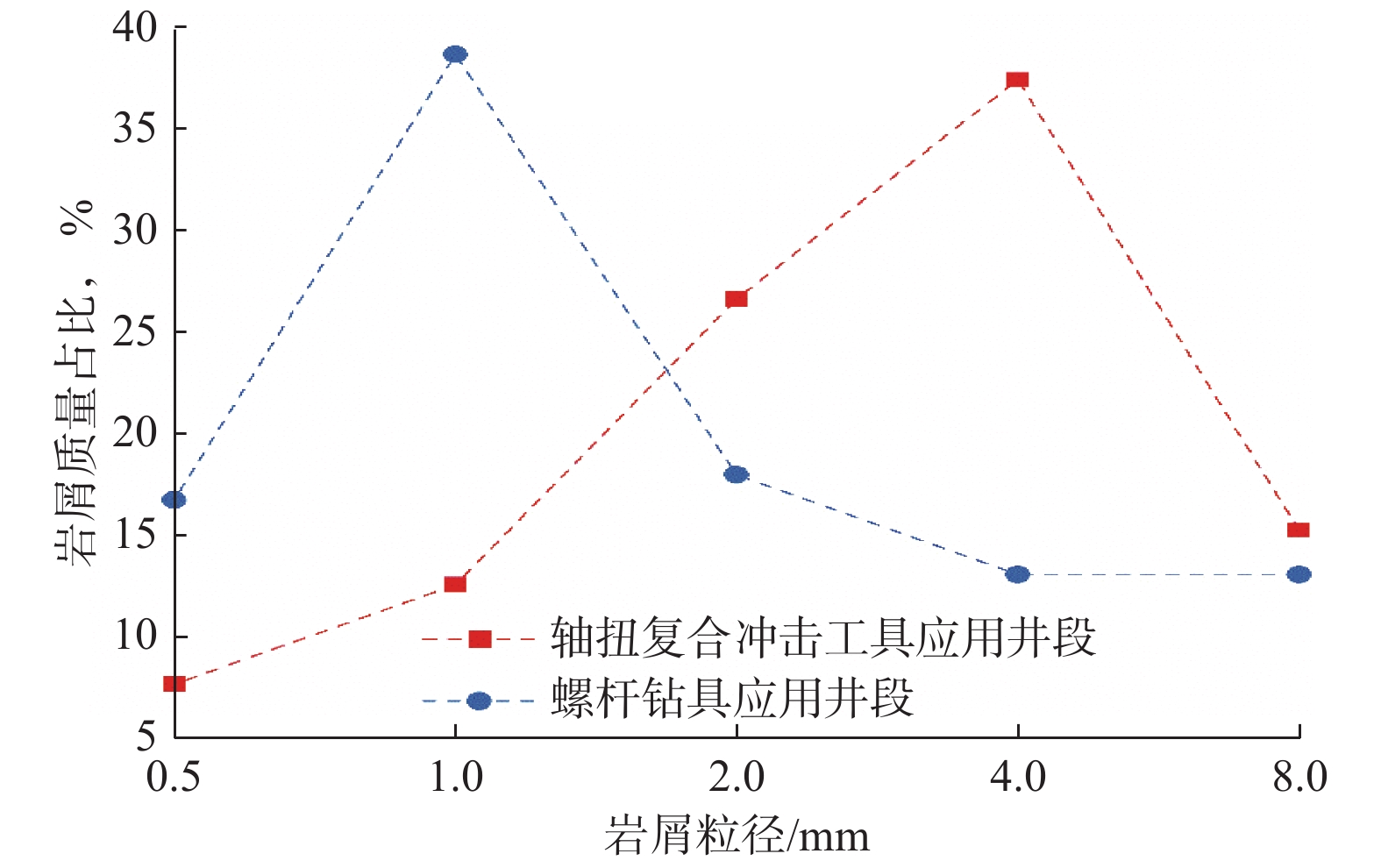
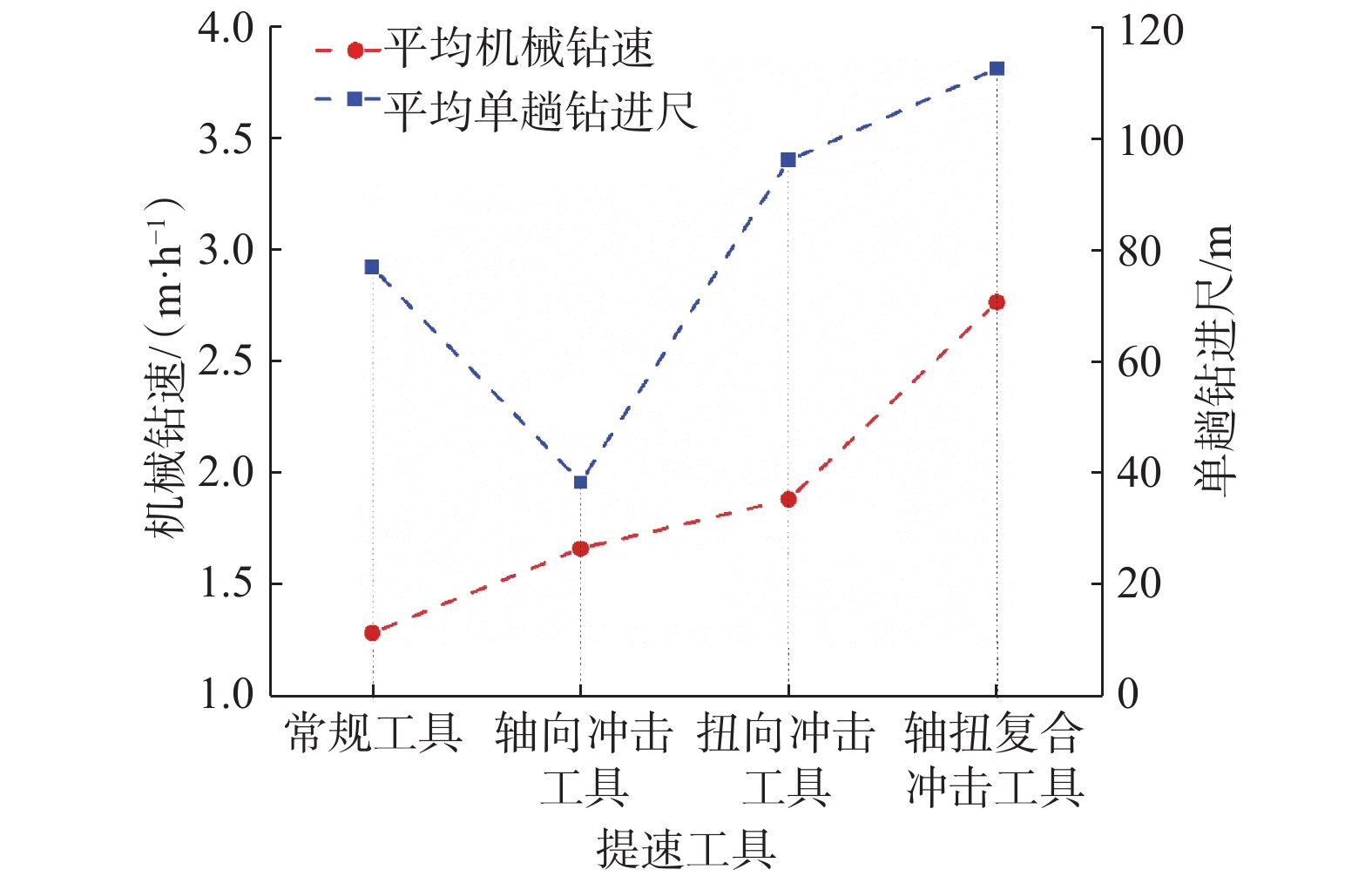
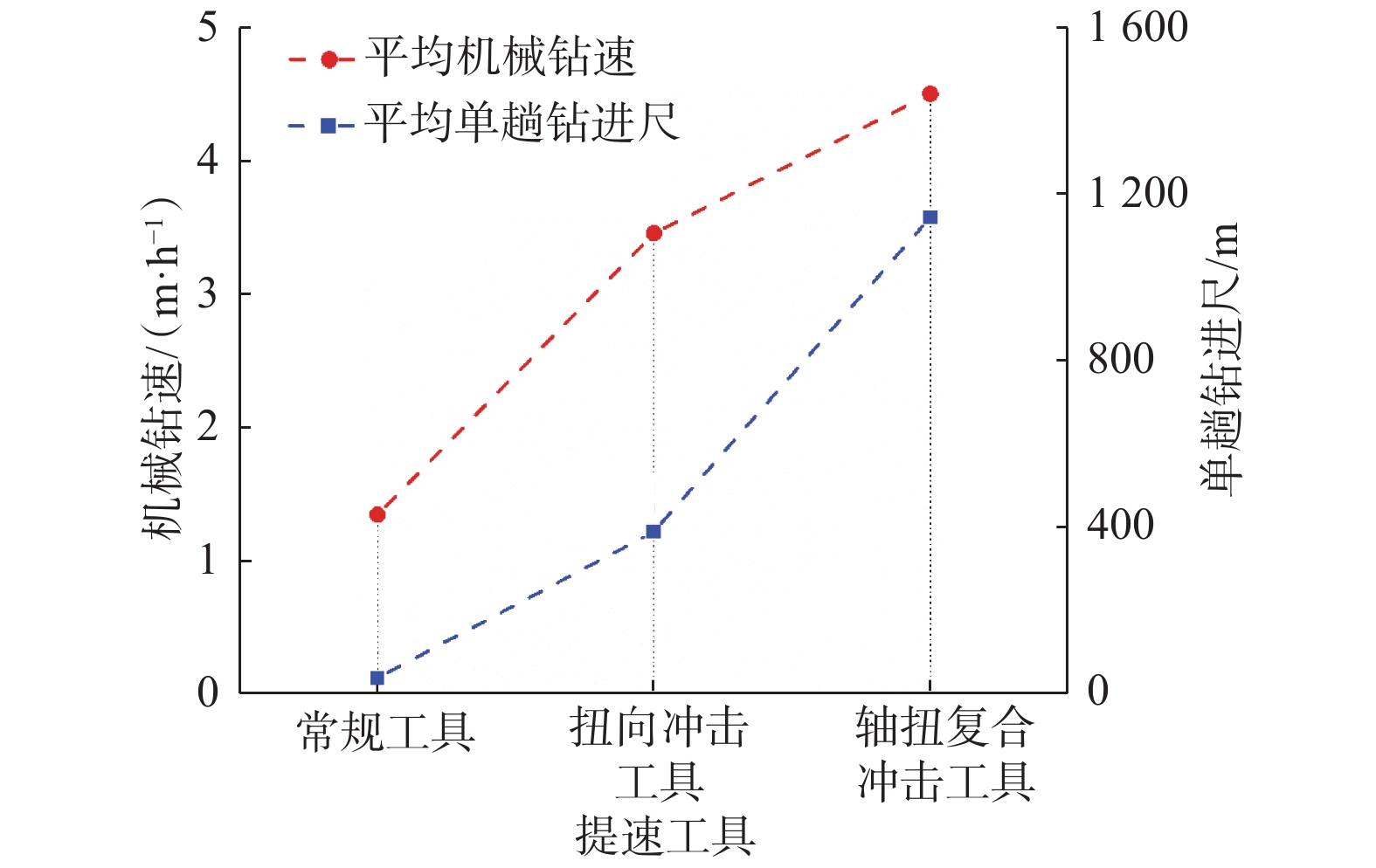
摘要: 为提高PDC钻头破岩效率并减小钻具的粘滑振动,研制了一种轴扭复合冲击工具。该工具以自激振荡脉冲射流为能量来源,通过螺旋面结构将轴向冲击力转换为轴扭复合冲击力进行破岩,具有结构简单和轴向、扭向冲击力同步作用的特点。现场应用结果表明:与常规钻具相比,轴扭复合冲击工具的机械钻速提高了95.2%~193.8%,单只钻头进尺增加了46.4%~229.2%;与螺杆钻具相比,轴扭复合冲击工具的机械钻速提高了71.0%;与轴向冲击工具相比,轴扭复合冲击工具的机械钻速提高了66.3%,单只钻头进尺增加了194.0%;与扭向冲击工具相比,轴扭复合冲击工具的机械钻速提高了30.2%~46.8%,单只钻头进尺增加了17.2%~191.8%。研究表明,轴扭复合冲击工具可以提高破岩效率,减小硬地层的粘滑振动,破岩提速效果显著,具有推广应用价值。Abstract: To improve the rock-breaking efficiency of PDC bits and reduce stick-slip vibration, a compound axial and torsional impact tool was developed. This tool, characterized by a simple structure and the synchronous action of axial and torsional impacts, is used to break rocks. To do so, it used a self-excited oscillation pulse jet as its energy source, and converted axial impact force into compound axial and torsional impacts through helical surface structure. Field applications showed that: compared with conventional drilling tools, the ROP of this compound axial and torsional impact tool was increased by 95.2%–193.8%, and the footage of a single bit was increased by 46.4%–229.2%. Compared with PDM drills, the ROP of this tool was increased by 71.0% while compared with axial impact tools, the ROP of this tool was increased by 66.3%, and the footage of a single bit was increased by 194.0%. Compared with torsional impact tools, the ROP of this tool was increased by 30.2%–46.8%, and the footage of a single bit was increased by 17.2%–191.8%. The research results showed that the developed compound axial and torsional impact tool can improve rock-breaking efficiency and reduce the stick-slip vibration in hard formations. With its remarkable rock-breaking effects and ROP improvement, this tool is worth of application and widespread implementation.
-
Keywords:
- impact tool /
- composite impact force /
- rock-breaking efficiency /
- stick-slip vibration /
- PDC bit /
- penetration rate /
- bit footage
-
-
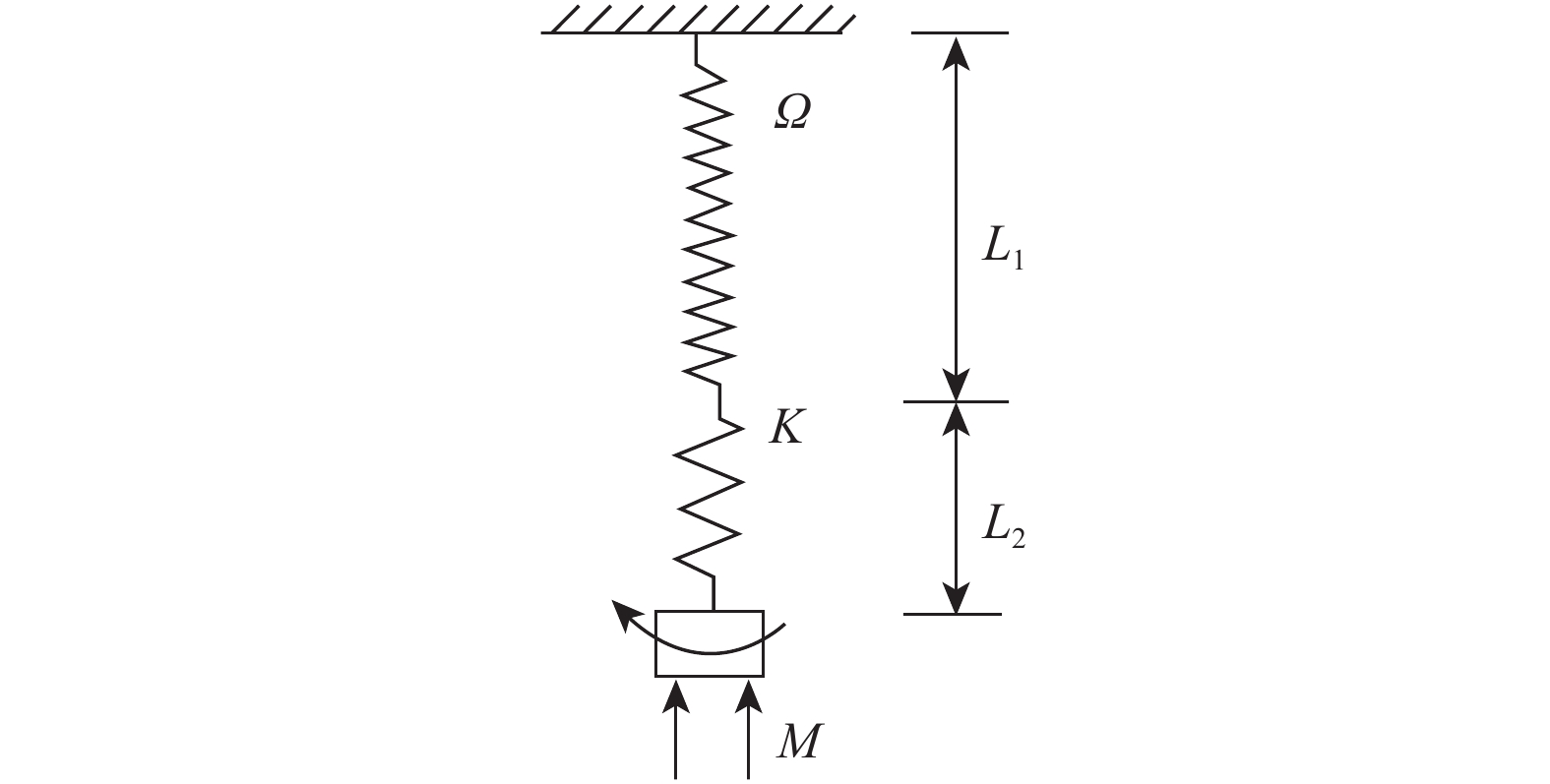
表 1 轴扭复合冲击工具的关键技术参数
Table 1 Key technical parameters of compound axial and torsionalimpact tool
外径/
mm螺旋面
半径/mm压力损
耗/MPa轴向冲击
力/kN扭向冲击扭
矩/(N·m)冲击频
率/Hz最小 最大 177.8 20.0 79.0 1.4 17 1 089 560 197.0 50.0 88.5 2.3 25 2 097 300 203.2 50.0 88.5 2.3 25 2 097 300 244.5 40.0 112.5 2.0 45 2 836 420 285.8 40.0 130.0 2.0 62 4 449 420 表 2 应用井段与邻井相近井段实钻数据对比
Table 2 Comparison of actual drilling data between intervals using compound axial and torsional impact tool and the adjacent intervals
井号 钻具 井段/m 钻压/kN 钻具转速/
(r·min–1)钻井液排量/
(L·s–1)钻井液密度/
(kg·L–1)纯钻时间/h 机械钻速/
(m·h–1)X-116H 轴扭复合冲击工具 4 897~5 241 80~120 60~70 32~34 1.24 60.0 5.73 X-8H 螺杆钻具 4 902~5 245 40~60 200~240 28~30 1.30 121.4 2.82 X-20H 螺杆钻具 4 915~5 242 40~60 200~240 28~30 1.30 105.5 3.10 X-24H 螺杆钻具 4 849~5 244 40~60 200~250 28~30 1.30 91.0 4.34 X-2H 常规钻具 4 862~5 247 40~60 80~100 28~30 1.25 144.7 2.66 X-3H 常规钻具 4 863~5 247 40~60 80~100 27~38 1.24 151.5 2.53 X4H 常规钻具 4 930~5 260 40~60 70~75 28~30 1.30 84.2 3.92 表 3 几种冲击工具的性能参数和应用井的钻井参数
Table 3 Performance parameters of several impact drilling tools and drilling parameters in their field applications
工具类型 地层 工具性能参数 钻井参数 工具压降/
MPa冲击频率/
Hz轴向冲击力/
kN扭向冲击力/
(N·m)钻压/kN 钻具转速/
(m·h–1)钻井液密度/
(kg·L–1)排量/
(L·s–1)轴向冲击
工具二叠系 2.0~3.0 17.0~23.0 20 100~140 60 1.25 36 扭向冲击
工具二叠系 1.7~2.7 12.5~25.0 1 627 100~120 60 1.25 35 石炭系及
以下2.4~4.1 14.0~30.0 1 220 80~120 70 1.27 32~37 轴扭复合
冲击工具二叠系 1.5~2.4 40.0~60.0 23 1 350 100~140 60 1.25 36 石炭系及以下 2.5~4.0 40.0~60.0 12 1 100 60~100 50~60 1.30 28 -
[1] 王德余,李根生,史怀忠,等. 高效破岩新方法进展与应用[J]. 石油机械, 2012, 40(6): 1–6. WANG Deyu, LI Gensheng, SHI Huaizhong, et al. Progress of the high-efficiency rock-breaking method[J]. China Petroleum Machi-nery, 2012, 40(6): 1–6.
[2] KHORSHIDIAN H, MOZAFFARI M, BUTT S D. The role of natural vibrations in penetration mechanism of a single PDC cutter[R]. ARMA-2012-402, 2012.
[3] DEEN C A, WEDEL R J, NAYAN A, et al. Application of a torsional impact hammer to improve drilling efficiency[R]. SPE 147193, 2011.
[4] OSTASEVICIUS V, GAIDYS R, RIMKEVICIENE J, et al. An approach based on tool mode control for surface roughness reduction in high-frequency vibration cutting[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2010, 329(23): 4866–4879. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2010.05.028
[5] LI X B, SUMMERS D A, RUPERT G, et al. Experimental investigation on the breakage of hard rock by the PDC cutters with combined action modes[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2001, 16(2): 107–114. doi: 10.1016/S0886-7798(01)00036-0
[6] WANG Peng, NI Hongjian, WANG Ruihe. A novel vibration drilling tool used for reducing friction and improve the penetration rate of petroleum drilling[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2018, 165: 436–443. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2018.02.053
[7] 祝效华,刘伟吉. 单齿高频扭转冲击切削的破岩及提速机理[J]. 石油学报, 2017, 38(5): 578–586. doi: 10.7623/syxb201705011 ZHU Xiaohua, LIU Weiji. The rock breaking and ROP rising mechanism for single-tooth high-frequency torsional impact cutting[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2017, 38(5): 578–586. doi: 10.7623/syxb201705011
[8] 柳贡慧,李玉梅,李军,等. 复合冲击破岩钻井新技术[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2016, 44(5): 10–15. LIU Gonghui, LI Yumei, LI Jun, et al. New technology with composite percussion drilling and rock breaking[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2016, 44(5): 10–15.
[9] POWELL S W, HERRINGTON D, BOTTON B, et al. Fluid hammer increases PDC performance through axial and torsional energy at the bit[R]. SPE 166433, 2013.
[10] LIU Shubin, NI Hongjian, WANG Xueying, et al. Rock-breaking mechanism study of axial and torsional impact hammer and its application in deep wells[R]. SPE 191077, 2018.
[11] 倪红坚,韩来聚,马清明,等. 水力脉冲诱发井下振动钻井工具研究[J]. 石油钻采工艺, 2006, 28(2): 15–17, 20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7393.2006.02.005 NI Hongjian, HAN Laiju, MA Qingming, et al. Study on downhole vibration drilling tool induced by hydropulse[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2006, 28(2): 15–17, 20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7393.2006.02.005
[12] 雷鹏,倪红坚,王瑞和,等. 自激振荡式旋冲工具在深井超深井中的试验应用[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2013, 41(6): 40–43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0890.2013.06.008 LEI Peng, NI Hongjian, WANG Ruihe, et al. Field test of self-excited vibration rotary percussion drilling tool in deep and ultra-deep wells[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2013, 41(6): 40–43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0890.2013.06.008
[13] RICHARD T, DAGRAIN F, POYOL E, et al. Rock strength determination from scratch tests[J]. Engineering Geology, 2012, 147: 91–100.
[14] 刘鹏飞.扭转冲击影响PDC钻头粘滑振动的机理研究[D].青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2017. LIU Pengfei. Study on the influence mechanism of PDC bit stick-slip vibration under torsional impact[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China), 2017.
[15] KYLLINGSTAD A, HALSEY G W. A study of slip/stick motion of the bit[J]. SPE Drilling Engineering, 1988, 3(4): 369–373. doi: 10.2118/16659-PA
[16] 熊继有,蒲克勇,周健. 库车坳陷山前构造超深井岩石可钻性研究[J]. 天然气工业, 2009, 29(11): 59–61. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2009.11.018 XIONG Jiyou, PU Keyong, ZHOU Jian. Rock drillability investigation for ultra-deep well drilling at thrust structure of Kuqa depression[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2009, 29(11): 59–61. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2009.11.018
[17] 滕学清,文志明,王克雄,等. 塔中岩石可钻性剖面建立和钻头选型研究[J]. 西部探矿工程, 2010, 22(11): 43–45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2010.11.014 TENG Xueqing, WEN Zhiming, WANG Kexiong, et al. Research on drillability sections of rocks and bit selection in Tazhong Area[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering, 2010, 22(11): 43–45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2010.11.014
[18] 白萍萍.准噶尔盆地中部区块钻头选型[D].青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2014. BAI Pingping. Bit selection in the center of Junggar Basin[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China), 2014.



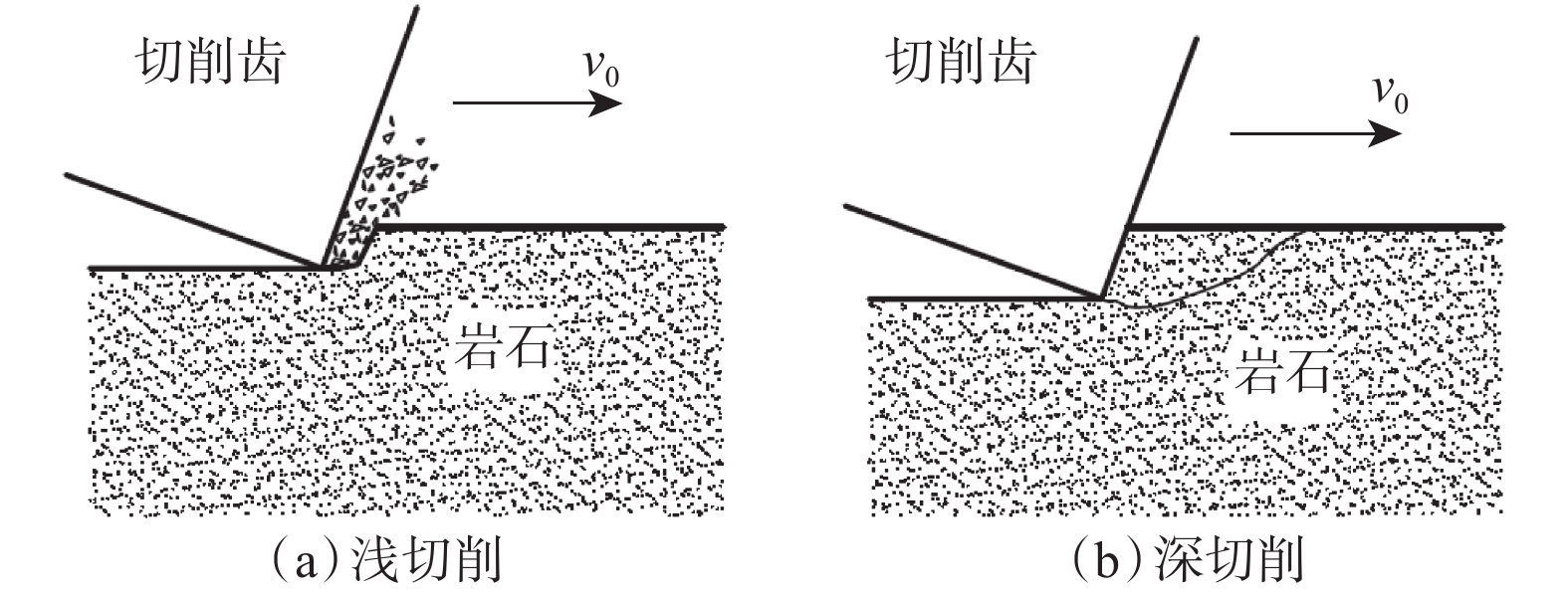
 下载:
下载: