2. 长江大学地球物理与石油资源学院, 湖北武汉 430100;
3. 中国石油塔里木油田分公司勘探开发研究院, 新疆库尔勒 841000
2. College of Geophysics and Oil Resources, Yangtze University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430100, China;
3. Research Institute of Petroleum Exploration and Development, Tarim Oilfield Company, CNPC, Korla, Xinjiang, 841000, China
阵列侧向测井仪器可以提供高分辨率的多条不同探测深度的电阻率曲线,能够提供丰富的地层电阻率信息,能满足油气储层的精细化评价[1-5]。该仪器同侧向测井仪器一样,受环境因素的影响,测量结果仍为视电阻率,需要根据影响因素进行定量校正,以获得储层的真电阻率值。围岩影响即为环境影响的一种,实现围岩影响下视电阻率的快速、准确校正,对油气储层的定性判识和油气饱和度的定量计算具有重要意义[6-7]。在水平井中,测井仪器在储层中的位置会不断进行调整,即会有不同的井眼偏心距[8],仪器在储层中的响应受上下围岩的影响,故有必要建立水平井中不同井眼偏心距下的围岩/层厚校正图版。
前人已在测井围岩/层厚校正方面做了一些研究。邓少贵等人[9]对双侧向测井仪器在水平井中的响应特性进行了分析,并形成了围岩、层厚影响校正方法;谭茂金等人[10]研究了定向井中围岩、层厚对双侧向测井响应的影响,并制作了校正图版;吴宝玉等人[11]通过数值模拟制作了随钻电磁波测井仪器的围岩、层厚校正图版,并提出了快速校正公式;付恩玲等人[12]利用几何因子理论研究了不同井斜角、不同围岩电阻率情况下双感应曲线连续围岩校正方法;于新娟等人[13]研究了围岩对井间电磁测井的影响。
但截至目前,关于围岩对阵列侧向测井响应的影响方面的研究较少, 更未见讨论井眼偏心距对阵列侧向测井响应影响方面的文献。为此,笔者利用三维有限元方法,分析了水平井中不同井眼偏心距下阵列侧向测井仪器响应受围岩影响的特征,制作了正演模拟校正图版,并通过非线性分析方法得到了快速校正图版。
1 地层模型阵列侧向测井仪器共可获得5种探测深度下的电阻率(随探测深度由浅至深,依次为R1,R2,R3,R4和R5),其电极系结构及具体工作模式见文献[14-15]。建立水平井模型(三维模型)研究围岩对仪器响应特性的影响,建立的阵列侧向测井水平井模型如图 1所示(图 1中:H为地层厚度,m;H1为井眼中心距较近一侧地层界面的距离,m;r为井径,m;Rt为目的层电阻率,Ω·m;Rs为围岩电阻率,Ω·m;Rm为钻井液电阻率,Ω·m)。
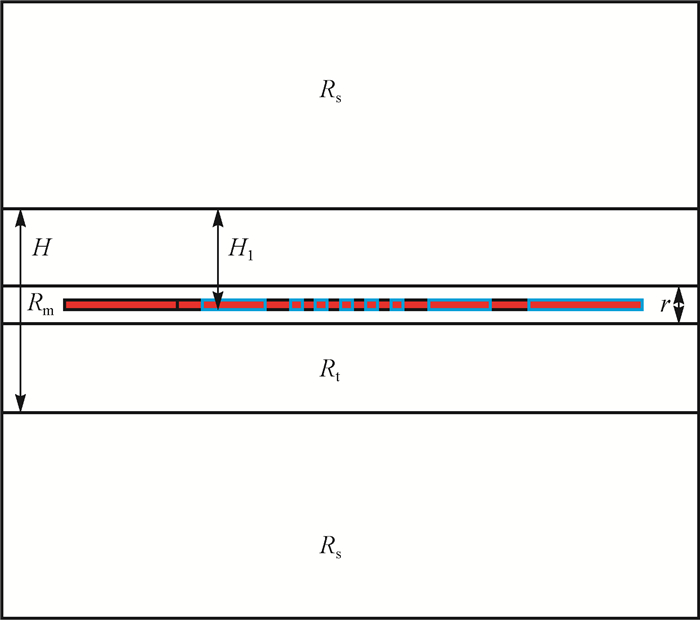
|
| 图 1 阵列侧向测井直井模型 Fig.1 Straight well model of array laterolog |
用井眼偏心程度系数表征井眼偏心程度的大小,该系数的表达式为:
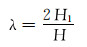
|
(1) |
式中:λ为井眼偏心程度系数。
2 阵列侧向测井有限元正演理论侧向测井仪器工作时的电流场可近似当作稳流场来处理[16]。求取阵列侧向测井正演响应的关键是构建出一条光滑的电位函数曲线[17],该电位函数应满足:
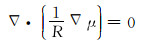
|
(2) |
式中:μ为电位,V;R为建立的地层模型中不同区域的电阻率值,Ω·m。
根据建立的地层模型给式(2)添加相应的边界条件形成定解问题。为了方便求解,往往将该定解问题转化为求泛函数ϕ的极值问题[18]:
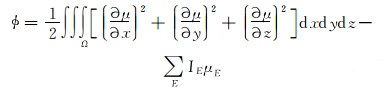
|
(3) |
式中:IE为电极发出的电流,A;μE为电极上的电位,V;Ω为积分区间,积分区间包括除去仪器的整个地层模型;E为仪器电极个数。
实际模拟过程中,阵列侧向测井5种探测模式的总电场可以由7个分场叠加形成[19], 对每个分场分配不同的加权系数,然后进行叠加合成总电场。
3 正演模拟结果 3.1 井眼偏心程度对阵列侧向测井响应特性的影响设模拟条件为:地层参数Rt=20.0 Ω·m,Rm= 1.0 Ω·m,r=0.1 m,H=1.0 m;测井仪器在井眼中居中测量,地层无钻井液侵入,上下围岩的范围为足够大。模拟井眼偏心程度系数λ变化时阵列侧向测井响应的变化特征,得到阵列侧向响应随井眼偏心程度变化的关系图版,围岩为低阻围岩(Rs=5.0 Ω·m)、高阻围岩(Rs=80.0 Ω·m)时测井仪器响应随井眼偏心程度系数λ变化的关系图版分别见图 2、图 3。
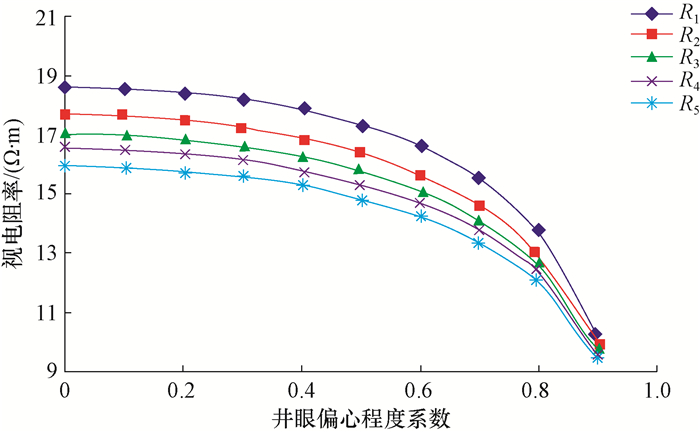
|
| 图 2 低阻围岩下井眼偏心程度对阵列侧向测井响应特性的影响 Fig.2 Influence of borehole eccentricity on array lateral logging response under low resistivity surrounding rocks |
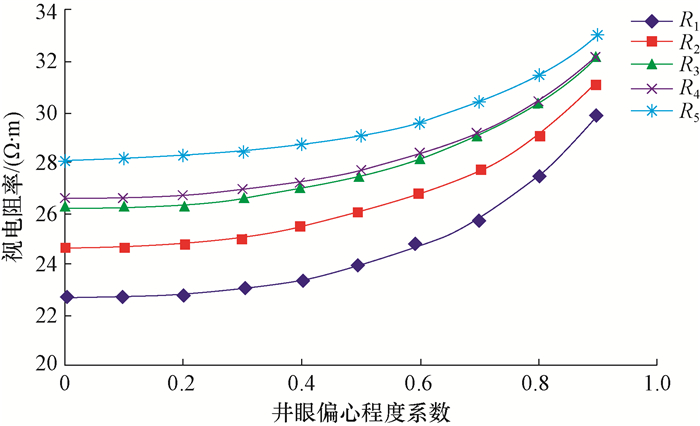
|
| 图 3 高阻围岩下井眼偏心程度对阵列侧向测井响应特性的影响 Fig.3 Influence of borehole eccentricity on array lateral logging response under high resistivity surrounding rocks |
由图 2、图 3可知:1)井眼偏心程度越大,仪器响应受到的影响越大;2)低阻围岩时,探测深度最浅的模式对应的视电阻率值最大;高阻围岩时,探测深度最浅的模式对应的视电阻率值最小,这说明探测深度越浅, 视电阻率受围岩的影响越小;3)当λ<20%时,随着λ的增大,各探测模式下的视电阻率基本不发生变化;λ>40%时,视电阻率值随着λ的改变变化剧烈;λ=90%时,低阻围岩条件下视电阻率下降幅度可达44.8%,高阻围岩条件下视电阻率上升幅度可达31.8%;这说明井眼偏心程度越大,视电阻率越向围岩电阻率靠近,即受围岩的影响越大。
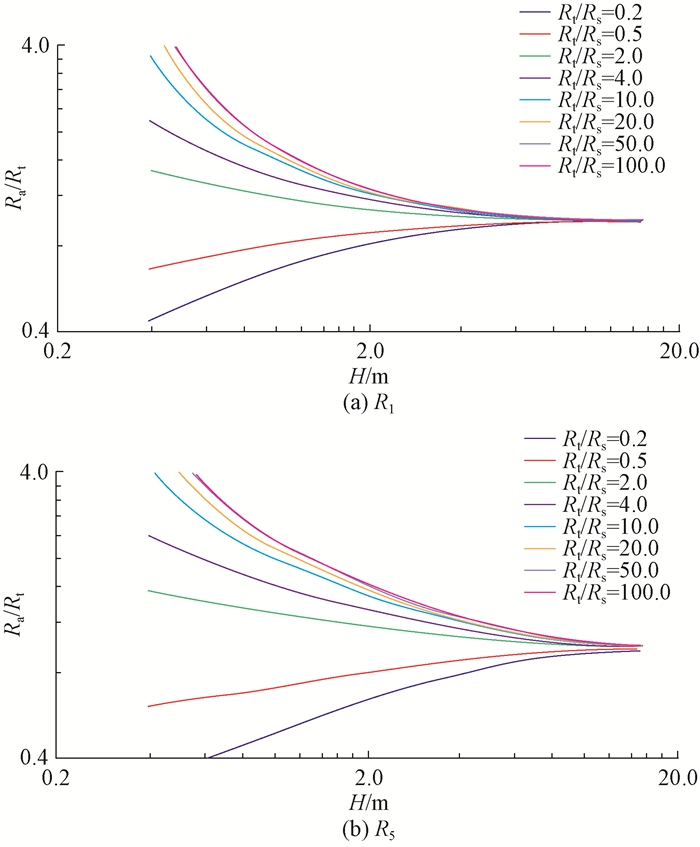
3.2 围岩对阵列侧向测井响应特性的影响设模拟条件为:地层参数Rt=20.0 Ω·m,Rm= 1.0 Ω·m,r=0.1 m;测井仪器中心处在目的层中部,在井眼中居中测量,地层无钻井液侵入,围岩的范围为足够大。模拟井眼偏心程度系数λ分别为0,25%和50%时阵列侧向测井响应随围岩、地层厚度条件改变的变化特征,得到了阵列侧向响应围岩校正图版,分别见图 4、图 5和图 6(选取R1和R5进行说明[15]; Ra为视电阻率,Ω·m)。
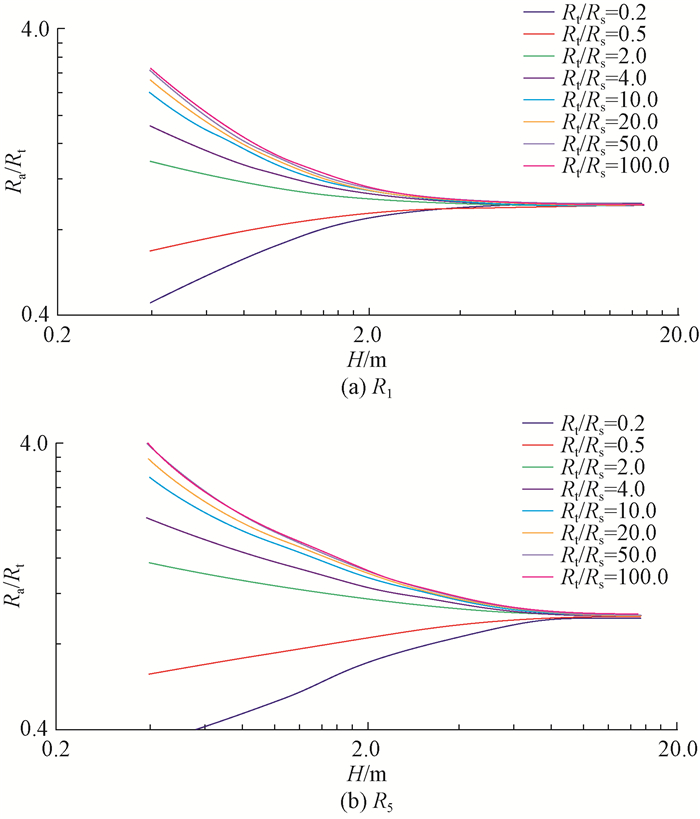
|
| 图 4 λ=0时阵列侧向测井围岩校正图版 Fig.4 Correction chart of array lateral logging surrounding rock at λ=0 |
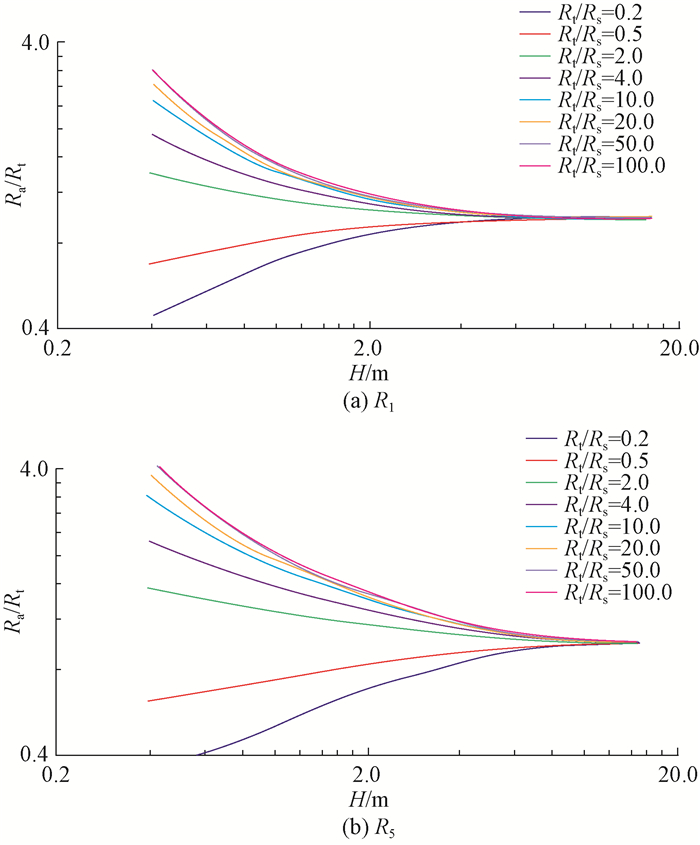
|
| 图 5 λ=25%时阵列侧向测井围岩校正图版 Fig.5 Correction chart of array lateral logging surrounding rock at λ=25% |
|
| 图 6 λ=50%时阵列侧向测井围岩校正图版 Fig.6 Correction chart of array lateral logging surrounding rock at λ=50% |
由图 4—图 6可知:在井眼偏心程度系数λ为0条件下,地层厚度H<8.0 m时,阵列侧向测井响应随层厚变化剧烈,不同围岩电阻率对应的视电阻率曲线分离明显,测井仪器响应受围岩影响明显;当H>8.0 m后,测井仪器响应基本不再受围岩的影响;随着井眼偏心程度系数的增大,测井仪器响应不再受围岩影响时,所对应的最小层厚也相应变大;井眼偏心程度在储层厚度较小时对测井仪器响应影响明显,井眼偏心程度越大,仪器响应受围岩的影响越大。不同井眼偏心程度下测井仪器响应受围岩的影响程度不同,故不同井眼偏心程度下测井仪器响应对应的围岩校正图版也不同。当Rt/Rs>50后,围岩电阻率继续减小对测井仪器响应的影响可忽略不计,可共用一套校正公式。
4 围岩影响快速校正方法水平井地层模型不满足轴对称特征,且由于阵列侧向测井仪器结构复杂,目前尚无求取其响应解析解的有效方法,大多采用数值解。三维有限元数值解法计算量大、效率低,用其进行电阻率测井的严格反演校正非常困难,会对现场围岩实时校正工作造成严重影响。通过对不同井眼偏心程度系数下阵列侧向测井围岩校正图版进行非线性分析[20],得到了围岩快速校正图版。
对阵列侧向测井围岩校正图版进行数据分析,得到了相应的围岩校正公式。以水平井中λ=0时的仪器响应为例,发现水平井中R1,R2,R3,R4和R5的视电阻率可描述为:
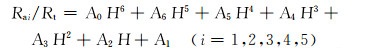
|
(4) |
式中:A0,A1,A2,A3,A4,A5和A6为校正系数;Rai/Rt为Ri的视电阻率的校正系数。
不同围岩背景对应不同的校正系数,水平井中R1和R5的围岩校正系数分别见表 1、表 2。
| Rt/Rs | A0 | A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | A5 | A6 |
| 0.2 | 0.000 028 8 | 2.936 678 8 | -2.305 726 7 | 1.047 361 0 | -0.227 250 1 | 0.025 142 3 | -0.001 364 9 |
| 0.5 | 0.000 008 7 | 1.700 004 3 | -0.767 319 2 | 0.335 089 2 | -0.071 010 6 | 0.007 739 7 | -0.000 416 0 |
| 2.0 | -0.000 004 3 | 0.571 919 3 | 0.444 481 6 | -0.181 897 0 | 0.036 995 1 | -0.003 922 6 | 0.000 206 8 |
| 4.0 | -0.000 006 3 | 0.316 146 4 | 0.680 233 7 | -0.273 396 3 | 0.055 011 1 | -0.005 794 1 | 0.000 304 1 |
| 10.0 | -0.000 007 3 | 0.148 397 3 | 0.824 439 3 | -0.326 837 8 | 0.065 224 1 | -0.006 834 3 | 0.000 357 5 |
| 20.0 | -0.000 007 7 | 0.089 640 4 | 0.872 864 3 | -0.344 272 2 | 0.068 493 4 | -0.007 163 1 | 0.000 374 2 |
| 50.0 100.0 |
-0.000 007 9 | 0.041 465 7 | 0.911 752 0 | -0.358 071 8 | 0.071 056 5 | -0.007 419 3 | 0.000 387 2 |
| Rt/Rs | A0 | A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | A5 | A6 |
| 0.2 | 0.000 020 3 | 3.588 279 1 | 2.296 019 0 | 0.894 271 6 | 0.178 323 2 | 0.018 763 0 | 0.000 986 5 |
| 0.5 | 0.000 004 9 | 1.802 867 1 | 0.619 960 1 | 0.226 744 8 | 0.043 926 7 | 0.004 560 3 | 0.000 238 2 |
| 2.0 | -0.000 002 3 | 0.555 096 6 | 0.316 558 2 | 0.109 601 3 | 0.020 846 0 | 0.002 151 9 | 0.000 112 2 |
| 4.0 | -0.000 003 5 | 0.303 642 4 | 0.476 927 5 | -0.164 469 4 | 0.031 439 9 | -0.003 266 4 | 0.000 171 3 |
| 10.0 | -0.000 004 3 | 0.143 944 4 | 0.573 305 7 | -0.197 283 0 | 0.037 856 1 | -0.003 266 4 | 0.000 207 9 |
| 20.0 | -0.000 004 6 | 0.089 142 2 | 0.605 277 1 | -0.208 146 1 | 0.039 998 3 | -0.004 180 2 | 0.000 220 3 |
| 50.0 100.0 |
-0.000 004 8 | 0.044 754 3 | 0.630 688 4 | -0.216 761 7 | 0.041 703 6 | -0.004 364 1 | 0.000 230 2 |
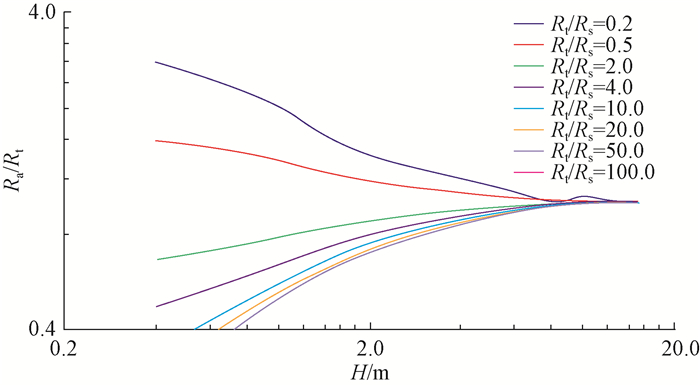
利用式(4)制作了λ=0时水平井中R5的层厚/围岩快速校正图版,如图 7所示。
|
| 图 7 λ=0时水平井中R5的层厚/围岩快速校正图版 Fig.7 Fast thickness correction chart of R5 thickness/surrounding rock of horizontal wells at λ=0 |
将图 7与图 4(b)相对比,发现两图版一致性较好,说明快速计算方法正确有效,当地层厚度H>8.0 m后,快速校正图版与数值模拟校正图版开始出现一定差距,不过以数值模拟图版为约定真值点相对误差小于5.3%,但根据数值模拟得到的结果,当H>8.0 m后,测井仪器响应基本不受围岩影响,无需进行校正。
5 结论1) 井眼偏心程度系数大于40%时,阵列侧向测井响应特性受井眼偏心距的影响较大。低阻围岩条件下,井眼偏心造成的视电阻率下降幅度最大可达44.8%;高阻围岩条件下,井眼偏心造成的视电阻率上升幅度最大可达31.8%。
2) 基于三维有限元模拟技术,绘制了阵列侧向测井响应围岩校正图版。分析发现,当地层厚度小于8.0 m时,阵列侧向测井响应受围岩影响较大;当地层厚度大于8.0 m时,阵列侧向测井响应不受围岩的影响。
3) 基于正演模拟图版进行非线性分析,得出不同井眼偏心距下的阵列侧向测井围岩快速校正公式与图版,该图版与数值模拟图版的一致性较好,最大相对误差小于5.3%,满足现场对围岩影响实时校正的需要。
| [1] |
刘振华, 胡启. 阵列侧向测井响应的计算及其特征[J]. 西安石油学院学报(自然科学版), 2002, 17(1): 53-57. LIU Zhenhua, HU Qi. Calculation and characteristics of array laterolog responses[J]. Journal of Xi'an Petroleum Institute(Natural Science Edition), 2002, 17(1): 53-57. |
| [2] |
仵杰, 谢尉尉, 解茜草, 等. 阵列侧向测井仪器的正演响应分析[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 23(1): 73-76, 80. WU Jie, XIE Weiwei, XIE Xicao, et al. Forward response analysis of array lateral logging tool[J]. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University(Natural Science Edition), 2008, 23(1): 73-76, 80. |
| [3] |
潘克家, 王文娟, 汤井田, 等. 高分辨率阵列侧向测井的数学模型及有限元快速正演[J]. 地球物理学报, 2013, 56(9): 3197-3211. PAN Kejia, WANG Wenjuan, TANG Jingtian, et al. Mathematical model and fast finite element modeling of high resolution array lateral logging[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2013, 56(9): 3197-3211. DOI:10.6038/cjg20130932 |
| [4] |
范宜仁, 蒋建亮, 邓少贵, 等. 高分辨率阵列侧向测井响应数值模拟[J]. 测井技术, 2009, 33(4): 333-336. FAN Yiren, JIANG Jianliang, DENG Shaogui, et al. Numerical simulation of high resolution array lateral logging responses[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2009, 33(4): 333-336. |
| [5] |
冯琳伟, 汪德刚, 贺飞, 等. 薄互层和倾斜地层阵列侧向测井响应计算分析[J]. 测井技术, 2013, 37(1): 80-84. FENG Linwei, WANG Degang, HE Fei, et al. On response characteristics analysis of HAL tool in thin inter-beds and deviated hole formation[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2013, 37(1): 80-84. |
| [6] |
秦绪英. 电阻率测井泥浆侵入影响校正方法研究:以鄂尔多斯盆地天然气储层为例[J]. 石油物探, 2006, 45(5): 537-541. QIN Xuying. Slurry invasion correction in resistivity logging:case study of natural gas reservoir in Ordos Basin[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2006, 45(5): 537-541. |
| [7] |
邓少贵, 李智强, 范宜仁, 等. 斜井泥浆侵入仿真及其阵列侧向测井响应数值模拟[J]. 地球物理学报, 2010, 53(4): 994-1000. DENG Shaogui, LI Zhiqiang, FAN Yiren, et al. Numerical simulation of mud invasion and its array laterolog response in deviated wells[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2010, 53(4): 994-1000. |
| [8] |
徐建华, 翟丽华, 朱德怀, 等. 水平井中双侧向测井的偏心井眼校正[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 1994, 29(4): 520-525. XU Jianhua, ZHAI Lihua, ZHU Dehuai, et al. Eccentric borehole correction for dual laterolog in horizontal wells[J]. Petroleum Geophysical Exploration, 1994, 29(4): 520-525. |
| [9] |
邓少贵, 李竹强, 李智强. 水平井双侧向测井响应及层厚/围岩影响快速校正[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2009, 36(6): 725-729. DENG Shaogui, LI Zhuqiang, LI Zhiqiang. Response of dual laterolog and fast correction for layer thickness and shoulder bed in horizontal wells[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2009, 36(6): 725-729. |
| [10] |
谭茂金, 高杰, 邹友龙, 等. 盐水泥浆条件下定向井双侧向测井环境校正方法研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2012, 55(4): 1422-1432. TAN Maojin, GAO Jie, ZOU Youlong, et al. Study on correction method of dual laterolog environment for directional wells under saltwater mud[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2012, 55(4): 1422-1432. |
| [11] |
吴宝玉, 夏宏泉, 张智勇. 随钻电阻率测井的围岩影响及校正方法研究[J]. 西南石油学院学报, 2006, 28(6): 20-23. WU Baoyu, XIA Hongquan, ZHANG Zhiyong. Effect of shoulder beds on resistivity logging while drilling and its correction method[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum Institute, 2006, 28(6): 20-23. |
| [12] |
付恩玲, 杨林, 张淑芝, 等. 斜井中双感应测井曲线围岩校正方法[J]. 测井技术, 2004, 28(2): 124-127, 179. FU Enling, YANG Lin, ZHANG Shuzhi, et al. Correction method of double induction log curves in inclined shafts[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2004, 28(2): 124-127, 179. |
| [13] |
于新娟, 刘迪仁, 蔡明, 等. 围岩对井间电磁测井的影响[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2011, 46(4): 654-656. YU Xinjuan, LIU Diren, CAI Ming, et al. Influence of surrounding rock of crosshole electromagnetic logging[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2011, 46(4): 654-656. |
| [14] |
舒心, 柯式镇, 许巍, 等. 高分辨率阵列侧向测井井眼影响自动校正研究[J]. 断块油气田, 2016, 23(4): 470-475. SHU Xin, KE Shizhen, XU Wei, et al. Auto-correction of borehole effect for high-resolution array laterolog[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2016, 23(4): 470-475. |
| [15] |
倪小威, 徐观佑, 敖旋峰, 等. 阵列侧向测井曲线极化角影响因素研究[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2018, 46(2): 120-126. NI Xiaowei, XU Guanyou, AO Xuanfeng, et al. The influencing factors on the polarizing angle of array laterolog curves[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2018, 46(2): 120-126. |
| [16] |
刘迪仁, 万文春, 夏培, 等. 不同井眼条件下的水平井双侧向测井响应[J]. 物探与化探, 2012, 36(3): 422-425. LIU Diren, WAN Wenchun, XIA Pei, et al. The response of dual laterolog to different borehole conditions in the horizontal well[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 36(3): 422-425. DOI:10.11720/wtyht.2012.3.19 |
| [17] |
张庚骥. 电法测井:上册[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1984: 72-77. ZHANG Gengji. Electrical logging:Ⅰ[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1984: 72-77. |
| [18] |
夏培, 刘迪仁, 万文春, 等. 水平井各向异性地层双侧向测井响应数值模拟[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2011, 33(8): 104-106. XIA Pei, LIU Diren, WAN Wenchun, et al. Numerical simulation of dual laterolog response in anisotropic formation of horizontal wells[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2011, 33(8): 104-106. |
| [19] |
倪小威, 徐观佑, 冯加明, 等. 斜井中各向异性储层阵列侧向测井正演响应特性[J]. 断块油气田, 2017, 24(5): 637-641. NI Xiaowei, XU Guanyou, FENG Jiaming, et al. Forward response of array lateral logging in anisotropic reservoir of inclined shaft[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2017, 24(5): 637-641. |
| [20] |
陈光, 任志良, 孙海柱. 最小二乘曲线拟合及Matlab实现[J]. 兵工自动化, 2005, 24(3): 107-108. CHEN Guang, REN Zhiliang, SUN Haizhu. Curve fitting in least-square method and its realization with Matlab[J]. Ordnance Industry Automation, 2005, 24(3): 107-108. |





