多层合采油藏在注水开发过程中, 随着含水率升高, 层间驱替程度差异加大, 层间干扰现象严重, 表现为无效水循环加剧、驱替效率降低、剩余油分布不均等[1-6]。分层注水技术能够有效改善层间驱替不均的状况, 而分层注水的关键是注水井各层配注量的优化调整。
目前常用的分层配注方法主要有静态法和动态法2类。静态法主要有厚度法和地层系数法[7-8], 但这些方法没有考虑不同开发阶段油水关系的动态变化。动态法有剩余油法、剩余油饱和度法、渗流阻力系数法以及综合劈分系数法等[9-15], 这些方法有的考虑参数太多, 部分参数难以获取或难以量化, 有的只适用于中低含水阶段或高含水前期, 对高含水后期适应性差。因此, 针对处于高含水后期的多层合采油藏, 研究一种充分考虑层间储层物性和驱替程度差异的分层配注方法意义重大。
为此, 笔者在分析多层合采油藏长期注水开发特点的基础上, 提出了采用驱替通量定量表征各层驱替程度差异的方法, 并以实现层间均衡驱替、减缓层间干扰为目的, 建立了基于驱替通量均衡化思想的注水井分层配注量确定方法(简称均衡驱替法)。同时, 论证了不同配注量确定方法在各含水阶段的适应性。先导试验表明, 利用均衡驱替法对处于高含水后期的多层合采油藏进行分层配注, 降水增油效果显著。
1 基于驱替通量的驱替定量表征方法常用驱替倍数[16], 即累计驱替流体的体积与孔隙体积之比表征驱替强度, 表达式为:

|
(1) |
式中:PV为驱替倍数; Q为累计驱替流体的体积, m3; Vφ为孔隙体积, m3。
国内外众多学者基于驱替倍数进行了大量的驱替试验和油藏驱替状况定量分析[17-19], 但是驱替倍数受孔隙体积的影响, 相同驱替量下, 孔隙体积越小(或划分网格越小)驱替倍数越大。因此, 不同尺度级别的驱替状况难以对比, 例如, 岩心尺度级别的驱替规律难以指导井组、油藏尺度级别的驱替。为此, 提出了一种不受孔隙体积影响的驱替定量表征新方法, 即驱替通量法。驱替通量定义为累计驱替流体的体积与驱替断面的孔隙面积之比, 表达式为:
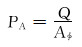
|
(2) |
式中:PA为驱替通量, m; Aφ为驱替断面的孔隙面积, m2。驱替通量物理意义明确。首先, 驱替通量和驱替倍数一样可以表征长期累计驱替冲刷强度; 其次, 利用驱替断面处的水相通量和油相通量可以计算含水率; 最后, 驱替通量的导数即为真实驱替速度, 可以表征瞬时驱替冲刷强度:
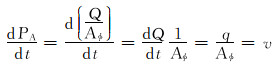
|
(3) |
式中:t为驱替时间, d; q为驱替流量, m3/d; v为真实驱替速度, m/d。
同时, 驱替通量克服了驱替倍数受孔隙体积(或划分网格)影响的问题, 更加客观唯一。将一维驱替岩心均等划分网格(见图 1), 分别计算不同网格大小条件下的驱替通量和驱替倍数(见表 1), 结果表明驱替通量不受网格划分影响。

|
| 图 1 一维驱替岩心均等划分网格示意 Fig.1 Diagram of the equally divided grids of one dimensional flooding cores |
| 均等划分 网格个数 |
1 | 2 | … | i | … | n |
| 孔隙体积 | Vφ | 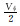 |
… | 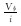 |
… | 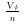 |
| 驱替倍数 | 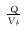 |
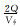 |
… | 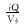 |
… | 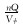 |
| 驱替通量 | 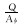 |
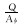 |
… | 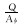 |
… | 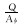 |
多层合采油藏进入高含水后期之后, 由于纵向各层的储层物性存在差异, 各层的吸水能力不同, 导致驱替不均衡, 注入水利用率低。驱替通量均衡化思想是指通过调配分层注水井各小层的注入量, 使各层的驱替通量相同, 实现各层均衡开发, 最大限度地降低层间干扰, 提高注水利用率及油藏采收率。
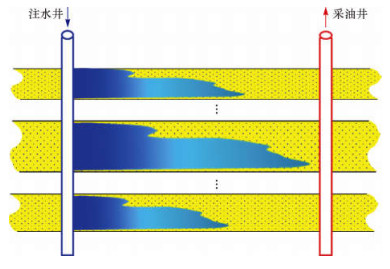
图 2为多层合采油藏示意图, 纵向共有n个小层, 其中各层累计注水量可由分层配注历史和吸水剖面测试资料计算得到。
|
| 图 2 多层合采油藏示意 Fig.2 Diagram of reservoir with multi-layer commingled productions |
分层调配前各层驱替通量为PAi, i=1, 2, …, n-1, n。基于均衡驱替思想, 进行分层配注量优化调整, 调配后各层驱替均衡, 驱替通量均为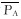
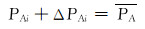
|
(4) |
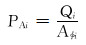
|
(5) |
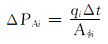
|
(6) |
式中:Qi为第i层累计注水量, m3; Aφi为第i层驱替断面的孔隙面积, m2; qi为第i层配注量, m3/d; Δt为调控周期, d; 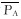
各层配注量之和等于该井总注水量:

|
(7) |
式中:q为注水井总注水量, m3/d。
由式(4)—式(7)可得分层配注模型为:
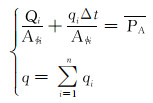
|
(8) |
求解上述模型, 可得各层配注量为:
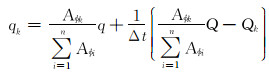
|
(9) |
第i小层的驱替断面孔隙面积为:
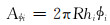
|
(10) |
式中:R为注水驱替半径, m; hi为第i层厚度, m; φi为第i层孔隙度。
将式(10)代入式(9), 化简为:
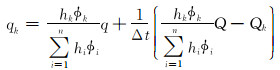
|
(11) |
因此纵向各层的分层配注系数ηk为:
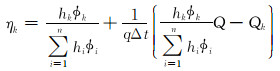
|
(12) |
从建立的分层配注量计算模型可以看出, 分层配注量主要与储层厚度、孔隙度、注水历史、调控周期以及注水量有关。若各层处于均衡驱替状态, 则各层所需的配注量与其孔隙度、厚度成正比; 若各层驱替不均, 但各层孔隙度、厚度相同, 则各层配注量差别与层间驱替强度差异正相关, 同时与调控周期呈负相关, 调控周期越短, 则各小层为了达到均衡驱替状态所需调配的水量差别越大。
式(12)所表达的分层配注系数确定方法简单实用, 利用油田基础资料、吸水剖面、注水历史及调控周期和注水量即可确定配注系数。
2.2 适应性分析根据渤海SZ油田D区块地质油藏特征, 建立了反九点井网的精细概念数值模型, 分析各分层配注方法的适应性。其中, Nx=Ny=51, Nz=12, 平面上x, y方向的网格步长均为14.00 m。原始地层压力为14.28 MPa, 油藏温度为65 ℃, 地面原油密度为970 kg/m3, 地下原油黏度为70.00 mPa·s, 原油压缩系数为1.30×10-3 MPa-1, 原油体积系数为1.08, 地层水黏度为0.49 mPa·s, 垂向渗透率与水平渗透率比为0.10, 原始含水饱和度为0.36, 油水相渗曲线如图 3所示。
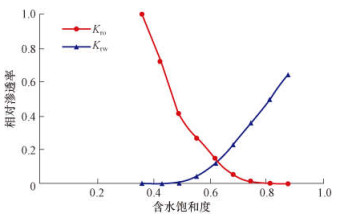
|
| 图 3 渤海SZ油田油水相对渗透率曲线 Fig.3 Curves of oil-water relative permeability in Bohai SZ Oilfield |
纵向厚度为40 m, 分4个防砂段, 各防砂段厚度分别为6.65, 8.90, 19.70和4.75 m, 渗透率分别为2 698.57, 1 325.66, 2 370.45和605.31 mD, 孔隙度分别为0.28, 0.29, 0.31和0.32。
假设投产时便开始注水, 采用笼统注水方案, 调控周期为6个月。采用数值模拟方法计算该油田在中(含水率20%~60%)、高(含水率60%~90%)、特高(含水率大于90%)含水阶段按照不同分层配注方法配注时的累计增油量, 分析各种配注方法对该油田不同开发阶段的适应性。模拟结果如图 4所示。
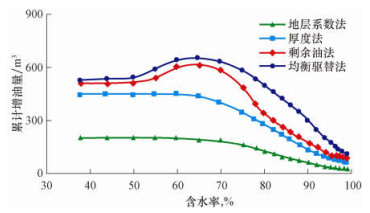
|
| 图 4 不同分层配注方法累计增油量对比结果 Fig.4 Contrast of accumulated oil increment with different methods of layered injection allocations |
由图 4可以看出:1)剩余油法与均衡驱替法的累计增油量随含水率增大先增大后减小, 厚度法与地层系数法的累计增油量随含水率增大而减小; 2)在相同含水率条件下, 均衡驱替法的累计增油量最大, 剩余油法次之, 厚度法更小, 地层系数法最小; 3)含水率小于50%时, 均衡驱替法略好于剩余油法和厚度法, 远好于地层系数法, 由于厚度法计算简便, 推荐使用厚度法; 含水率为50%~80%时, 均衡驱替法略好于剩余油法, 远好于厚度法和地层系数法, 推荐使用剩余油法; 含水率为80%~90%时, 均衡驱替法远好于其他3种配注方法, 此时, 推荐使用均衡驱替法。
厚度法未考虑注水过程中各层驱替程度、剩余油和水淹程度的差异, 导致水驱效果逐渐变差; 地层系数法容易导致注入水沿着高渗层突破, 造成无效水循环和纵向驱替不均加剧; 剩余油法没有考虑各层驱替不均衡造成的水淹差异, 尤其在高含水后期, 无法区分水淹强的厚层和水淹弱的薄层, 注入水利用率降低、无效水循环加剧。因此, 在高含水阶段, 尤其是高含水后期, 采用均衡驱替法分层配注的效果明显好于其他方法。
3 现场应用渤海SZ油田X1井纵向上分13个小层、4个防砂段。该井于2005年4月转注, 2008年11月开始采用厚度法进行分层配注, 2011年采用剩余油法进行分层配注, 截至目前配注效果逐渐变差, 2016年10月, 该井组平均含水率达到86%。为优化X1井的分层配注量进行了均衡驱替法分层配注先导试验。
根据各小层的注入情况, 利用上文建立的分层配注量确定方法, 以2年为调控周期, 计算各小层及防砂段配注量, 结果见表 2。
| 小层 | 厚度/
m |
孔隙度,
% |
累计注水量/
104 m3 |
小层配注量/
(m3·d-1) |
防砂段配注量/
(m3·d-1) |
| 1 | 9.5 | 33.6 | 49.95 | 88.23 | 132 |
| 2 | 3.2 | 33.4 | 16.83 | 43.76 | |
| 3 | 7.8 | 32.2 | 41.01 | 354.75 | 355 |
| 4 | 14.3 | 34.3 | 75.19 | 293.71 | 380 |
| 5 | 5.5 | 27.1 | 28.92 | 19.22 | |
| 6 | 5.1 | 31.1 | 26.81 | 66.78 | |
| 11 | 1.5 | 32.1 | 7.89 | 58.89 | 184 |
| 12 | 2.1 | 34.0 | 11.04 | 34.86 | |
| 13 | 4.7 | 33.3 | 24.71 | 89.84 |
X1井于2016年11月开始采用均衡驱替法调整分层配注量, 截至2017年4月1日, 该井组含水率由86%降至82%, 产油量由358 m3/d升至475 m3/d, 净增油12 241 m3, 平均日净增油80.5 m3。X1井组开采曲线如图 5所示。
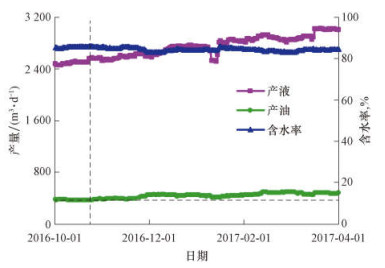
|
| 图 5 X1井组开采曲线 Fig.5 Production curve of well group X1 |
从图 5可以看出, 在高含水后期, 基于驱替定量表征的均衡驱替分层配注方法能够有针对性地增加累计驱替强度较弱层的注水量, 能够更好地动用剩余油, 降低无效水循环, 提高注入水利用率。
4 结论1) 提出采用驱替通量定量表征驱替程度。驱替能量不受孔隙体积及网格划分的影响, 物理意义更加明确和客观。
2) 以均衡驱替为目标, 建立了基于驱替通量表征的均衡驱替分层配注量确定方法, 该方法综合考虑了储层厚度、孔隙度、注水历史、调控周期等因素的影响。
3) 均衡驱替分层配注量确定方法在高含水后期比其他常用方法调控效果更好, 矿场先导试验也表明, 该配注量确定方法科学合理、简单实用, 对于多层合采油田高含水后期具有很好的推广应用价值。
| [1] |
黄世军, 康博韬, 程林松, 等.
海上普通稠油油藏多层合采层间干扰定量表征与定向井产能预测[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2015, 42(4): 488–495.
HUANG Shijun, KANG Botao, CHENG Linsong, et al. Quantitative characterization of interlayer interference and productivity prediction of directional wells in the multilayer commingled production of ordinary offshore heavy oil reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2015, 42(4): 488–495. |
| [2] |
苏彦春.
海上大井距多层合采稠油油田剩余油定量描述技术及其应用[J]. 中国海上油气, 2012, 24(s1): 82–85.
SU Yanchun. A set of techniques to describe quantitatively remaining oil in offshore heavy oilfields under commingling production in large well spacing[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2012, 24(s1): 82–85. |
| [3] |
罗宪波, 赵春明, 武海燕, 等.
海上油田多层合采层间干扰系数确定[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2012, 31(5): 102–104.
LUO Xianbo, ZHAO Chunming, WU Haiyan, et al. Determination of the interference coefficient among the commingled production layers in offshore oilfield[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2012, 31(5): 102–104. |
| [4] |
许家峰, 张金庆, 程林松, 等.
多层合采砂岩稠油油藏层间干扰动态表征及应用[J]. 中国海上油气, 2016, 28(4): 48–54.
XU Jiafeng, ZHANG Jinqing, CHENG Linsong, et al. The dynamic characterization and application of interlayer interference for sandstone heavy oil multilayer commingled producing[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2016, 28(4): 48–54. |
| [5] |
苏彦春, 贾晓飞, 李云鹏, 等.
多层合采油藏层间动态干扰定量表征新技术[J]. 特种油气藏, 2015, 22(6): 101–103.
SU Yanchun, JIA Xiaofei, LI Yunpeng, et al. New technology for quantitative characterization of interlayer dynamic interference in commingled producing oil reservoir[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2015, 22(6): 101–103. |
| [6] |
贾晓飞, 苏彦春, 邓景夫, 等.
多层合采砂岩油藏动态干扰及其影响因素[J]. 断块油气田, 2016, 23(3): 334–337.
JIA Xiaofei, SU Yanchun, DENG Jingfu, et al. Interlayer dynamic interference caused by commingled production and its influencing factors on sandstone reservoir[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2016, 23(3): 334–337. |
| [7] |
王波. 高含水油田分层注水优化研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2015.
WANG Bo. Optimization of separate zone water injection in the high water-cut oilfield[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (Huadong), 2015. |
| [8] |
叶剑川. 分层注水配注量计算与优化研究[D]. 武汉: 长江大学, 2014.
YE Jianchuan. Study on the method of calculation and optimization of separated layer water flooding amount[D]. Wuhan: Yangzte University, 2014. |
| [9] |
贾晓飞, 李其正, 杨静, 等.
基于剩余油分布的分层调配注水井注入量的方法[J]. 中国海上油气, 2012, 24(3): 38–40.
JIA Xiaofei, LI Qizheng, YANG Jing, et al. A method to allocate injection volume for separate layers in a water-injection well based on the remaining oil distribution[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2012, 24(3): 38–40. |
| [10] |
吴家文, 王家春, 刘剑, 等.
基于剩余油分布的分层注水方案优选[J]. 大庆石油学院学报, 2006, 30(4): 12–15.
WU Jiawen, WANG Jiachun, LIU Jian, et al. Optimization method for layered water injection project based on the distribution of remaining oil[J]. Journal of Daqing Petroleum Institute, 2006, 30(4): 12–15. |
| [11] |
贾晓飞, 马奎前, 李云鹏, 等.
基于剩余油分布的分层注水井各层配注量确定方法[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2012, 40(5): 72–76.
JIA Xiaofei, MA Kuiqian, LI Yunpeng, et al. Injection allocation determination method for separate injection well based on remaining oil distribution[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2012, 40(5): 72–76. |
| [12] |
尹洪军, 张俊廷, 张欢欢, 等.
应用灰色关联分析方法确定分层注水量公式[J]. 数学的实践与认识, 2012, 42(13): 94–99.
YIN Hongjun, ZHANG Junting, ZHANG Huanhuan, et al. Appling grey correlation analysis method to determine the separated layer water injection[J]. Mathematics in Practice and Theory, 2012, 42(13): 94–99. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0984.2012.13.012 |
| [13] |
张玉荣. 分层注水储层参数变化机理与配注参数动态调配方法研究[D]. 大庆: 东北石油大学, 2011.
ZHANG Yurong. Research on mechanism of reservoir parameter variation under the condition of layered water injection and dynamic allocation method of injection allocation parameters[D]. Daqing: Northeast Petroleum University, 2011. |
| [14] |
杜庆龙, 朱丽红.
油、水井分层动用状况研究新方法[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2004, 31(5): 96–98.
DU Qinglong, ZHU Lihong. A new approach to study layered producing performance of oil and water wells[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2004, 31(5): 96–98. |
| [15] |
石晓渠, 马道祥.
注水井合理配注水量计算方法研究[J]. 西部探矿工程, 2008, 20(9): 94–96.
SHI Xiaoqu, MA Daoxiang. Study on calculation method of reasonable water injection in water injection well[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering, 2008, 20(9): 94–96. |
| [16] |
冯其红, 王相, 王端平, 等.
水驱油藏均衡驱替开发效果论证[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2016, 23(3): 83–88.
FENG Qihong, WANG Xiang, WANG Duanping, et al. Theoretical analysis on the performance of equilibrium displacement in water flooding reservoir[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2016, 23(3): 83–88. |
| [17] |
张士奇, 周志军, 张小静, 等.
双河油田注水倍数和驱替倍数对采出程度影响[J]. 特种油气藏, 2014, 21(3): 93–96.
ZHANG Shiqi, ZHOU Zhijun, ZHANG Xiaojing, et al. Influence of water injection ratio and displacement multiplier on Shuanghe oilfield[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2014, 21(3): 93–96. |
| [18] |
焦龙. S油田特高含水期驱替倍数对驱油效果的影响研究[D]. 大庆: 东北石油大学, 2014.
JIAO Long. The research on the influence of displacement multiplier on oil displacement efficiency in extra high water cut period of S Oilfield[D]. Daqing: Northeast Petroleum University, 2014. |
| [19] | JACKSON M D, VALCATENE P H, BLUNT M J. Prediction of wettability variation and its impact on flow using pore-to reservoir-scale simulations[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science & Engineering, 2003, 39(3-4): 231–246. |


