Prediction Model and Distribution Law Study of Temperature and Pressure of the Wellbore in drilling in Arctic Region
-
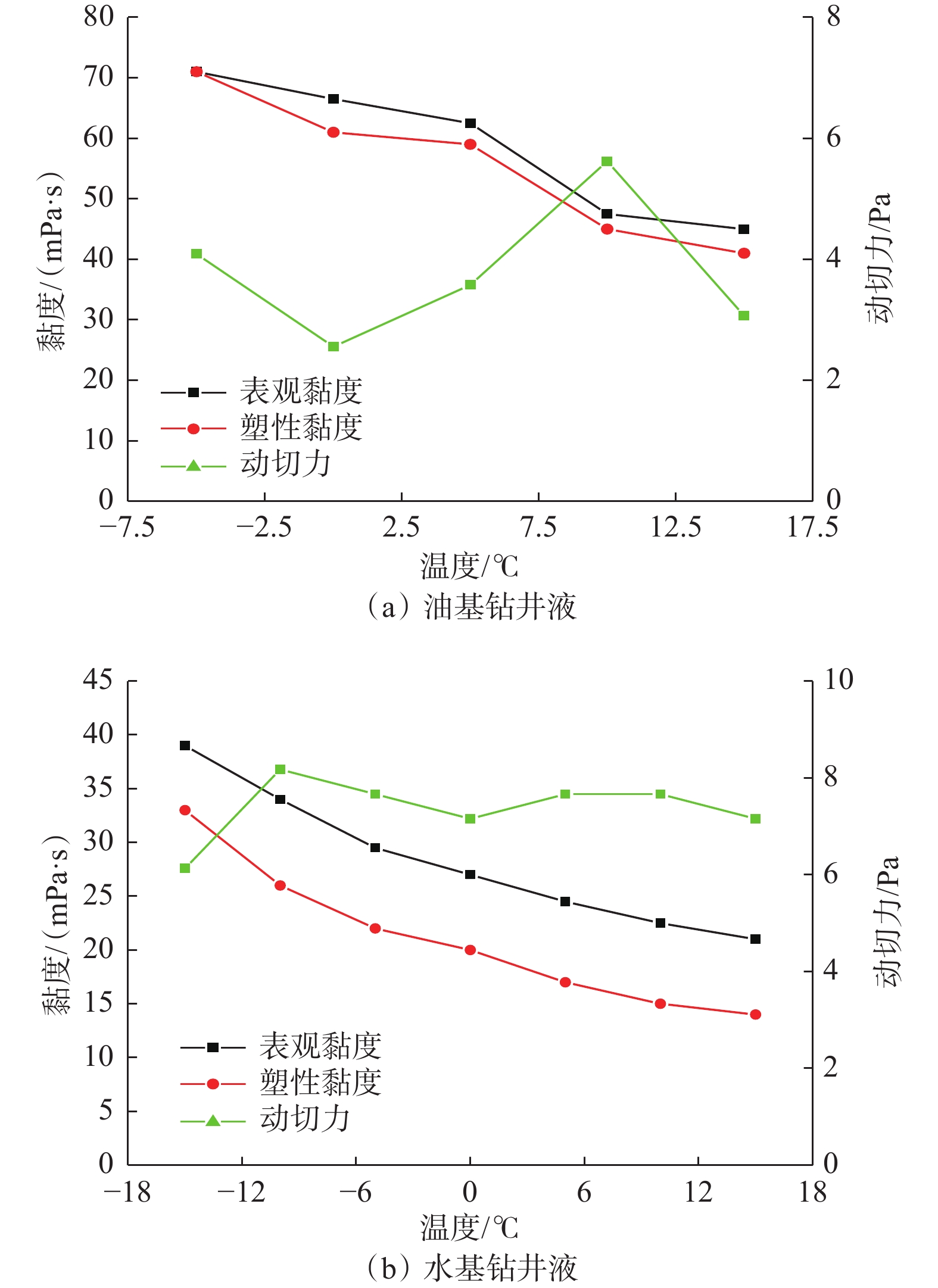
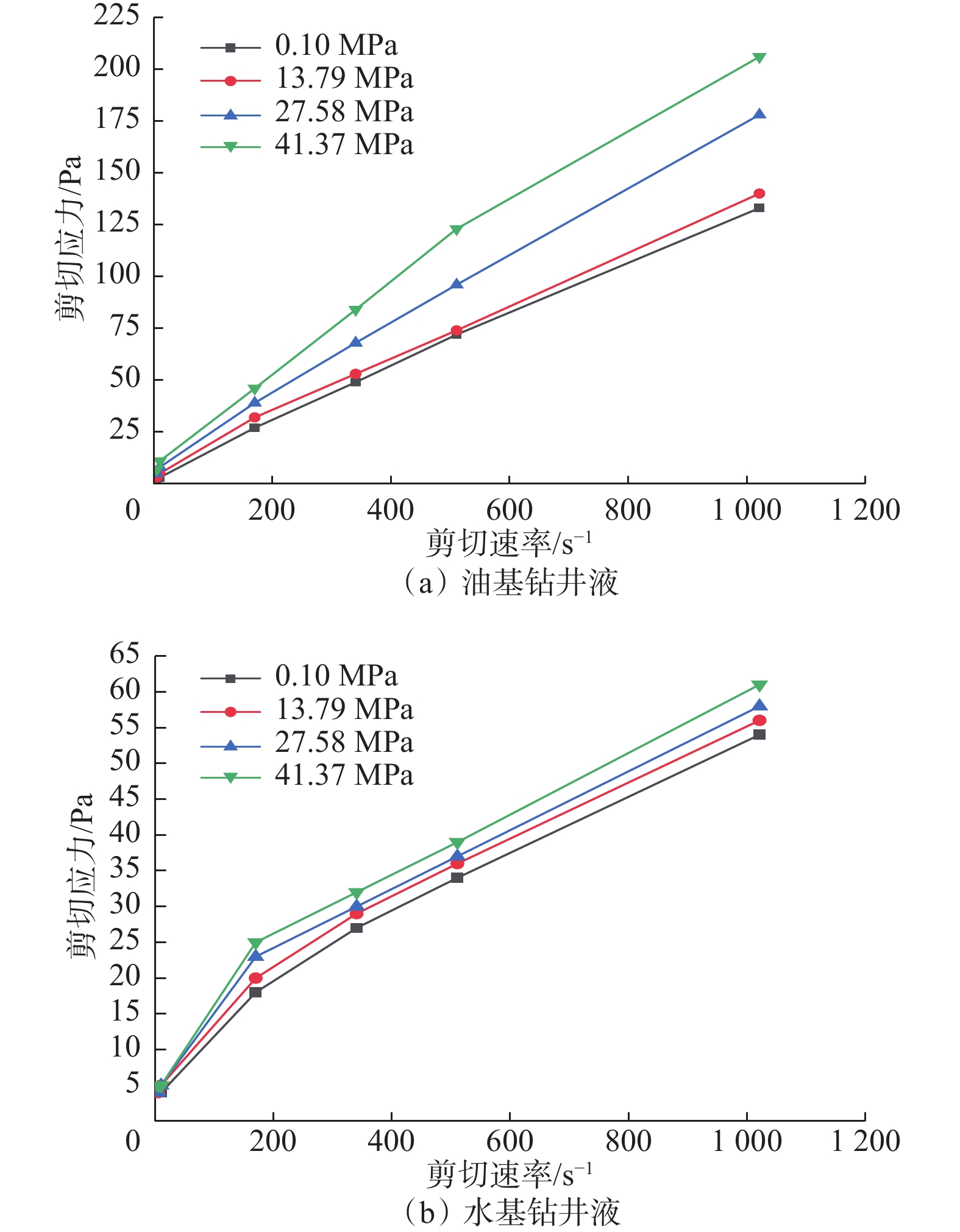
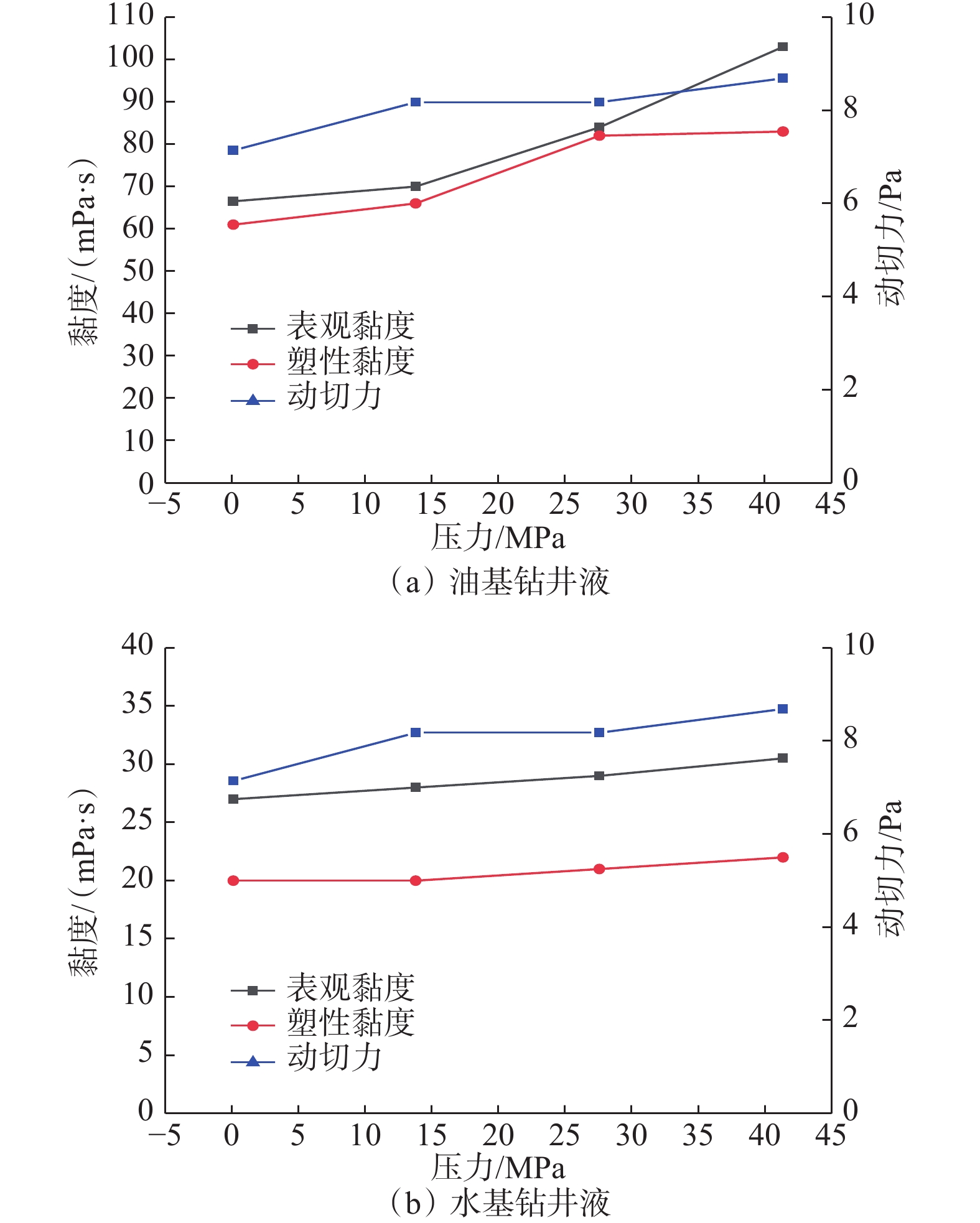
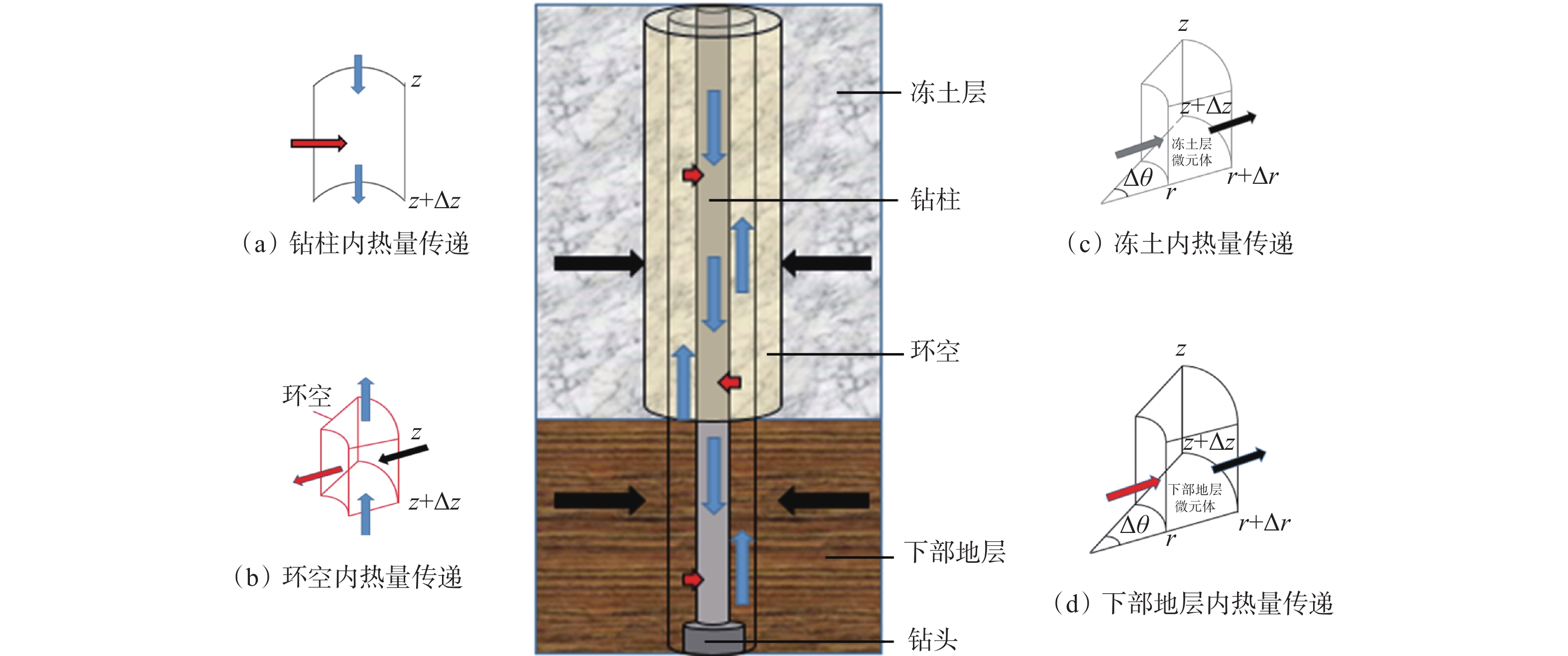
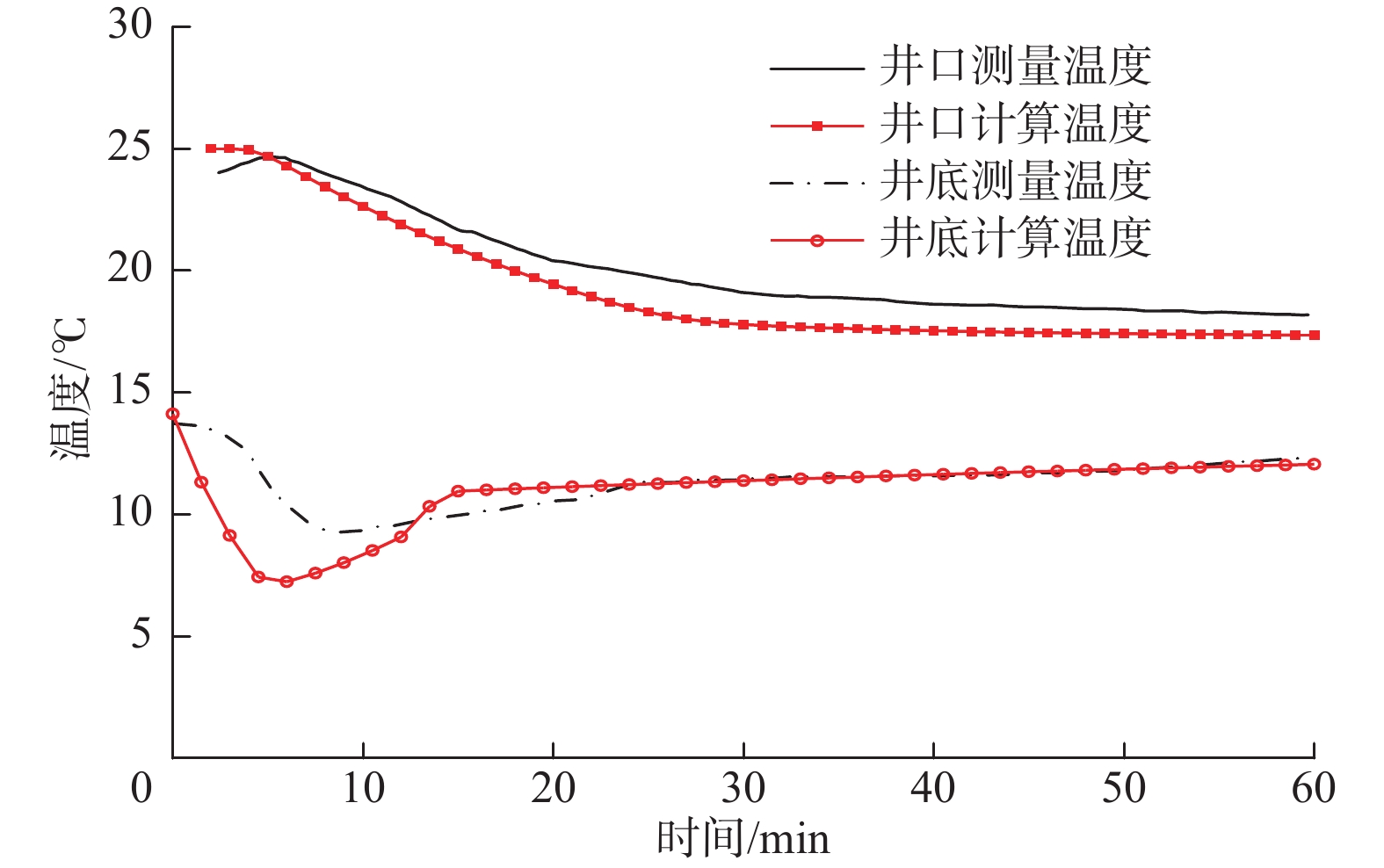
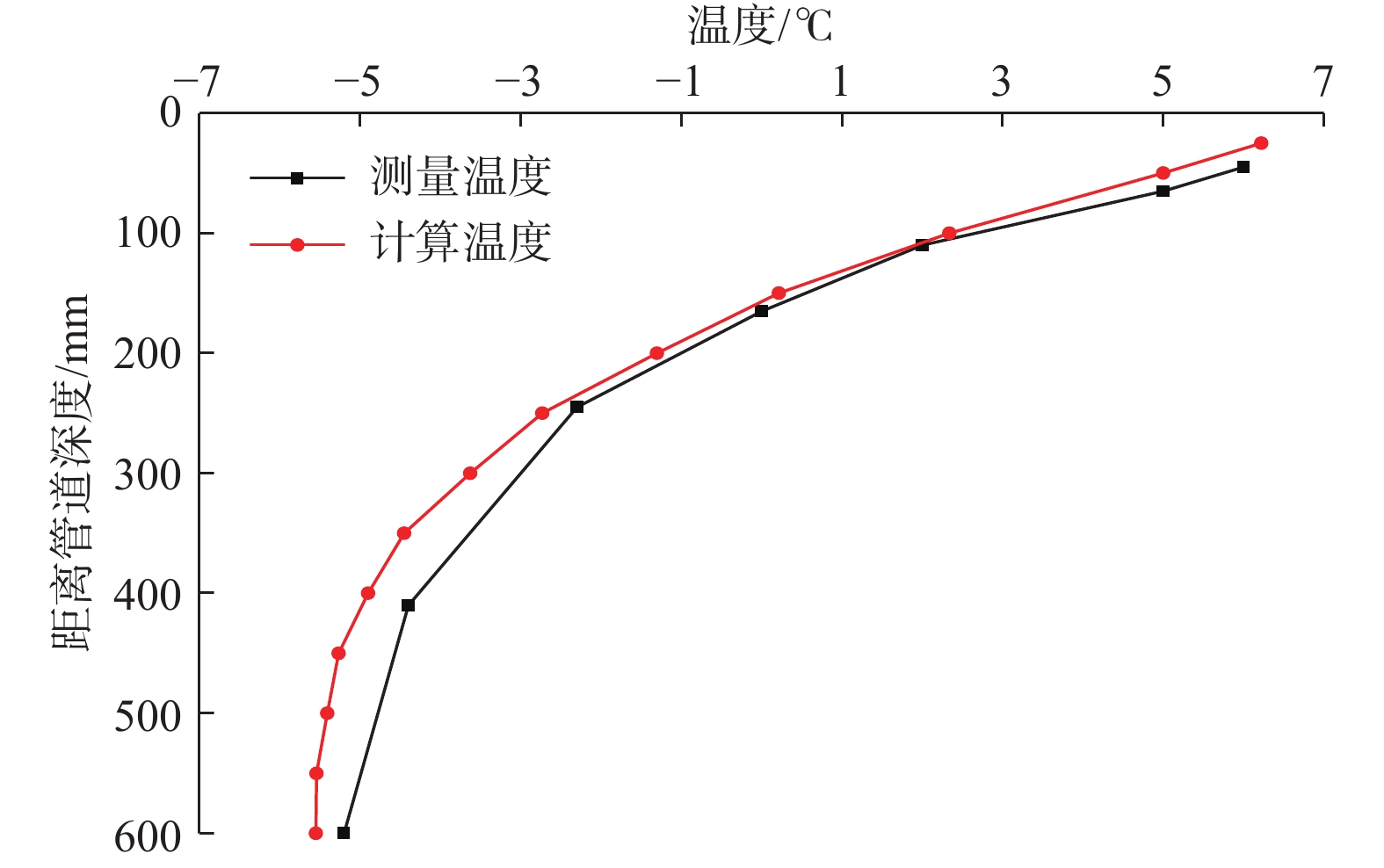
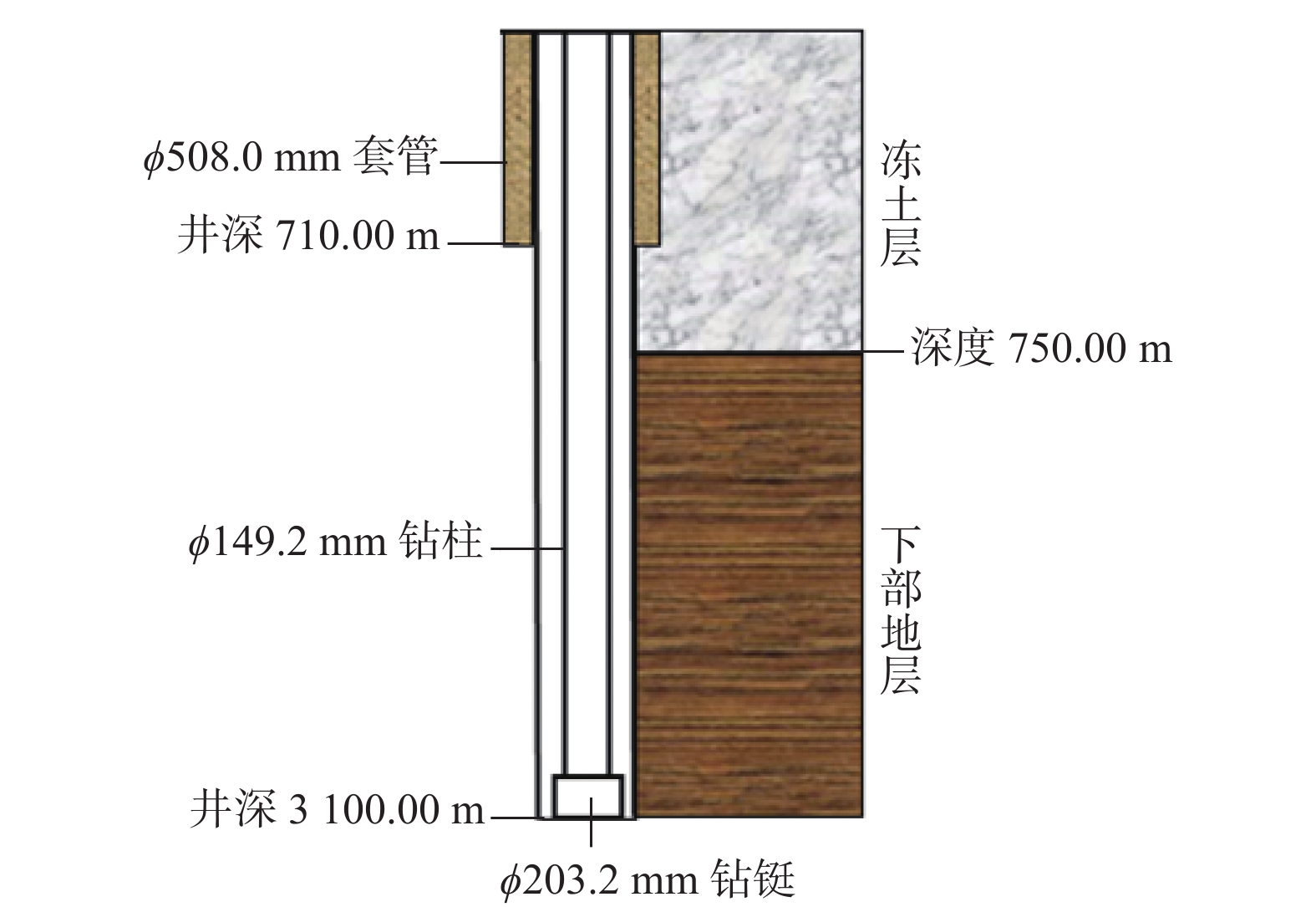
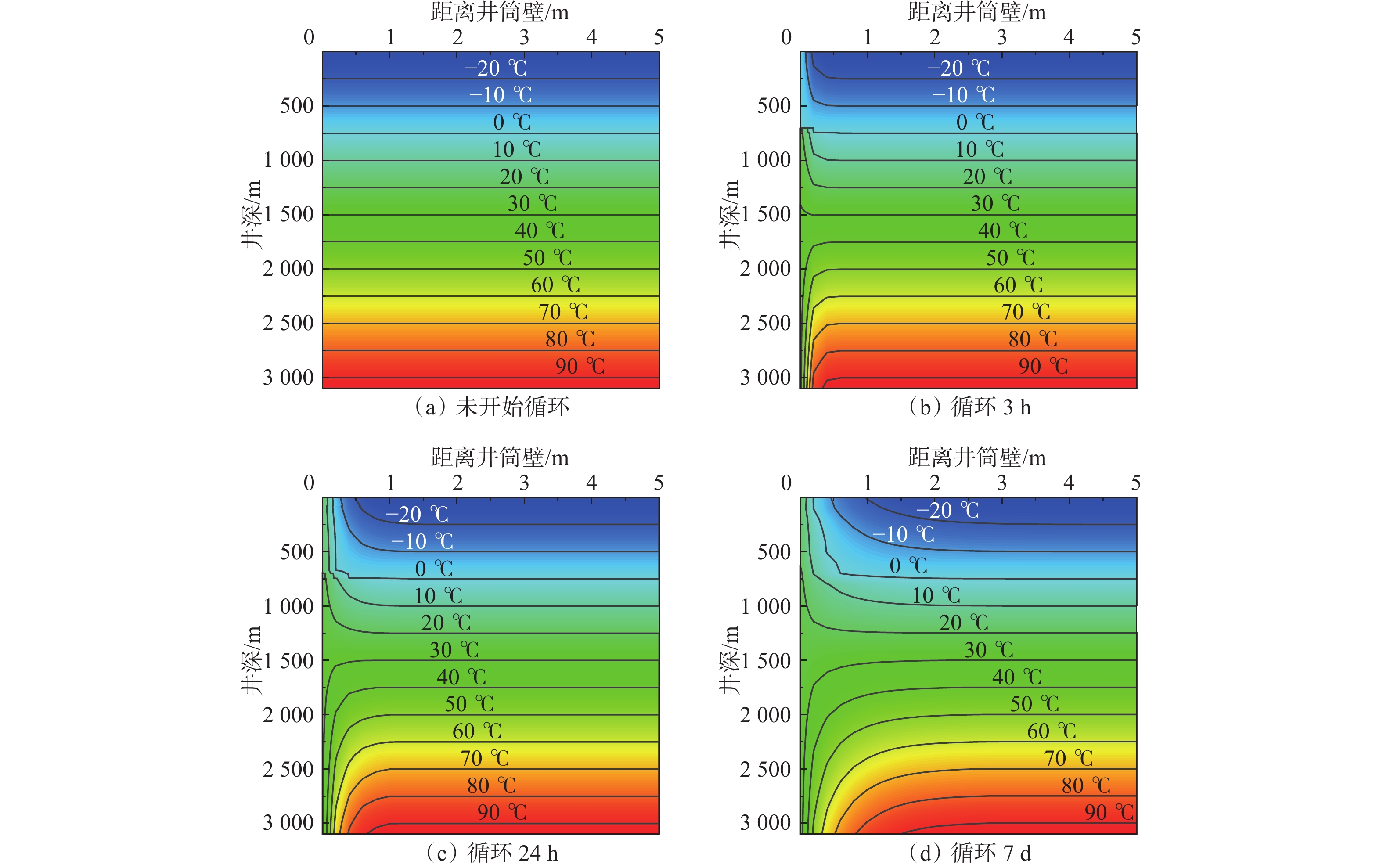
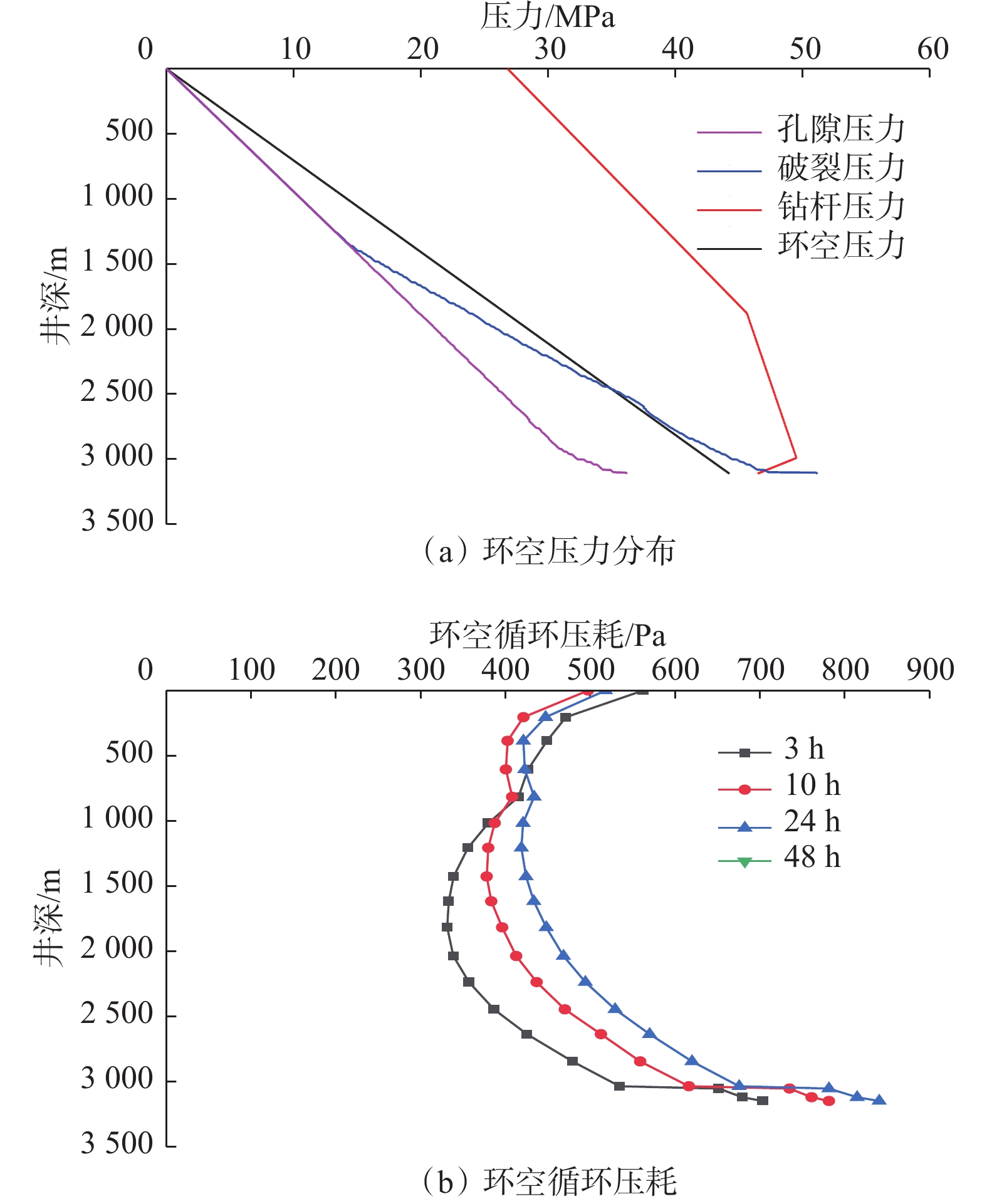
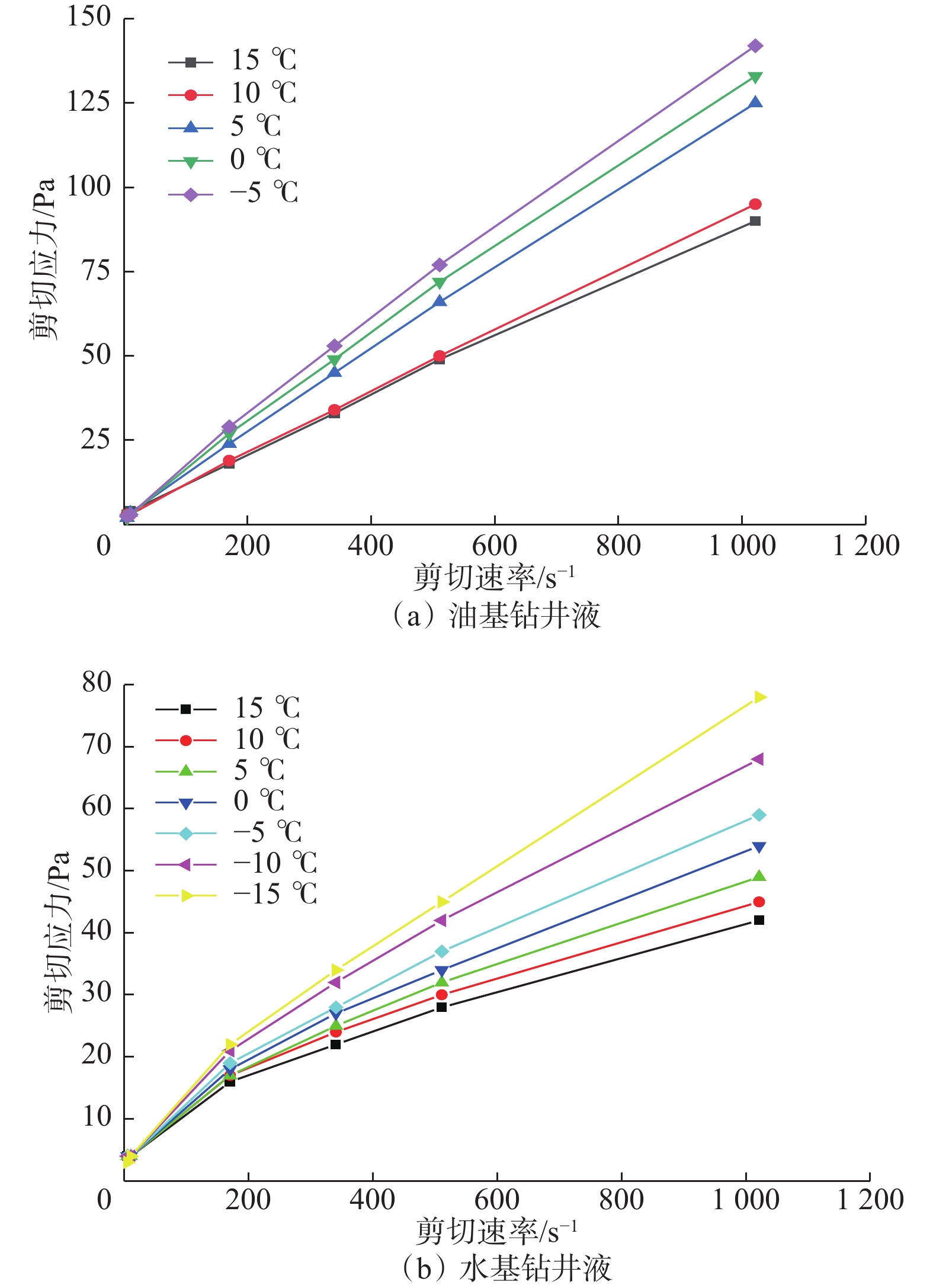
摘要: 极地永久冻土层的低温条件会影响钻井液的流变性,从而影响极地钻井中井筒温度和压力的分布。为了解极地永久冻土层低温条件对钻井中井筒温度和压力分布的影响规律,为极地钻井设计和钻井施工提供依据,分析了低温对水基和油基钻井液流变性的影响,考虑低温对钻井液流变性的影响、永久冻土层与井筒之间的耦合作用,建立了极地钻井井筒温度压力预测模型。通过与实测结果和试验结果对比,证明极地钻井井筒温度压力预测模型的预测精度达到了极地钻井要求。利用所建模型模拟了一口极地井钻井循环和停泵工况下的温度和压力分布,结果表明:循环期间,钻井液吸收下部高温地层的热量,通过环空上返时将热量传递至井筒浅部永久冻土层,导致近井地带冻土层融化,冻土层融化消耗热量使井筒温度降低;随着循环时间增长,环空循环摩阻增大;停泵时间越长,井筒钻井液的温度越接近地层环境温度,开井时环空循环压耗越大,开井泵压也越高。研究结果可为极地井钻井设计和钻井施工提供依据和指导。Abstract: The low temperature condition of permafrost in Arctic region affects the rheology of drilling fluids and the distribution of temperature and pressure in the wellbore during drilling. In order to understand the influence law of permafrost in Arctic region on the temperature and pressure distribution in wellbore and provide a basis for the design and construction for drilling in Arctic region, a model to predict the wellbore temperature and pressure of drilling in Arctic region was built. It was based on the analysis of the influence of low temperatures on the rheology of water-based and oil-based drilling fluids, considering the coupling between permafrost and wellbore. By comparing the measured and test results, it was verified that the prediction accuracy of the proposed model met the requirements of drilling in Arctic region. The model was used to simulate the temperature and pressure distribution in a wellbore in Arctic region under the conditions of no circulation or pump function. The results showed that the drilling fluids absorbed the heat of the high-temperature formation and returned to the annulus transferring the heat to the permafrost in shallow part of the wellbore during the circulation. This process thawed the permafrost near the wellbore and the wellbore temperature was lowered due to the heat consumed by thawing. The circulating friction in annulus increases with the increase of circulation time. The longer the pump shutdown lasts, the closer the temperature of drilling fluid to the formation temperature in the wellbore. The larger the annular circulation pressure loss, and the higher the pump pressure. The research results can provide a basis and guidance for design and construction of drilling in Arctic region.
-
-
表 1 实测立压与计算立压的对比
Table 1 Comparison of measured and calculated vertical pressure
井深/m 排量/(L·s–1) 立压/MPa 相对误差,% 实测 计算 3 098.50 28.83 22.89 22.71 0.79 3 182.80 29.35 25.29 25.11 0.71 3 237.40 28.80 24.41 24.17 0.98 3 249.30 29.35 25.62 25.80 0.70 3 270.90 26.75 19.21 19.45 1.10 3 357.30 31.57 24.21 24.46 1.00 3 464.67 32.01 24.7 24.46 0.97 3 516.56 30.69 24.00 23.45 2.30 3 654.34 29.91 23.04 23.23 0.82 3 739.48 29.91 23.95 23.64 1.31 3 840.26 29.91 23.43 23.65 0.89 3 888.73 29.82 24.9 25.40 2.00 -
[1] 王淑玲,姜重昕,金玺. 北极的战略意义及油气资源开发[J]. 中国矿业,2018,27(1):20–26, 39. WANG Shuling, JIANG Chongxin, JIN Xi. The strategic significance of the Arctic and the development of oil and gas resources[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2018, 27(1): 20–26, 39.
[2] 孙宝江. 北极深水钻井关键装备及发展展望[J]. 石油钻探技术,2013,41(3):7–12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0890.2013.03.002 SUN Baojiang. Progress and prospect of key equipments for Arctic deepwater drilling[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2013, 41(3): 7–12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0890.2013.03.002
[3] HARRISON G R. Exploratory drilling: the polar challenge[R]. WPC 18128, 1979.
[4] DAVISON J M, CLARY S, SAASEN A, et al. Rheology of various drilling fluid systems under deepwater drilling conditions and the importance of accurate predictions of downhole fluid hydraulics[R]. SPE 56632, 1999.
[5] 吴彬,向兴金,张岩,等. 深水低温条件下水基钻井液的流变性研究[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2006,23(3):12–13, 19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2006.03.004 WU Bin, XIANG Xingjin, ZHANG Yan, et al. Rheology study of the water based drilling fluids at deep water and low temperature[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2006, 23(3): 12–13, 19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2006.03.004
[6] 纪健,袁华玉,李建,等. 深水钻井环境下低温高压对油基钻井液流变性的影响[J]. 内蒙古石油化工,2009,35(21):134–136. JI Jian, YUAN Huayu, LI Jian, et al. Influence of low temperature and high pressure on rheological properties of oil-based drilling fluids in deep offshore conditions[J]. Inner Mongolia Petrochemical Industry, 2009, 35(21): 134–136.
[7] 田荣剑,王楠,李松,等. 深水作业中钻井液在低温高压条件下的流变性[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2010,27(5):5–7,87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2010.05.002 TIAN Rongjian, WANG Nan, LI Song, et al. Research on drilling fluid rheology with low temperature and high pressure in deep water operation[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2010, 27(5): 5–7,87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2010.05.002
[8] 胡三清,雷昕,余姣梅,等. 深水低温合成基钻井液的室内研究[J]. 石油天然气学报,2010,32(3):120–123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2010.03.027 HU Sanqing, LEI Xin, YU Jiaomei, et al. Laboratory study on deep low-temperature synthetic-based drilling fluids[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2010, 32(3): 120–123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2010.03.027
[9] 易灿,闫振来,赵怀珍. 超深井水基钻井液高温高压流变性试验研究[J]. 石油钻探技术,2009,37(1):10–13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0890.2009.01.003 YI Can, YAN Zhenlai, ZHAO Huaizhen. Rheological properties of water-based drilling fluids in ultra-deep wells at high temperature and high pressure[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2009, 37(1): 10–13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0890.2009.01.003
[10] RAMEY H J Jr. Wellbore heat transmission[J]. Journal of Petroleum Technology, 1962, 14(4): 427–435. doi: 10.2118/96-PA
[11] WILLHITE G P. Over-all heat transfer coefficients in stream and hot water injection wells[J]. Journal of Petroleum Technology, 1967, 19(5): 607–615. doi: 10.2118/1449-PA
[12] WU Yushu, PRUESS K. An analytical solution for wellbore heat transmission in layered formations[J]. SPE Reservoir Engineeing, 1990, 5(4): 531–538. doi: 10.2118/17497-PA
[13] HASAN A R, KABIR C S, AMEEN M, et al. A fluid circulating temperature model for workover oprations[J]. SPE Journal, 1996, 1(2): 133–144. doi: 10.2118/27848-PA
[14] 高永海,孙宝江,王志远,等. 深水钻探井筒温度场的计算与分析[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版),2008,32(2):58–62. GAO Yonghai, SUN Baojiang, WANG Zhiyuan, et al. Calculation and analysis of wellbore temperature field in deepwater drilling[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum(Edition of Natural Science), 2008, 32(2): 58–62.
[15] 李梦博,柳贡慧,李军,等. 考虑非牛顿流体螺旋流动的钻井井筒温度场研究[J]. 石油钻探技术,2014,42(5):74–79. LI Mengbo, LIU Gonghui, LI Jun, et al. Research on wellbore temperature field with helical flow of non-Newtonian fluids in drilling operation[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2014, 42(5): 74–79.
[16] PETERS E J, CHENEVERT M E, ZHANG C. A model for predicting the density of oil-based muds at high pressures and temperatures[R]. SPE 18036, 1990.
[17] OSISANYA S O, HARRIS O O. Evaluation of equivalent circulating density of drilling fluids under high-pressure/high-temperature conditions[R]. SPE 97018, 2005.
[18] 卢秋平,邵忠,陆红锋,等. 深水天然气水合物连续管水平井钻井井筒多相流动规律研究[J]. 中国石油和化工标准与质量,2019,39(5):70–71. LU Qiuping, SHAO Zhong, LU Hongfeng, et al. Study on multiphase flow in wellbore of deepwater gas hydrate coiled tubing horizontal well[J]. China Petroleum and Chemical Standard and Quality, 2019, 39(5): 70–71.
[19] WANG Xuerui, WANG Zhiyuan, DENG Xuejing, et al. Coupled thermal model of wellbore and permafrost in Arctic regions[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2017, 123: 1291–1299. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.05.186
[20] 樊洪海. 实用钻井流体力学[J]. 北京: 石油工业出版社,2014. FAN Honghai. Practical drilling fluid mechanics[J]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2014.
[21] CHEN Zhongming, XIE Liangjun. Special considerations for deepwater well temperature prediction[R]. SPE 176089, 2015.
[22] XU Guofang, QI Jilin, JIN Huijun. Model test study on influence of freezing and thawing on the crude oil pipeline in cold regions[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2010, 64(3): 262–270. doi: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2010.04.010
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 杨开吉,张颖,魏强,程艳,刘全刚. 海上油田开发用抗温抗盐乳液聚合物研制与性能评价. 石油钻探技术. 2024(04): 118-127 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 李硕轩,赵东睿,高红茜,刘誉. 超高分子聚合物驱提高高盐稠油油藏采收率机理及现场应用. 钻采工艺. 2023(01): 132-139 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 白佳佳,顾添帅,司双虎,陶磊,张娜,史文洋,朱庆杰. 高盐稠油油藏聚合物驱提高采收率研究. 常州大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(05): 60-66 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)



 下载:
下载: